2、协议设计与解析
2.1、Redis 协议
协议格式:
set name mianbao # 测试命令
*3 # 命令的元素个数 3个
$3 # 命令(set)的长度
set # 命令内容
$4 # key 长度
name # key 内容
$7 # value 长度
mianbao # value 内容
测试代码:
@Slf4j
public class TestRedis {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final byte[] LINE = {
13, 10}; // \r \n
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override // Channel 建立连接成功后触发
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
byteBuf.writeBytes("*3".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("set".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("$4".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("name".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("$7".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
byteBuf.writeBytes("mianbao".getBytes());
byteBuf.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(byteBuf);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6379).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
运行测试
启动 Redis 后,运行程序:

2.2、HTTP 协议
Netty 提供的 HTTP 协议实现
@Slf4j
public class TestHttp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
// HttpServerCodec 即是入站处理器 也是出站处理器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
// 第一种
/*ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// class i.n.h.codec.http.DefaultHttpRequest 和 i.n.h.codec.http.LastHttpContent$1
// 请求行、请求头 和 请求体
log.debug("{}", msg.getClass());
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest){}
else if (msg instanceof HttpContent){}
}
});*/
// 第二种 接收特定消息类型的
// ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpContent>() {});
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
// 获取请求
log.debug(msg.uri());
// 返回响应
DefaultFullHttpResponse response =
new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, World!</h1>".getBytes();
// 响应长度,不设置浏览器会一直转圈读取
response.headers().setInt(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
// 写回响应
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
}finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
运行访问测试

2.3、自定义协议
1)自定义协议-要素
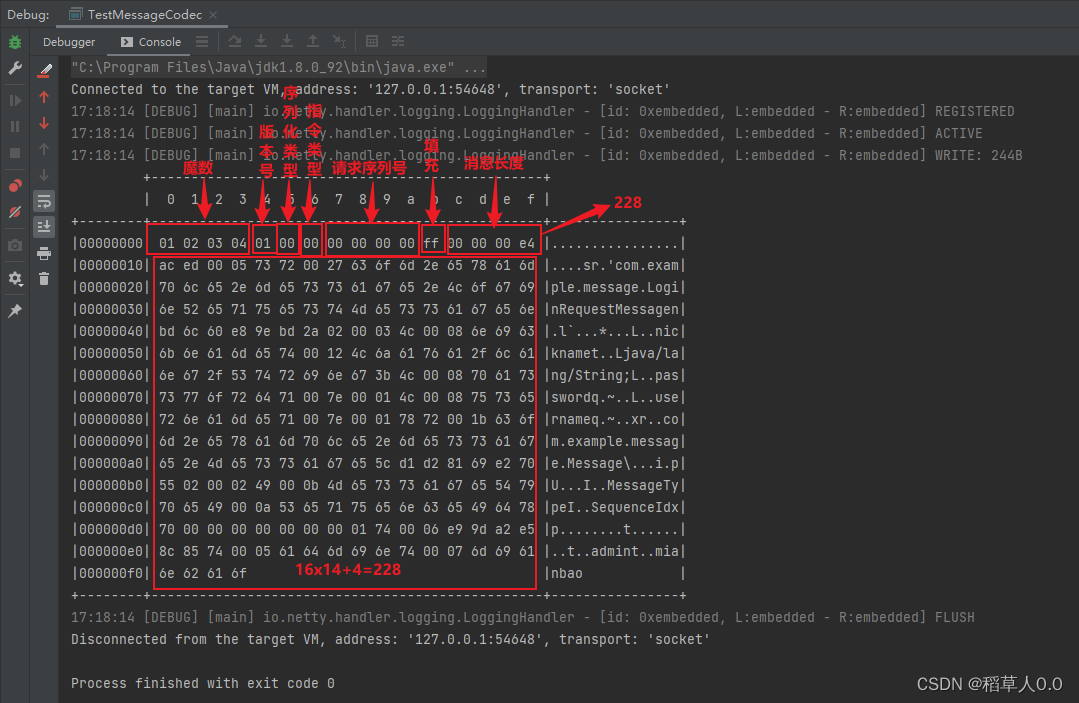
- 魔数,用来在第一时间判定是否是无效数据包
- 版本号,可以支持协议的升级
- 序列化算法,消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式,可以有此扩展。如
json、protobuf、hessian、jdk - 指令类型,是登录、注册、单聊、群聊…跟业务相关
- 请求序号,为了双工通信,提供异步能力(不按顺序发送和接收)
- 正文长度(解决粘包半包问题)
- 消息正文(使用序列化算法,编码和解码,json、xml、对象流等)
2)自定义协议-编解码处理器
编解码处理器代码:
@Slf4j
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
// 编码
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
// 1、 4 字节的魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{
1, 2, 3, 4});
// 2、 1 字节的版本
out.writeByte(1);
// 3、 1 字节的序列化方式:jdk 0, json 1
out.writeByte(0);
// 4、 1 字节的指令类型
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 5、 4 字节的请求序号
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 无意义,对其填充
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 6、 获取内容的字节数组
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
// 7、 4 字节的长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 8、 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
// 4 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 16 字节,控制在 2^n ,可以添加无意义的字节
}
// 解码
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
Message msg = null;
if (serializerType == 0){
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
msg = (Message) ois.readObject();
}
log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.debug("{}", msg);
out.add(msg);
}
}
测试
Message 类
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
private int SequenceId;
public abstract int getMessageType();
public static final int LOGIN_REQUEST_MESSAGE = 0;
public int getSequenceId(){
return SequenceId;
}
}
LoginMessage 类
@Data
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class LoginRequestMessage extends Message{
private String username;
private String password;
private String nickname;
public LoginRequestMessage() {
}
public LoginRequestMessage(String username, String password, String nickname) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return LOGIN_REQUEST_MESSAGE;
}
}
测试类:
public class TestMessageCodec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LoggingHandler(),
new MessageCodec()
);
// 解码 decode
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("mianbao", "admin", "面包");
// 出站
channel.writeOutbound(message);
// 编码 encode
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// encode protected方法,此类必须和 MessageCodec 类在同一个包下
new MessageCodec().encode(null, message, buf);
// 模拟半包
// 入站
channel.writeInbound(buf);
}
}
编码测试结果

