单链表的实现
- 1.链表的分类
- 2.(单)链表的实现
- 3. 单链表OJ练习
-
-
-
- 1. [移除链表元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
- 2. [合并两个有序链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/)
- 3. [反转链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- 4. [链表的中间结点](https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
- 5. [链表中倒数第k个结点](https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a)(只能遍历链表一遍)
- 6. [链表分割](https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70)
- 7. [链表的回文结构](https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
- 8. [相交链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
- 9. [环形链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
- 10.[ 环形链表 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- 11.[复制带随机指针的链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
-
-
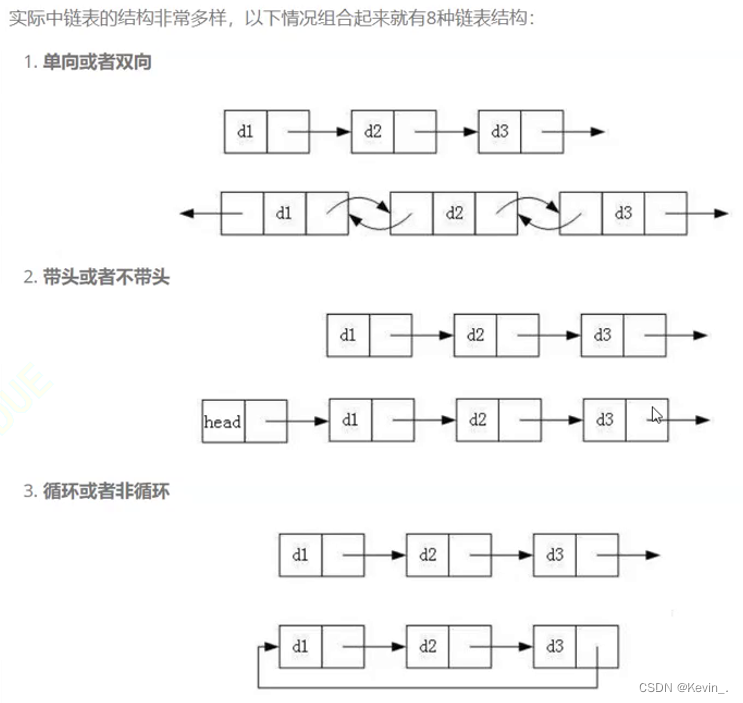
引入: 顺序表的缺点:
- 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间,会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般二倍增长,会有一定的空间浪费。
1.链表的分类
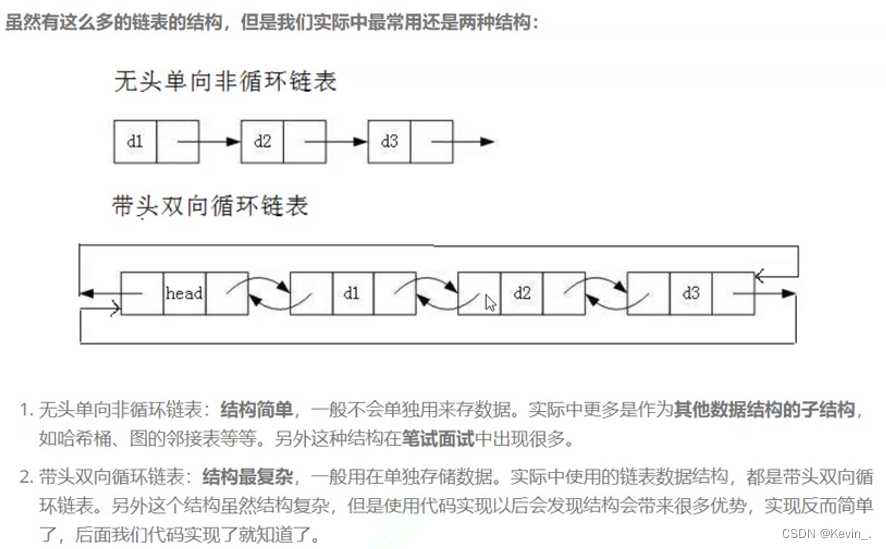
2.(单)链表的实现
无头+单向+非循环链表增删查改的实现
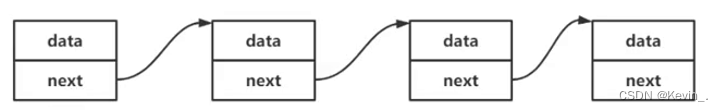
1. 链表结构的定义
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
2. 链表的打印
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
//额外定义一个头指针cur来用,防止经过遍历后再次使用时找不到头指针
SLTNode* cur=phead;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
printf("%d",cur->data);
cur=cur->next; //
}
printf("NULL");
}
3. 头插
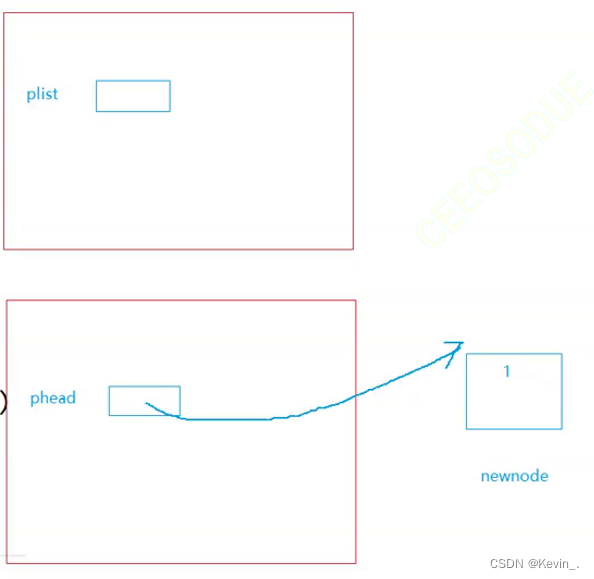
错误示范:
// 进入这个函数就会创建临时变量phead
void SLPushFront(SLNode* phead,SLDataType x)
// phead是一个SLNode*类型的名为plist的指针变量的形参,phead与plist都指向同一空间(值域相同),但是他们自身分别在不同的空间存储着(地址域不同)。
{
SLTNode* newnode=BuySLTNode(x); //开辟出新的节点
newnode->next=phead; //这一步操作将phead的值域赋给了next
phead=newnode; //这一步操作将newnode的值域赋给了phead
}
// 退出运行函数后形参phead就被释放
