1.编程题 Homework01.java
(1)在判断e盘下是否有文件夹mytemp,如果没有就创建mytemp
(2)在e:\\mytemp目录下,创建文件hello.txt
(3)如果hello.txt已经存在,提示该文件已经存在,就不要再重复创建了。
(4)并且在hello.txt文件中,写入hello,world~.
我们设计的代码如下所示:
package com.rgf.work; import java.io.*; public class Homework01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* (1)在判断e盘下是否有文件夹mytemp,如果没有就创建mytemp (2)在e:\\mytemp目录下,创建文件hello.txt (3)如果hello.txt已经存在,提示该文件已经存在,就不要再重复创建了。 (4)并且在hello.txt文件中,写入hello,world~. */ String directoryPath="e:\\mytemp"; File file = new File(directoryPath); if(!file.exists()) { //创建 if (file.mkdirs()) { System.out.println("创建" + directoryPath + "创建成功"); } else { System.out.println("创建" + directoryPath + "创建失败"); } } String filePath=directoryPath+"\\hello.txt"; // e:\mytemp\hello.txt file = new File(filePath); if(!file.exists()) { //创建文件 if (file.createNewFile()) { System.out.println(filePath + "创建成功"); //如果文件存在,我们就使用BufferedWriter字符输入流写入内容 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); bufferedWriter.write("hello,world~~蕾峰编程"); bufferedWriter.close(); } else { System.out.println(filePath + "创建失败"); } }else { //如果文件已经存在,给出提示信息 System.out.println(filePath+"已经存在,不再重复创建"); } } }我们运行之后如下所示:
我们打开该路径进行查看:
我们发现我们成功的创建了该文件。
我们再次运行的时候我们发现如下所示:
2.编程题 Homework02.java
要求:使用BufferedReader读取一个文本文件,为每行加上行号,再连同内容一并输出到屏幕上。
我们设计的代码如下所示:
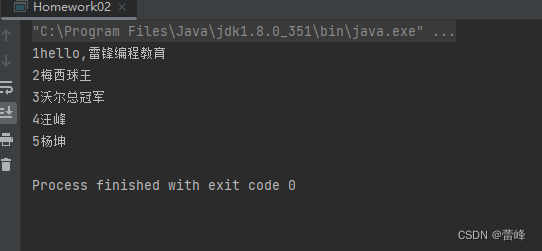
package com.rgf.work; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Homework02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用BufferedReader读取一个文本文件,为每行加上行号,再连同内容一并输出到屏幕上。 String filePath="e:\\b.txt"; String line=""; int lineNum=0; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); while((line=br.readLine())!=null){//循环读取 System.out.println(++lineNum+line); } if(br!=null){ br.close(); } } }我们运行之后如下所示:
如果我们将文件的编码进行修改:
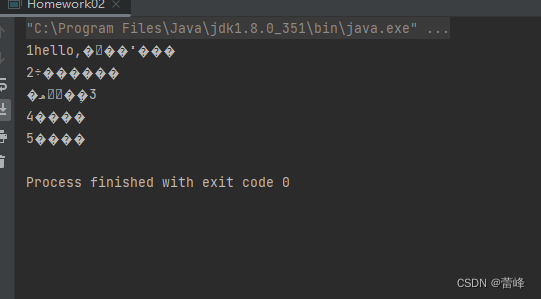
我们重新运行之后发现如下所示:
我们发现出现了乱码。我们将编码格式从utf-8改为了gbk,出现了中文乱码。
1.默认是按照utf-8处理,开始没有乱码
2.提示:使用我们的转换流,将 FileInputStream ->InputStreamReader【可以指定编码】->BufferedReader.
我们设计的代码如下所示:
package com.rgf.work; import java.io.*; public class Homework02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用BufferedReader读取一个文本文件,为每行加上行号,再连同内容一并输出到屏幕上。 String filePath="e:\\b.txt"; String line=""; int lineNum=0; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),"gbk")); while((line=br.readLine())!=null){//循环读取 System.out.println(++lineNum+line); } if(br!=null){ br.close(); } } }我们运行之后如下所示:
3.编程题Homework03.java
(1)要编写一个dog.properties
name=tom
age=5
color=red
(2)编写Dog类(name,age,color)创建一个dog对象,读取dog.properties用相应的内容完成属性初始化,并输出。
(3)将创建的Dog对象,序列化到文件dog.dat文件
我们设计的代码如下所示:
package com.rgf.work; import java.io.*; import java.util.Properties; public class Homework03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* (1)要编写一个dog.properties name=tom age=5 color=red (2)编写Dog类(name,age,color)创建一个dog对象,读取dog.properties用相应的内容完成属性初始化,并输出。 (3)将创建的Dog对象,序列化到文件dog.dat文件 */ //创建Properties对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); //在文件中写入要求的内容 properties.setProperty("name","tom"); properties.setProperty("age","5"); properties.setProperty("color","red"); properties.store(new FileOutputStream("com\\dog.properties"),null); String filePath="com\\dog.properties"; properties.load(new FileReader(filePath)); properties.list(System.out); //读取dog.properties用相应的内容完成属性初始化,并输出。 String name = properties.get("name")+""; //Object-->String String color = properties.get("color") + ""; //Object-->String int age =Integer.parseInt(properties.get("age")+"") ; //Object-->int Dog dog = new Dog(name,age,color); System.out.println("====dog对象信息===="); System.out.println(dog); //将创建的Dog对象,序列化到文件dog.dat文件 String serFilepath="e:\\dog.dat"; ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serFilepath)); oos.writeObject(dog); //关闭流 oos.close(); System.out.println("dog对象,序列化完成..."); } } class Dog implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; private String color; public Dog(String name, int age, String color) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", color='" + color + '\'' + '}'; } }我们运行之后如下所示:
我们打开文件进行查看:
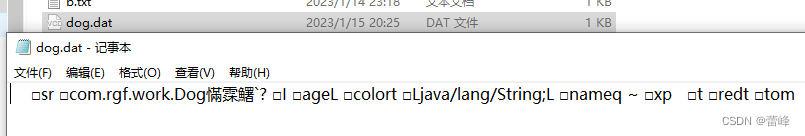
我们下来进行编写一个方法进行反序列化:
我们设计的代码如下所示:
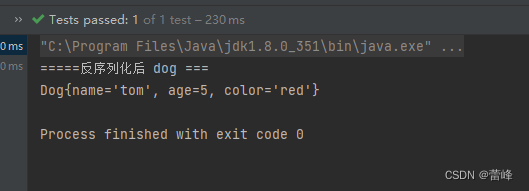
//再编写一个方法,反序列化dog @Test public void m1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { String serFilepath="e:\\dog.dat"; ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serFilepath)); Dog dog=(Dog)ois.readObject(); System.out.println("=====反序列化后 dog ==="); System.out.println(dog); ois.close(); } }我们运行之后如下所示: