1. SAP IDT - Overview & User Interface
Information Design Tool (IDT) is a Business Objects design tool that extracts the data from different data sources using an OLAP and Relational connection to create Universes. There are different Universe parameters that can be passed at time of Universe creation.
A Universe is called as logical collection of dimensions and objects that allow business users to analyze the business data. Objects and dimension represent different hierarchies, measures, custom calculations, and attributes.
Universe can be created on the top of relational databases like SQL Server, Oracle or also on top of an InfoCube in SAP Business Warehouse (BW) system. Different types of connections can be created to these data sources like personal connection, shared connection and a public connection. A SQL or MDX statement is generated according to data source respectively - Relational and an OLAP.
A Universe created using an IDT can be used with different reporting tools in Business Objects. When a Universe is published to a central repository, it can be used in the following reporting and dashboard tools −
- SAP Business Objects Web Intelligence (WebI)
- SAP Business Objects Dashboard Designer (Earlier known as Xcelsius)
- SAP Business Objects Crystal Reports
- SAP Business Objects Explorer

1.1 Different Components in IDT while Designing a Universe
An OLAP or a Relational connection to data source
Extracting the tables and joins from Relational database or an OLAP cube.
Building a data foundation from extracted tables and joins.
Creating metadata objects from data foundation layer and these objects are managed in Business layer.
Using Universe parameters and to share the resources in Universe.
Publishing a Universe which includes Business layer, Data Foundation and a Universe connection to database
Security profiles are used to provide access on Universe data and metadata objects.
IDT is primary used by application managers and report developers who wants to create analytical reports on the top of data stored in the different data sources. To create reports on top of Universes, a person needs technical understanding of IDT tool and functional knowledge of Data Warehouse.
2.SAP IDT - Resources
There are various resources in Information Design Tool that can be used to extract the data from data sources and to create a Universe −
2.1. Project
A Project is a local workspace where you store the resources used to build one or more Universes. This is used to manage the local objects, which are used for Universe creation. A single project can contain objects for one or multiple Universe. A local project can contain multiple number of objects like data foundation layer, business foundation, and data source connection, etc.

2.2. Data Foundation
Data Foundation layer allows you to import tables and joins from different relational databases. All the joins are imported and you can also define derived tables, custom calculations, additional joins, contexts and prompts.
2.3.Relational and OLAP Connection
A connection is used to define how data is extracted from a relational or an OLAP data source. A Universe always uses at least one connection to extract the data. You can also build a multisource that extracts data from one or more data sources using multiple connections.
A connection can be saved locally with .cnx file and all Universes created on the top of local connections can’t be published to BO repository. To publish a Universe to repository, you should use a secured central connection with .cns file.
.cns- secured Repository connection
.cnx-local unsecured connection. If you use this connection, it will not allow you to publish anything to repository.
2.4.Business Layer
In Business layer, you define measures and dimensions. You can also apply Aggregations like Sum, Count, Avg, Min, Max.
To complete the Universe creation, you need to save the project and then publish the business layer to the repository.

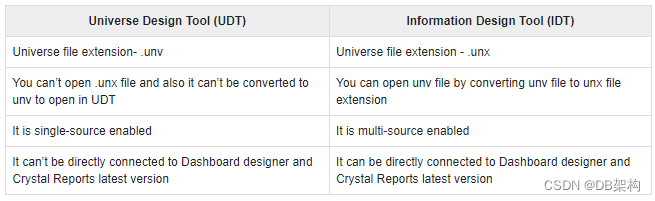
2.5. UDT vs IDT
In UDT, a Universe is created with file extension as .unv. In IDT, a Universe file extension is changed to .unx file.
To open unv file in IDT, it can’t be directly opened but you can convert unv file to unx file to open in Information Design tool. You can’t open an IDT .unx file in Universe Design tool nor you can convert it to unv file.
Universe Design Tool is a single-source enabled tool. However, IDT is a multi-source enabled tool meaning you can extract the data from different data sources while creating a Universe.
2.6. User Interface in IDT(Information Design Tool)
When you retrieve an existing Universe in IDT by connecting to the repository, following are the available interfaces. These are the same when you design a new Universe in Information Design Tool.

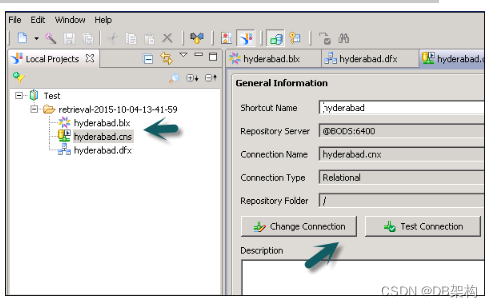
2.7.Local Projects
It defines the existing connection in use (.cnx or.cns), Data foundation layer (.dfx) and Business Layer that are local in Universe as shown above.
You can click on each object under Local Projects to see the details and to make any changes. Click on the connection .cns file to see the connection details. Similarly, you can open .dfx or .blx object.
2.8.Repository Resources
Once you connect to the Repository, you can retrieve all the objects that are designed and published to that repository.
To insert objects from the Repository, click on + sign and select Insert Session. Enter the system details, the username and password, and you can see all the objects in the Repository.