// 整个过程中没有改变plist
正确示范:
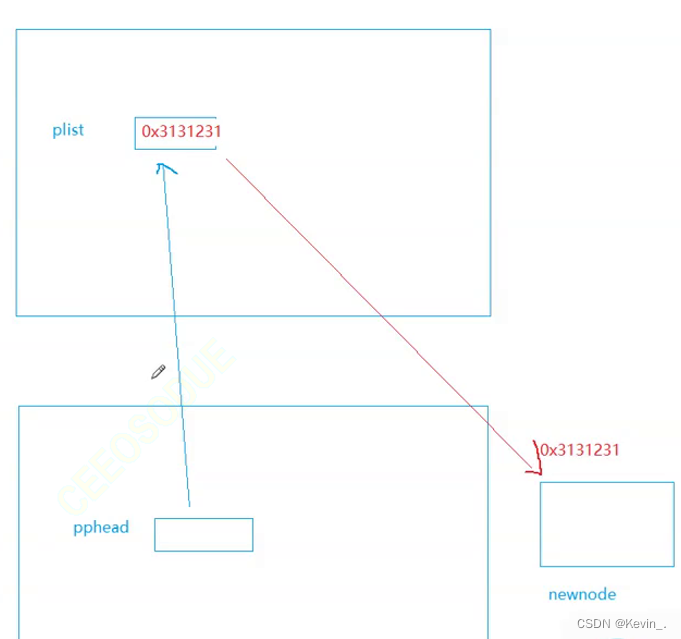
//传过来的是一级指针变量的地址,所以用二级指针变量接收
void SLNodePushFront(SLTNode** pphead,SLTDataType x)
//pphead是一个SLNode*类型且名为plist的指针变量的地址的临时拷贝,存的是一级指针变量plist的地址 (pphead的值域是plist的地址)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode=BuySLTNode(x);
newnode->next=*pphead; //二级指针变量pphead解引用得到一级指针变量plist
*pphead=newnode; //通过解引用pphead将链表的头指针plist更替为newnode
}
错误示范:
正确示范:
4. 创建节点
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x)
{
// SLTNode newnode; // 创建的是局部变量,出了函数之后就会被销毁掉,不能创建出新节点
SLTNode* newnode=(SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
}
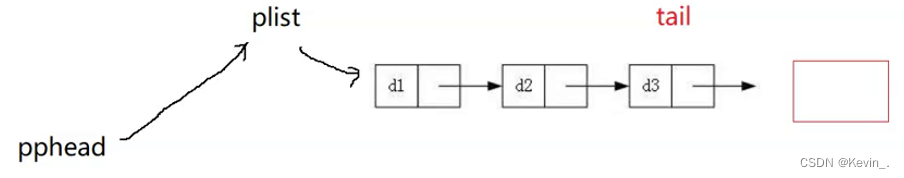
5. 尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead,SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode=BuySLTNode(x);
if(*pphead==NULL) //plist为空
{
*pphead=newnode; //将链表的头指针plist更替为newnode
}
else
{
//找尾
SLTNode* tail=*pphead;
while(tail->next!=NULL)
{
tail=tail->next;
}
tail->next=newnode;
}
}
6. 尾删
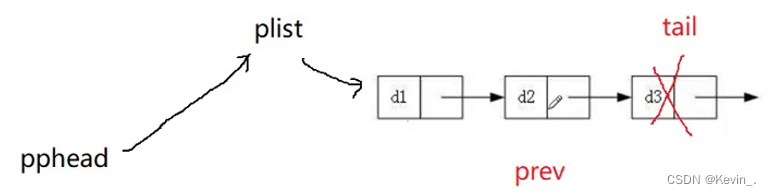
方法一:
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//找尾
SLTNode* prev=NULL; //用来标识紧挨尾节点前面的节点
SLTNode* tail=*pphead;
while(tail->next!=NULL)
{
prev=tail;//更替tail之前先将tail赋给prev,更替tail之后prev就变成tail前面的节点
tail=tail->next;
}
prev->next=NULL;
free(tail);
tail=NULL;
}
方法二:
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* tail=*pphead;
while(tail->next->next!=NULL)
{
tail->tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next=NULL;
}
7. 头删
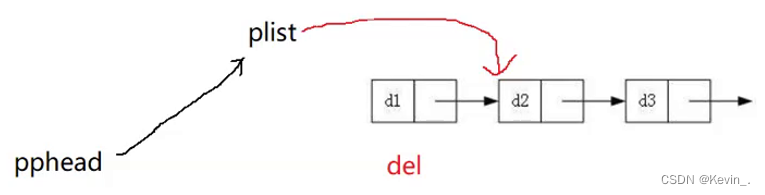
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//检查链表是否已经为空
// 1
if(*pphead==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
// 2
// assert(*pphead!=NULL);
SLTNode* del=*pphead; //备份一个头指针del来用,防止更新头指针后找不到原来的头指针
*pphead=(*pphead)->next; //更新头指针
