问题
根据配置文件re.properties指定信息,创建Cat对象并调用其hi方法(通过反射)
配置文件
classfullpath=com.zjh.reflection.Cat
method=hi
Cat类
public class Cat {
private String name = "招财";
public void hi(){
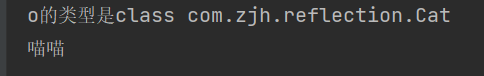
System.out.println("喵喵");
}
}
实现
public void test1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
// 获取配置文件对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("D:\\Tools\\ideaProducts\\JAVASE\\reflection\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zjh\\reflection\\re.properties"));
// 加载属性
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath");
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method");
// 1. 加载类,返回一个class类型的对象
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classfullpath);
// 2. 通过class对象可以创建加载的类
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
// 可以看到o的类型是Cat
System.out.println("o的类型是"+o.getClass());
// 3. 通过class来得到加载类com.zjh.reflection.Cat的methodName的方法对象,在反射中可以把方法是为对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
// 通过Method对象来调用方法,invoke方法,传入class获取的实例
method.invoke(o);
}
反射的好处是可以通过外部文件配置,在不修改源码的情况下来控制程序,也符合设计模式的ocp原则(开闭原则:不修改源码,扩容功能)
如果说要调用Cat的cry方法,那么在原始的方法(new对象,调用方法)中需要修改源码,即将cat.hi()改为cat.cry()。在使用反射后,只需要修改配置文件的method属性值即可,不需要修改源码。
1. 反射
- 反射机制允许程序在执行期借助Reflection API获取任何类的内部信息(比如成员变量,构造器,成员方法等等),并能操作对象的属性及方法
- 加载完类后,在堆中产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象包含了类的完整结构信息,通过这个对象得到类的结构,这个对象就像一面镜子,通过这个镜子可以看到类的结构,所以称这个镜子为反射
1.1 反射的能力
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
- 在运行时得到任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员方法和变量
- 生成动态代理
1.2 反射相关的类
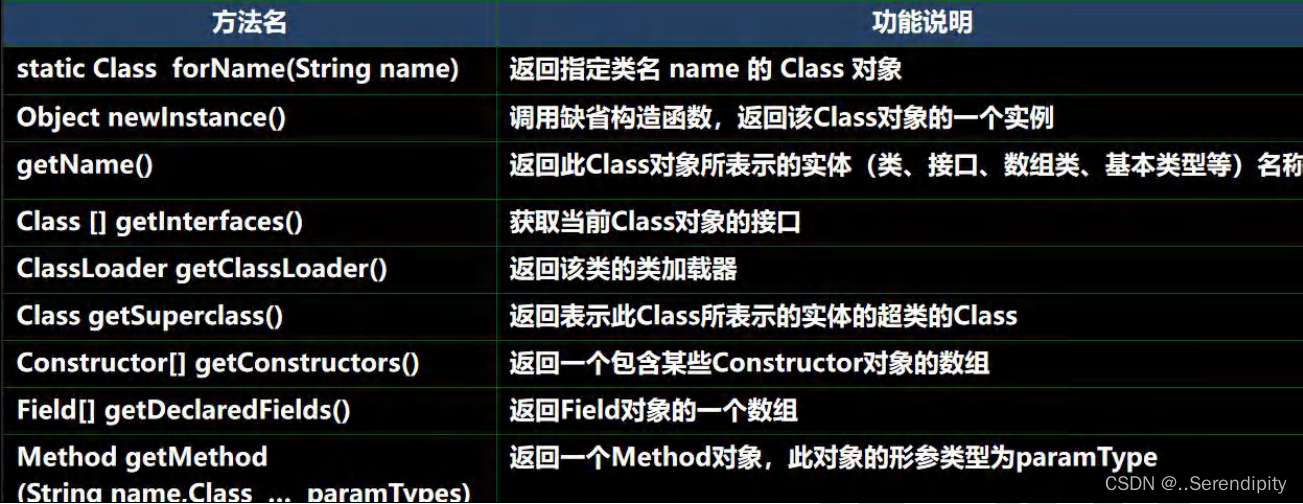
- java.lang.Class
- java.lang.reflect.Method
- java.lang.reflect.Field
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor
public class Cat {
public String name = "招财";
public void hi(){
System.out.println("喵喵");
}
public Cat(){
}
public Cat(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public void test1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
// 获取配置文件对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("D:\\Tools\\ideaProducts\\JAVASE\\reflection\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zjh\\reflection\\re.properties"));
// 加载属性
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath");
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method");
// 1. 加载类,返回一个class类型的对象
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classfullpath);
// 2. 通过class对象可以创建加载的类
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
// 可以看到o的类型是Cat
System.out.println("o的类型是"+o.getClass());
// 3. 通过class来得到加载类com.zjh.reflection.Cat的methodName的方法对象,在反射中可以把方法是为对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
// 通过Method对象来调用方法,invoke方法,传入class获取的实例
method.invoke(o);
// 4. 通过class来的到类的属性
Field name = aClass.getField("name");
System.out.println(name.get(o));
//5. 通过class来获取构造器 aClass.getConstructor()方法中指定构造器的参数类型
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor);
Object o1 = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(o1.getClass());
// 这里是获取String参数的构造器
Constructor<?> constructor1 = aClass.getConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor1);
}
1.3 反射机制
反射的优缺点
- 优点:可以动态的创建和使用对象(也是框架的底层核心),使用灵活,没有反射机制,框架会失去底层支持
- 缺点:使用反射基本是解释执行,对执行速度有影响
编写代码测试两者的执行速度