2.9.Business Layer
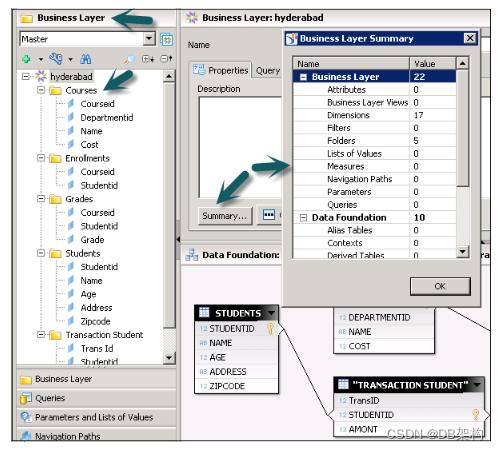
This layer contains all the classes and objects, you can check dimensions and measures that are defined in a Universe. When you publish the business layer in the repository, this shows the completion of Universe creation.
You can check the summary of Business Layer to see the number of attributes, dimensions, measures, classes, LOVs, etc.
2.10. Data Foundation Layer
This layer is used to define data foundation that includes tables from data source, joins, etc.
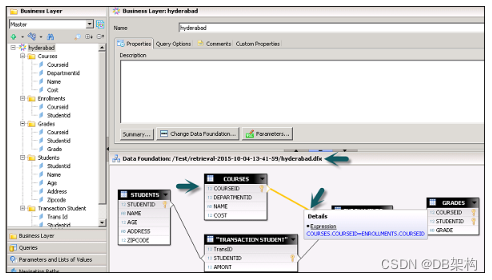
To check the structure of data foundation, you can click on .dfx under local projects and it will take you to Data Foundation layer and its components.

2.11. Setting and Resetting Preferences in IDT
You can customize Information Design tool user interface by setting preferences. This can be reset to default using Reset to default display option. To set the preferences in IDT, go to Windows → Preferences.

Once you click on Preferences, a new window will open. You can define preferences under General, Help and Information Design Tool preferences.
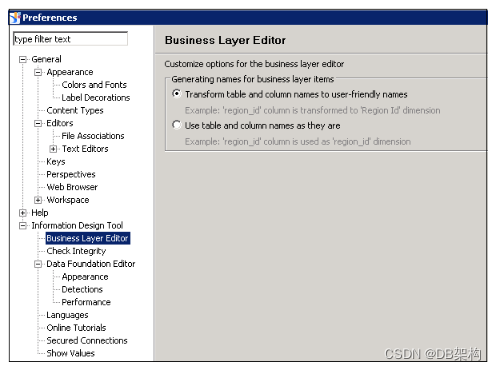
Information Design Tool Preferences
- Business Layer Editor
- Check Integrity
- Data Foundation Editor
- Languages, etc.
Using Reset to Default display option under Window tab allows you to reset all the values to default or you can also use Restore Default option on Preferences window.

3.SAP IDT - Creating Universe
To create a Universe in IDT, go to Start → All Programs → SAP Business Intelligence → SAP Business Objects BI Platform 4 Client Tool.

In Information Design Tool, you have to create a New Project. Go to File → New → Project. Enter the Project Name and Click on Finish.

Once the project is created, next is to create an OLAP or Relational connection to connect to a data source. A Relational connection is used to connect to the Database layer to import tables and Joins. An OLAP connection is used to connect to the multidimensional model like an Information View in SAP HANA.

Right-click on Project name → New → Select Relational Connection → Enter connection/resource name → Next.

Choose SAP from the list → SAP HANA → Select Drivers JDBC → Next → Enter details.

Enter the system details, username, password, and click Next.
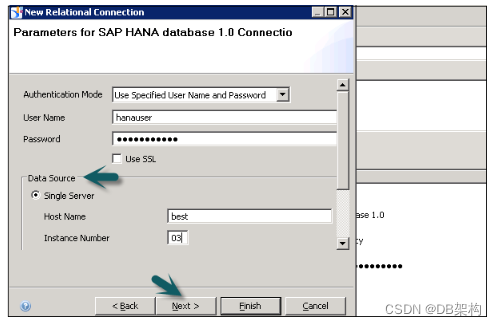
Click Finish.
Under General Information → Click on Test Connection → Successful.

We have to publish this connection to the Repository to make it available for use.
Right-click on the connection name → Publish the connection to the Repository → Enter BO repository password → Click on Connect → Finish → Yes.


Once you click on finish, it will create a secure Repository connection.