free(del); //free掉原来的头指针
del=NULL;
}
8. 链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SLTNode** lpphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* cur=*pphead;
while(cur)
{
SLTNode* next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=next;
}
*pphead=NULL;
}
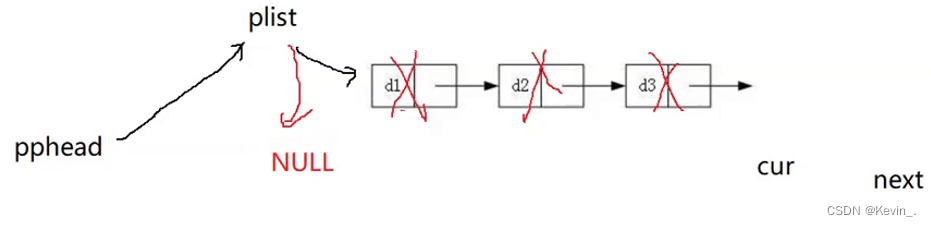
9.查找
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead,SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur=phead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->data==x)
{
return cur;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
10. 在pos之前插入
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead,SLTNode* pos,SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if(pos==*pphead)
{
SListPustFront(pphead,x);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev=*pphead
while(prev->next!=pos)
{
prev=prev->next;
// 检查pos是否为空,prev为空,还没有找到pos,说明pos传错了
assert(prev);
}
SLTNode*newnode=BuySLTNode(x);
prev->next=newnode;
newnode->next=pos;
}
}
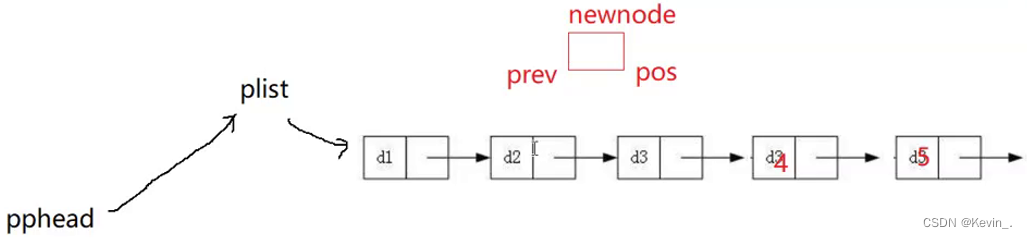
11. 在pos之后插入
错误示范:
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos,SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode=ButSLTNode(x);
pos->next=newnode;
newnode->next=pos->next;//此时pos的next已经指向newnode
//再次赋给newnode的next会使newnode自己指向自己,无法插入
}
正确示范:
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos,SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode=BuySLTNode(x);
newnode->next=pos->next;
pos->next=newnode;
}
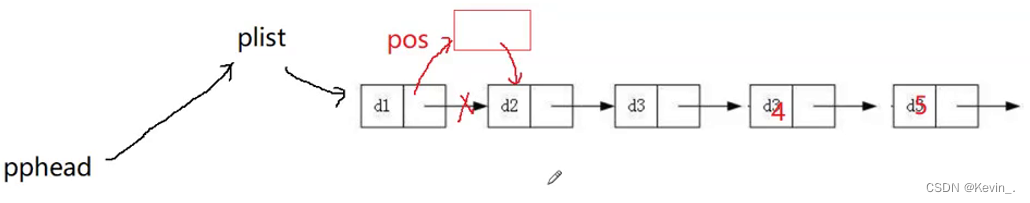
12. 删除pos位置
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead,SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if(*pphead==pos)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
// 找的pos前面的节点并用prev标记
SLTNode* prev=*pphead;
while(prev->next!=pos)