public void test2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
// 使用new对象来调用方法
Cat cat = new Cat();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<90000000;i++){
cat.hi();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
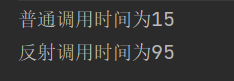
System.out.println("普通调用时间为"+(end-start));
// 获取配置文件对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("D:\\Tools\\ideaProducts\\JAVASE\\reflection\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zjh\\reflection\\re.properties"));
// 加载属性
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath");
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method");
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classfullpath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<90000000;i++){
method.invoke(o);
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射调用时间为"+(end1-start1));
}
1.3.1 反射优化
- Method和Field、Constructor对象都有setAccessible()方法
- setAccessible作用是启动和禁用访问安全检查的开关
- 参数为true表示反射对象在使用时取消访问检查,提高反射效率,参数值为false则表示反射对象执行访问检查
public void test2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
// 使用new对象来调用方法
Cat cat = new Cat();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<90000000;i++){
cat.hi();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
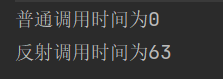
System.out.println("普通调用时间为"+(end-start));
// 获取配置文件对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("D:\\Tools\\ideaProducts\\JAVASE\\reflection\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zjh\\reflection\\re.properties"));
// 加载属性
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath");
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method");
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classfullpath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
method.setAccessible(true);
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<90000000;i++){
method.invoke(o);
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射调用时间为"+(end1-start1));
}
2. Class类
- class 也是类,因此也继承 Object 类
- Class 类对象不是 new 出来的,而是系统创建的
- 对于某个类的 Class 类对象,在内存中只有一份,因为类只加载一次
- Class存放于堆
- 通过Class可以的到类对象获取其API
- 每个实例都知道自己是由哪个Class所生成
2.1 Class的常用方法
public void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
//1 . 获取到 Car 类 对应的 Class 对象 //<?> 表示不确定的 Java 类型
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(classAllPath);
//2. 输出 cls
System.out.println(cls);
//显示 cls 对象, 是哪个类的 Class 对象 com.hspedu.Car
System.out.println(cls.getClass());
//输出 cls 运行类型 java.lang.Class
// 3. 得到包名
System.out.println(cls.getPackage().getName());
//4. 得到全类名
System.out.println(cls.getName());
//5. 通过 cls 创建对象实例
Cat cat = (Cat) cls.newInstance();
System.out.println(cat);//car.toString()
// 6. 通过反射获取属性
Field field = cls.getField("name");
System.out.println(field.get(cat));
//7. 通过反射给属性赋值
field.set(cat, "通过反射给属性赋值");
System.out.println(field.get(cat)); //8 得到所有的属性(字段)
System.out.println("=======所有的字段属性====");
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
System.out.println(f.getName());//名称
}
}
2.2 获取Class对象的方式
- Class.forName
- 类.class
- 对象.getClass
- 通过类加载器来获取:ClassLoad.loadClass
public void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 1.知道类的全路径,此场景应用于配置文件,读取全类名来加载
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(classAllPath);
