利用IO流实现文件的拷贝
通俗解释:
实现一个类似Windows下的复制功能即ctrl + c -----> ctrl + v.
核心思想
- 将源文件读入到内存中
- 将读入的数据写入目标文件
其中,不需要将源文件的数据彻底读入完才进行写入目标文件。这样做一方面效率很低,而且当文件很大内存容纳不了时,就会出现问题。
因此采用边读边写的方式进行文件拷贝.
图示:
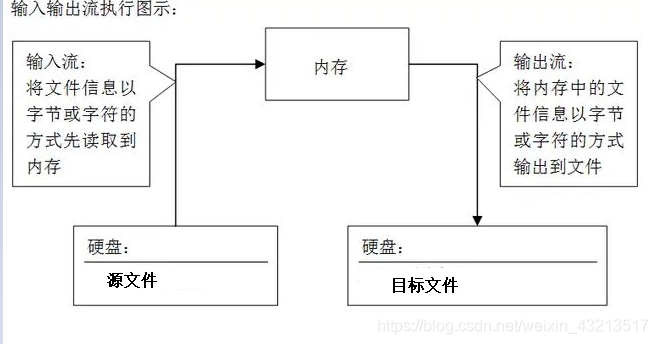
具体步骤
- 进行路径校验
用户传进来源文件和目标文件的路径,以字符串的形式,因此很有必要对传入的路径进行校验。
校验规则:源文件必须存在,且是一个文件,没有源文件,何谈拷贝?
目标文件也必须是一个文件,但可以不存在,因为在对一个文件进行写入时若该文件不存在,会自行进行创建.
但不会自行创建该文件的目录,因此若目标文件的目录不存在,则必须事先创建。
- 校验完毕,进行拷贝
代码实现
对路径进行检验
private static boolean checkSourcePath(File file){
if(file == null){
return false;
}
// 确保源文件存在,且是一个文件
return file.exists() && file.isFile();
}
private static boolean checkAndCreatDestPath(File file){
if(file == null || file.isDirectory()){
return false;
}
// 判断目标文件的目录是否存在,不存在则进行创建
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
return true;
}采用字节流对文件进行读写,因为拷贝的文件不一定是文本文件
private static boolean fileCopy(File source,File dest){
//JDK 1.7引入的新写法,可以实现自动关闭,即自动调用close()方法
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(source);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);){
int len = -1;
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
while((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
out.write(buff,0,len);
}
out.flush(); // 刷新缓冲区
return true;
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}用户使用的方法
public static boolean fileCopy(String sourcePath,String destPath){
File sourceFile = new File(sourcePath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
if(!checkSourcePath(sourceFile)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sourcePath is illegal!");
}
if(! checkAndCreatDestPath(destFile)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("destPath is illegal!");
}
return fileCopy(sourceFile,destFile);
}测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sourceParh = "F:\\VMWareWorkstation 12.0.0.exe";
String destPath = "E:\\VMWareWorkstation 12.0.0.exe";
System.out.println(fileCopy(sourceParh,destPath));
}整体代码
import java.io.*;
/**
* @auther plg
* @date 2019/4/9 17:22
*/
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sourceParh = "F:\\VMWareWorkstation 12.0.0.exe";
String destPath = "E:\\VMWareWorkstation 12.0.0.exe";
System.out.println(fileCopy(sourceParh,destPath));
}
public static boolean fileCopy(String sourcePath,String destPath){
File sourceFile = new File(sourcePath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
if(!checkSourcePath(sourceFile)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sourcePath is illegal!");
}
if(! checkAndCreatDestPath(destFile)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("destPath is illegal!");
}
return fileCopy(sourceFile,destFile);
}
private static boolean checkSourcePath(File file){
if(file == null){
return false;
}
// 确保源文件存在,且是一个文件非一个目录
return file.exists() && file.isFile();
}
private static boolean checkAndCreatDestPath(File file){
if(file == null || file.isDirectory()){
return false;
}
// 判断目标文件的目录是否存在,不存在则进行创建
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
return true;
}
private static boolean fileCopy(File source,File dest){
//JDK 1.7引入,可以实现自动关闭,即自动调用close()方法
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(source);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);){
int len = -1;
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
while((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
out.write(buff,0,len);
}
return true;
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
}