{
prev=prev->next;
//检查pos不是链表中的节点,参数传错了
assert(prev);
}
prev->next=pos->next;
free(pos);
// pos=NULL;
}
}
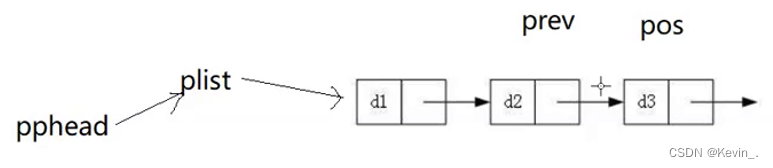
13. 删除pos后面的位置
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if(pos->next==NULL)
{
return ;
}
else
{
SLTNode* next=pos->next;// 用next记录pos后面的节点
pos->next=next->next;
free(next);
}
}

14. 测试函数
#inlcude <stdio.h>
void TestSList1()
{
SLNode* plist=NULL;
//可以理解为此时内存中已经存在一个SLNode类型的空间,但是在内存中的位置是未知的
//单链表不需要初始化,直接定义并且指向NULL即可
SListPushFront(plist,1); //传的是指针变量plist
SListPushFront(&plist,1);//传的是指针变量plist的地址
SListPushFront(&plist,2);
SListPushFront(&plist,3);
SListPushFront(&plist,4);
SListPrint(plist);
}
void TestList2()
{
SLTNode* plist=NULL;
SListPustBack(&plist,1);
SListPustBack(&plist,2);
SListPustBack(&plist,3);
SListPustBack(&plist,4);
//修改
SLTNode* pos=SListFind(plist,3)
if(pos)
{
pos->data*=10;
}
SListPrint(plist);
SListDestory(&plist);
}
int main()
{
void TestList2();
return 0;
}
3. 单链表OJ练习
1. 移除链表元素
思路一:
- 非头删
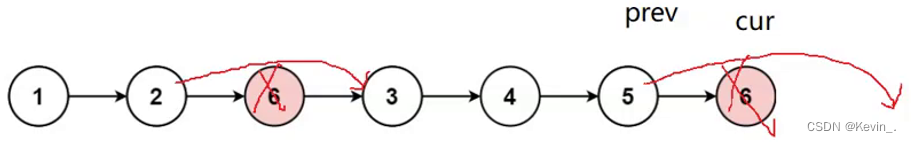
- 头删
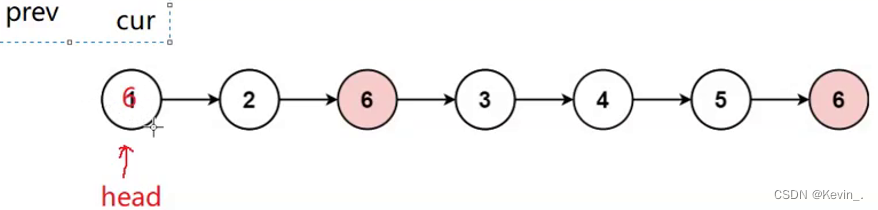
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head,*prev=NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val==val)
{
//1.头删
//2.非头删
if(cur==head)
{
head=head->next;
free(cur);
cur=head;
}
else
{
prev->next=cur->next;// 使cur前面的节点指向cur后面的节点
free(cur);
cur=prev->next;
}
}
else
{
//向后遍历
prev=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
思路二:
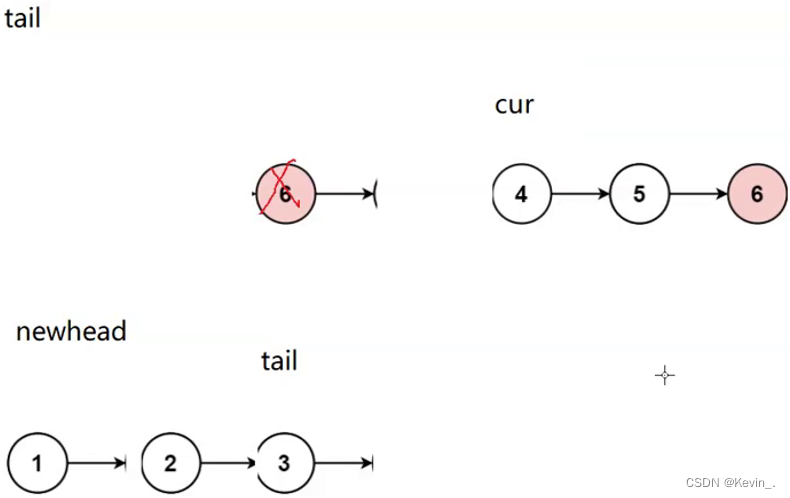
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head,int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val!=val)
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
//新链表为空链表,插入第一个节点
newhead=tail=cur;
}
else
{
//尾插
tail->next=cur;
//更新tail
tail=tail->next;
}
//向后遍历
cur=cur->next;
}
else
{