// 2.类名.class 适用于参数的传递
Class<Cat> cls2 = Cat.class;
// 3. 对象的getClass 适用于已经知道有了对象实例
Cat cat = new Cat();
Class<? extends Cat> cls3 = cat.getClass();
// 4.ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = cat.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?> cls4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.zjh.reflection.Cat");
}
2.3 哪些对象有Class对象
- 外部类,成员内部类,静态内部类,局部内部类,匿名内部类
- 接口
- 数组
- 枚举
- 注解
- 基本数据类型
- void
3. 通过反射创建对象
- newInstance 调用类的无参构造器,且修饰符为pubilc
- getConstructor(Class…clazz) 根据参数列表获取对应的构造器(公开的),再由构造器来获取对象
- getDecalaedConstructor(Class…clazz) 返回所有的构造器对象(包括私有的)根据参数列表,获取对应的构造器对象,
public void test5() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
// 方式1
Cat cat = (Cat) aClass.newInstance();
// 方式2
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getConstructor();
Cat cat2 = (Cat) constructor.newInstance();
// 方式3
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = aClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> declaredConstructor : declaredConstructors) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = declaredConstructor.getParameterTypes();
// 获取构造器的参数属性
for (Class<?> parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println(parameterType);
}
}
}
3.1 爆破获得对象
注意,在调用getDecalaedConstructor(Class…clazz)获取私有的构造器,虽然能获取构造器,但是不能根据构造器去创建实例,除非使用构造器.setAccessible(true)即使用爆破
public class Cat {
public String name = "招财";
public void hi(){
System.out.println("喵喵");
}
public Cat(){
}
private Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
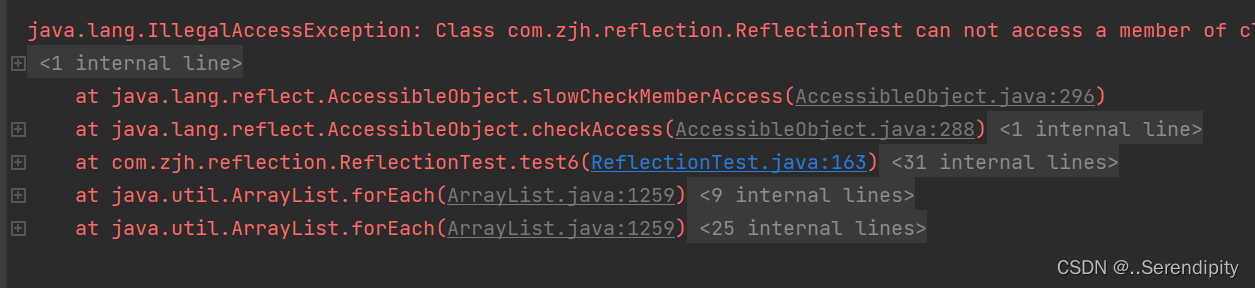
public void test6() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
Cat cat = (Cat) declaredConstructor.newInstance("hello,world");
System.out.println(cat.name);
}
使用爆破
public void test6() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Cat cat = (Cat) declaredConstructor.newInstance("hello,world");
System.out.println(cat.name);
}
3.2 爆破获取属性
public class Cat {
public String name = "招财";
private String nickName = "oh";
public Cat(){
}
private Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hi(){
System.out.println("喵喵");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
}
public void test7() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Field nickName = aClass.getDeclaredField("nickName");
nickName.set(o,"爆破");
Cat cat = (Cat)o;
System.out.println(cat.getNickName());
}
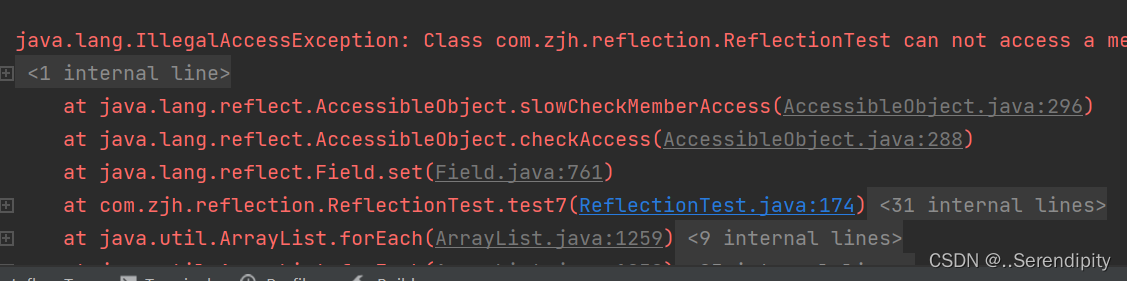
获取私有属性并赋值失败,因为没有进行爆破
public void test7() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Field nickName = aClass.getDeclaredField("nickName");
nickName.setAccessible(true);
nickName.set(o,"爆破");
Cat cat = (Cat)o;
System.out.println(cat.getNickName());
}
3.3 爆破访问方法
public class Cat {
public String name = "招财";
public Cat(){
}
private Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hi(){
System.out.println("喵喵");
}
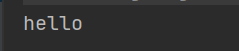
private void hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
@Test
public void test8() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
String classAllPath = "com.zjh.reflection.Cat";
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(classAllPath);
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("hello");
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(o);
}