22.验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
二叉搜索树的中序遍历是个有序的数组,可以利用这个特性,来判断是否是二叉搜索树,中序遍历,验证遍历的元素是不是从小到大
代码实现:
class Solution {
private long prev = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if(root.val<=prev){
return false;
}
prev = root.val;
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return right&&left;
}
}
23.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
中序遍历:中序遍历之后就是一个有序的数组
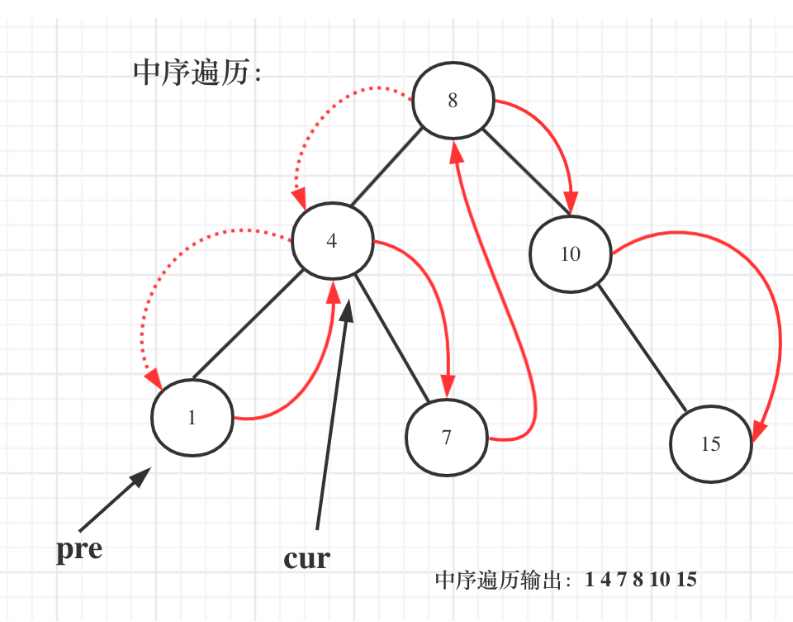
双指针法实现代码
class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
dfs(root);
return result;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
dfs(root.left);
if(pre!=null){
result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
}
pre = root;
dfs(root.right);
}
}
24.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
递归三部曲:
-
确定递归函数参数以及返回值
-
确定终止条件
终止条件就是找到遍历的节点为null的时候,就是要插入节点的位置了,并把插入的节点返回。
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
代码实现:
递归法
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null) return new TreeNode(val);
if(root.val<val) root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
if(root.val>val) root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
return root;
}
}
迭代法
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode newRoot = root;
TreeNode pre = root;
while (root != null) {
pre = root;
if (root.val > val) {
root = root.left;
} else if (root.val < val) {
root = root.right;
}
}
if (pre.val > val) {
pre.left = new TreeNode(val);
} else {
pre.right = new TreeNode(val);
}
return newRoot;
}
}