sturct ListNode* del=cur; //备份一下当前的指针,防止更新cur后找不到原来的位置
cur=cur->next;
free(del);
}
}
// 最后一个节点是val,就会出现此问题
if(tail)
tail->next=NULL;
return newnode;
}
思路二升级版:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head,int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head;
//struct ListNode* newhead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
//创建一个guard节点,不存储有效数据
struct ListNode* guard =(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail=gaurd;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val!=val)
{
//尾插到tail/guard后面
tail->next=cur;
tail=tail->next;
//遍历
cur=cur->next;
}
else
{
sturct ListNode* del=cur; //备份一下当前的指针,防止更新cur后找不到原来的位置
cur=cur->next;
free(del);
}
}
// 最后一个节点是val,就会出现此问题
if(tail)
{
tail->next=NULL;
}
return head=guard->next;
free(guard);//释放掉guard节点
return head;
}
2. 合并两个有序链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
//创建guard节点,不存储有效数据
struct ListNode* guard=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
guard->next=NULL;
struct ListNode* tail=guard;
struct ListNode* cur1=list1,*cur2=list2;
//取较小的尾插
while(cur1&&cur2)
{
if(cur1->val<cur2->val)
{
tail->next=cur1;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next=cur2;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
tail=tail->next;
}
//将剩余的节点插入
if(cur1)
{
tail->next=cur1;
}
if(cur2)
{
tail->next=cur2;
}
struct ListNode* head=guard->next;
free(guard);
return head;
}
3. 反转链表
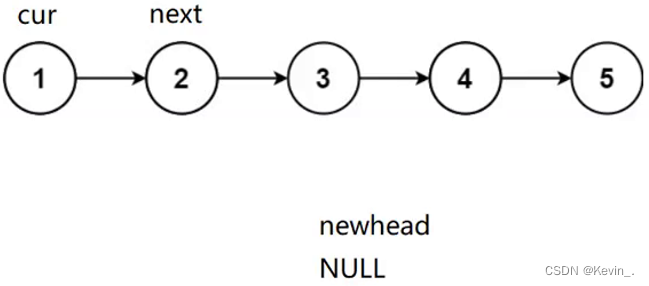
思路一:异地头插
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL; //定义一个空指针作为新链表的头指针
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;//next定义在while()内部,以防在cur为空指针的情况下被解引用
// 尾插
cur->next=newhead; // 更改原链表中头指针的指向,指向新链表的头
newhead=cur; // 更新新链表的头节点,把新插入的头节点作为新链表的头节点
cur=next; // 更新原链表的头节点,往后走
}
return newhead;
}