粘包与半包问题
模拟半包问题
ByteBuf buf1 = buf.slice(0, 100);
ByteBuf buf2 = buf.slice(100, buf.readableBytes() - 100);
// 模拟半包
channel.writeInbound(buf1);

发送完整
ByteBuf buf1 = buf.slice(0, 100);
ByteBuf buf2 = buf.slice(100, buf.readableBytes() - 100);
// 模拟半包
// writeInbound 后会 release, 再用 buf2 会报错
buf1.retain(); // 引用计数器 +1 = 2
channel.writeInbound(buf1);
channel.writeInbound(buf2);

解决粘包和半包问题,必须加帧解码器
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 12, 4, 0, 0)

3)@shareable
将处理器提取公用的情况
public class TestMessageCodec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程不安全
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder frameDecoder = new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 12, 4, 0, 0);
// 没有记录状态信息的 handler 可以多线程使用,线程安全
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler();
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(loggingHandler, frameDecoder, new MessageCodec());
}
}
Netty 加 @Sharable 注解的 handler 表示多线程安全的。
- LoggingHandler
@Sharable
@SuppressWarnings({
"StringConcatenationInsideStringBufferAppend", "StringBufferReplaceableByString" })
public class LoggingHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
}
- LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
public class LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
}
自定义的 MessageCodec ,不能使用
@Sharable。 父类源码:
/**
* A Codec for on-the-fly encoding/decoding of bytes to messages and vise-versa.
*
* This can be thought of as a combination of {@link ByteToMessageDecoder} and {@link MessageToByteEncoder}.
*
* Be aware that sub-classes of {@link ByteToMessageCodec} <strong>MUST NOT</strong>
* annotated with {@link @Sharable}.
*/
public abstract class ByteToMessageCodec<I> extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
protected ByteToMessageCodec(boolean preferDirect) {
CodecUtil.ensureNotSharable(this); // <===
outboundMsgMatcher = TypeParameterMatcher.find(this, ByteToMessageCodec.class, "I");
encoder = new Encoder(preferDirect);
}
}
可以使用 MessageToMessageCodec 作为父类
注意: 必须和 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用。LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 处理粘包和半包问题,确保 MessageCodecSharable 处理器接到的 ByteBuf 是完整的。(无需记录状态信息)
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 1、 4 字节的魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{
1, 2, 3, 4});
// 2、 1 字节的版本
out.writeByte(1);
// 3、 1 字节的序列化方式:jdk 0, json 1
out.writeByte(0);
// 4、 1 字节的指令类型
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 5、 4 字节的请求序号
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 无意义,对其填充
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 6、 获取内容的字节数组
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
// 7、 4 字节的长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 8、 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
// 4 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 16 字节,控制在 2^n ,可以添加无意义的字节
outList.add(out);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
Message msg = null;
if (serializerType == 0){
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
msg = (Message) ois.readObject();
}
log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.debug("{}", msg);
out.add(msg);
}
}