.cns − secured Repository connection
.cnx − local unsecured if you use this connection it will not allow you to publish anything to repository.

The next step is to create a Data Foundation Layer on this secure connection.
Right-click on .cns Repository connection → New Data Foundation.

Enter Resource Name and click on Finish. It will show you a list of all available schemas in the database. You can add Tables and Joins from Schema to Data Foundation layer. This can be done by dragging the table or by a double-click. Apply the joins on Dimension and Fact tables to create a logical schema.

To define a Join, double-click on Join between tables. It will show you both the tables. You can select from different Joins as per data requirement and click on detect Cardinality to define cardinality - 1:1, 1:n, n:n.

Next is to create a Business Layer on the Data Foundation. Click the Save All icon at the top of the screen. Then, right-click on Data foundation .dfx → New Business Layer.

Enter Resource Name → (Generating Business Layer for Data Foundation) Finish. It will add Business Layer .blx under the Local Project.
It will show a list of all dimensions and measures under Data Foundation. You can define dimensions, measures, aggregation, etc.

To define an Aggregation, you can select from Projection Function. You can also hide few objects in the report if you want by using the dropdown next to measures and dimension. You can select Hidden for a particular object.

Once you define Business Layer, click Save All icon at the top of the screen as shown in the following screenshot.

To publish a Universe to the Repository, right-click on .blx → Publish → To a Repository.

Select Resources → Next → In Publish Universe window, select Next → Select the Repository folder where you want to publish Universe and click Finish.

You will get a confirmation that Universe published successfully.
To check the Universe under Repository, go to Repository resources and check for the Universe that has been created.

3.2 Creating a Universe on SAP ERP
You can build a universe on SAP ERP by using Data Foundation in IDT. You have to create a relational connection to ERP data source, info sets, SAP queries, and ABAP functions that are treated as tables in the connection.
You can create a single source Data Foundation to support local connections but it doesn’t support Joins and calculated columns between the tables inserted from an ERP connection.
To use a calculated column, joins, you need to create a Data foundation that is multi-source-enabled on a secured connection.

When a table is added in Data Foundation layer, the table type of info set, SAP query, or ABAP function is saved as a table property in the data foundation. To add an ABAP Function table, there is one data foundation table created to map the main function.
The table contains input columns for the input parameters of the function. These parameters can be mandatory or optional. To assign a value to mandatory parameters, you need to edit the input columns.
Limitations of Using SAP ERP
When you use measures that contain aggregate functions it can’t be used as filters in the Query Panel as the output SQL expression consists of HAVING clause, and it is not supported by the SAP ERP connection. Hence, if a measure is added that contains Aggregation function as filter, it throws an error while refreshing the query.
3.3 Creating a Universe on SAP BW
If you want to use SAP BW to design a Universe, you should use a data foundation based on multi-source enabled structure. All the tables and joins in SAP BW are automatically imported to Data Foundation. When a Business Layer is created on Data Foundation, all objects are automatically moved to the Business Layer.

If you don’t want to insert tables and joins automatically, you can unselect the Detect tables by going to advance properties while adding connection to Data Foundation.
You can also turn off insertion of Business Layer objects by unchecking the option to automatically create classes and objects when selecting data foundation in New Business Layer.
3.4 Creating a Universe on Microsoft Analysis Services
You have to create Business Layer on Microsoft Analysis Services (MAS) and business layer objects are created by default. Following is the mapping of objects in Business Layer −
Dimension − Analysis dimensions are created in the business layer for each dimension in the cube.
Display Folder − Folders are created in the analysis dimension to contain the hierarchies in the display folder.
Hierarchy − For value-based (parent-child) hierarchies, a value-based hierarchy is created in the analysis dimension. The attributes are created in the Attributes folder in the hierarchy.
Attribute Hierarchy − Attribute hierarchies in the cube are created as level-based hierarchies in the analysis dimension.
Named Set − Named sets are created in the related analysis dimension, in the folder Named sets.
Measures and Calculated Measures − Measures and calculated measures are created as measures in the appropriate measure group folder. A measure attribute is created for the formatted value.
3.5 Creating a Universe on SAS
You can build a Universe on SAS by using multi-source enabled data foundation and using a secure connection.
Connection to SAS data source are managed by data federation service.
Multilingual Universes
You can also create multilingual Universe in Information Design tool. This allows you to use multilingual solution by using single Universe metadata model.
Following are the steps to use multilingual Universe for report creation −
Step 1 − Use Universe designer to design Universe in source language in IDT.
Step 2 − Use translation management tool to translate the metadata in the data foundation and business layer.
Step 3 − Use report designers to build the reports on the same Universe, which can be displayed in different languages as per user preferences.
Step 4 − Go to Information Design Tool → Preferences → Preferred Viewing Locale determines the language of the metadata and data in the Query Panel.

This can be used if you have support for the following −
-
Translations are available in the language (metadata).
-
The connection supports the language parameter (data).