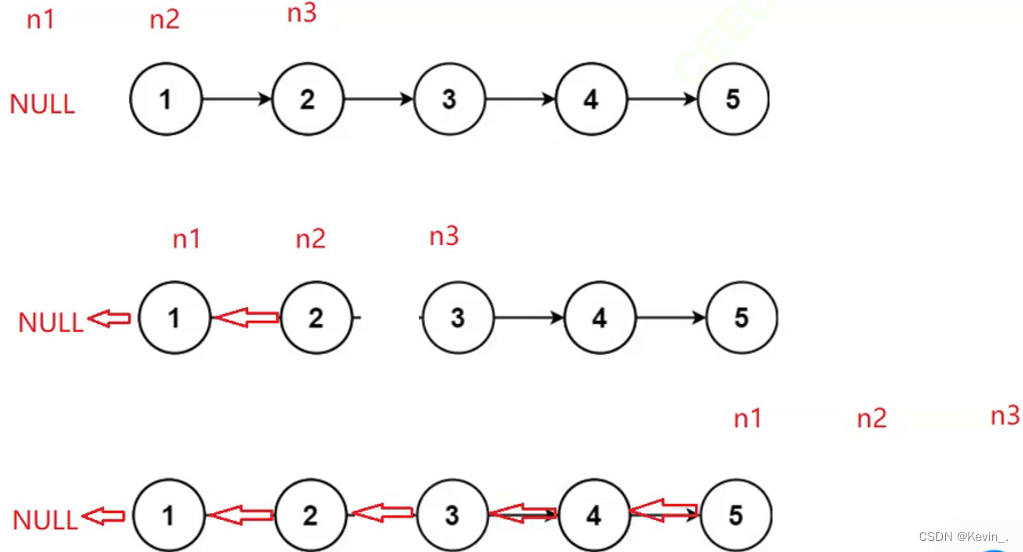
思路二:原地逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
n3=NULL; //先置空,防止n2为空指针的情况下对n2解引用
while(n2)
{
n3=n2->next;
n2->next=n1; // 更改链表中第二个节点的指向,指向第一个节点
// 迭代,将n1,n2向后移动
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
}
return n1,
}
4. 链表的中间结点

struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow=fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
5. 链表中倒数第k个结点(只能遍历链表一遍)

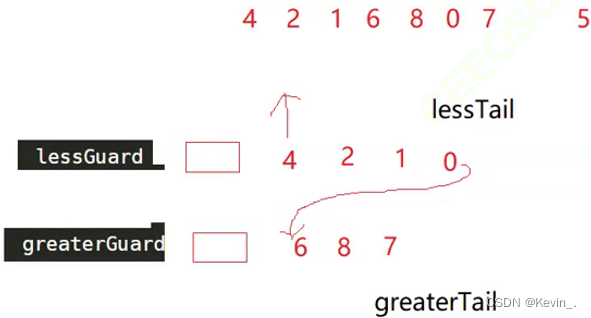
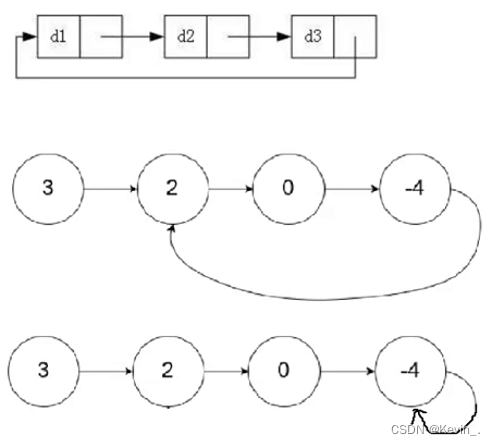
6. 链表分割
图一:
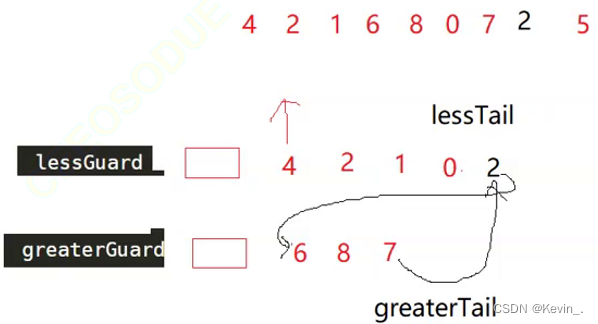
图二:
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
struct ListNode* lessGuard,*lessTail,*greaterGuard,*greaterTail;//创建guard节点,不存储有效数据
lessGuard=lessTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
greaterGuard=greaterTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
lessGuard->next=NULL;
greaterGuard->next=NULL;
struct ListNode* cur=pHead;//重新定义一个指针用于遍历
//遍历
while(cur)
{
//分类尾插到新链表
if(cur->val<x)
{
lessTail->next=cur; //将存储较小值的链表的尾节点指向当前节点
lessTail=lessTail->next;//将存储较小值的链表的尾节点更新为刚插入的节点
}
else
{
greaterTail->next=cur;//将存储较大值的链表的尾节点指向当前节点
greaterTail=greaterTail->next;//将存储较大值的链表的尾节点更新为刚插入的节点
}
cur=cur->next;//遍历原链表
}
lessTail->next=greaterGuard->next;//将存储较小值的链表的尾节点指向存储较大值的链表的guard节点的下一个节点
greaterTail->next=NULL;//将较大值链表的尾节点指向NULL,防止在原链表为图二的情况下组成的新链表成环
//原因:
//原链表中的最后一个节点指向NULL,如果原链表中的最后一个节点的值比x大,那么它刚好在插入新链表后也使得新链表的最后一个节点指向NULL
//如果原链表中倒数第二个节点比x大,倒数第一个节点比x小,在它们组成新链表后,原链表中的倒数第二个节点依然指向倒数第一个节点,会在新链表中出现环
pHead=lessGuard->next;//lessGuard的下一个节点就是新链表的头节点
free(greaterGuard);
free(lessGuard);
return pHead;
}
};
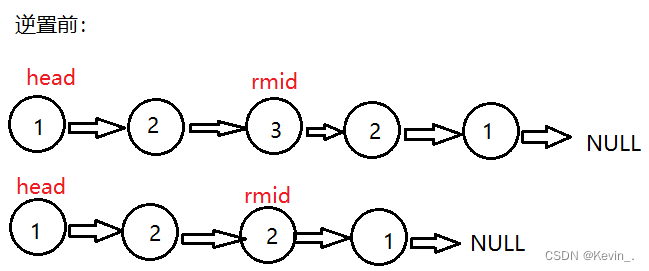
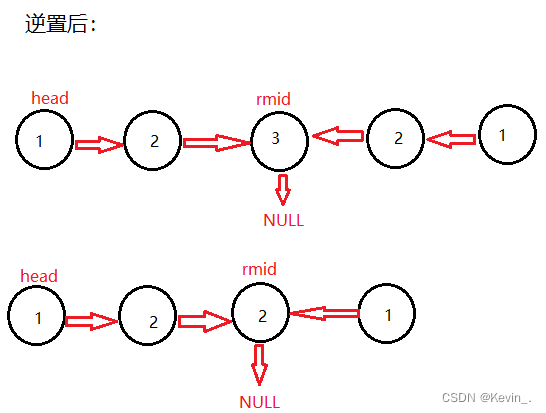
7. 链表的回文结构
思路一:将后半段逆置
class PalindromeList {
public:
// 找出中间节点
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow=fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
// 将中间节点以及后半段逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
n3=NULL;
while(n2)
{
n3=n2->next;
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
}
return n1;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* mid=middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* rmid=reverseList(mid);
while(head&&rmid)
{
if(head->val!=rmid->val) //判断是否相等
//无论原链表的节点是奇数还是偶数个,
//经过逆置后原链表中的中间节点前的那个节点依旧指向中间节点,
//新的两端链表的尾节点是同一个节点,所以只需判断剩余部分是否相等即可
return false;
//遍历
head=head->next;
rmid=rmid->next;
}
return true;
}
};
思路二:将整个链表逆置
// 错误示范:(逆置后原链表的原始结构被改变)
class PalindromeList {
public:
// 逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
n3=NULL;
while(n2)
{
n3=n2->next;
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
}
return n1;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* rhead=reverseList(head);
while(head&&rhead)
{
if(head->val!=rhead->val) //判断是否相等
return false;
//遍历
head=head->next;
rhead=rhead->next;
}
return true;
}
};
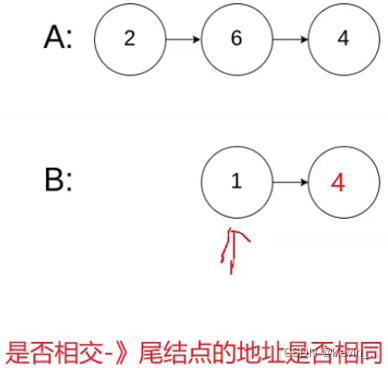
8. 相交链表
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB)
{
//空链表时为没有交点
if(headA==NULL||headB==NULL)
return NULL;
//计算两个链表的长度
struct ListNode* curA=headA,*curB=headB;
int lenA=1;
while(curA->next)
{
curA=curA->next;
++lenA;
}
int lenB=1;
while(curB->next)
{
curB=curB->next;
++lenB;
}
//如果两个链表的尾节点不同,则他们没有相交
if(curB!=curB)
{
return NULL;
}
//先假设headA为长链表,headB为短链表
struct ListNode* longList=headA,*shortList=headB;
if(lenA<lenB)
{
longList=headB;
shortList=headA;
}
//算出两个链表的节点数之差
int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);
//长的链表先走差距步
while(gap--)
{
longList=longList->next;
}
//两链表的节点相等时就是交点
while(longList!=shortList)
{
longList=longList->next;
shortList=shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}
};
9. 环形链表
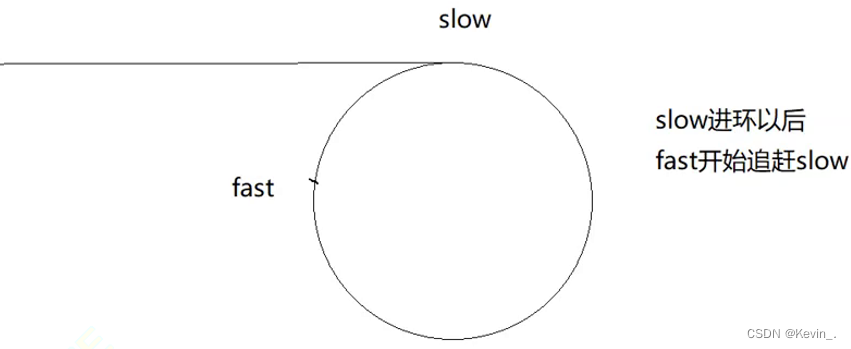
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* fast,*slow;
fast=slow=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)//如果fast或者fast->next有一个为空则不带环
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->nex t->next;
if(slow==fast)//fast和slow在环中追赶,如果他们相等则证明带环
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
3. 带环单链表问题
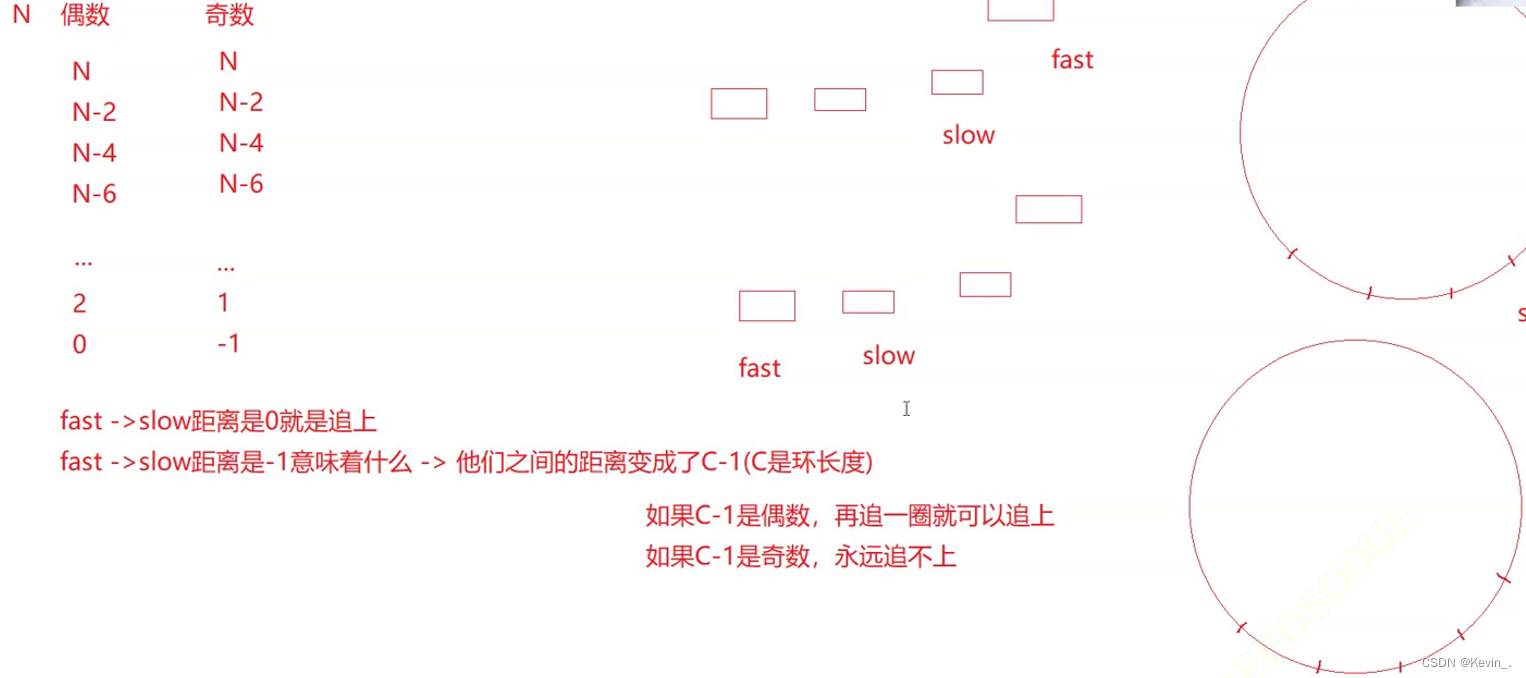
10. 环形链表 II
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* fast=head,*slow=head;
//判断是否有环
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
//如果有环
if(slow==fast)
{
struct ListNode* meet =slow;//找到fast和slow在环中的相遇点
while(meet!=head)
{
meet=meet->next;//相遇点在环中往前走
head=head->next;//头节点从头走,它们会在环的入口点相遇
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
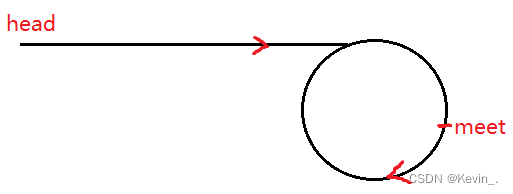
11.复制带随机指针的链表

/
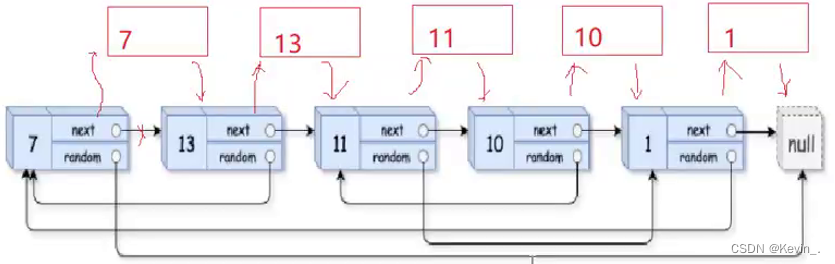

/

class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head)
{
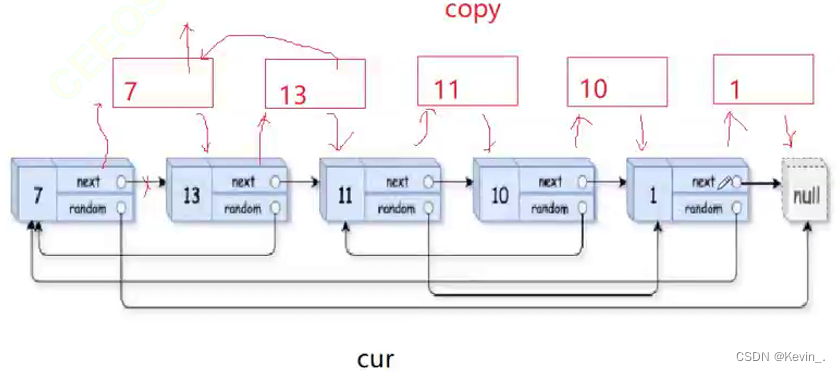
// 1. 插入copy节点
struct Node*cur=head;
struct Node* copy=NULL;
struct Node* next=NULL;
while(cur)
{
// 复制连接
struct Node* next=cur->next;
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
cur->next=copy;
copy->next=next;
//迭代
cur=next;
}
// 2. 更新copy->random
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
//迭代
cur=cur->next->next;
}
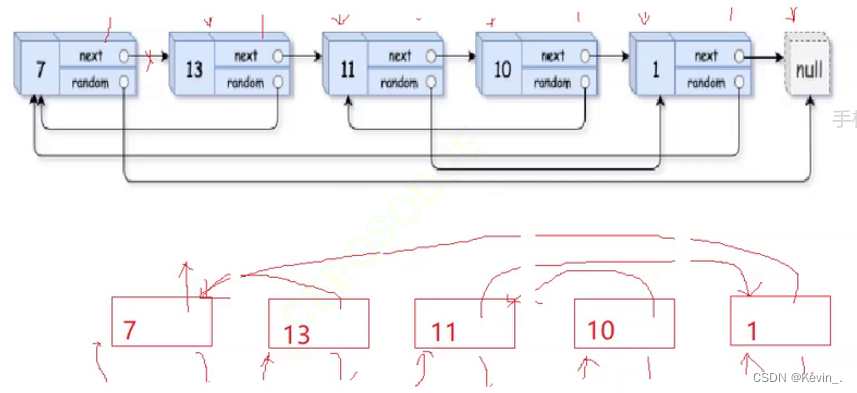
// 3. copy节点解下来,恢复原链表
struct Node* copyHead=NULL,*copyTail=NULL;
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
copy=cur->next;
next=copy->next;
// 取节点尾插
if(copyTail==NULL)
{
copyHead=copyTail=copy;
}
else
{
copyTail->next=copy;
copyTail=copyTail->next;
}
// 恢复原链表链接
cur->next=next;
// 迭代
cur=next;
}
return copyHead;
}
};