一、Java标准资源管理
1、Java 标准资源定位
| 职责 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 面向资源 | 文件系统、artifact(jar、war、ear 文件)以及远程资源(HTTP、FTP等) |
| API 整合 | java.lang.ClassLoader#getResource、java.io.File 或 java.net.URL |
| 资源定位 | java.net.URL 或 java.net.URI |
| 面向流式存储 | java.net.URLConnection |
| 协议扩展 | java.net.URLStreamHandler 或 java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory |
2、Java URL 协议扩展
基于 java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory
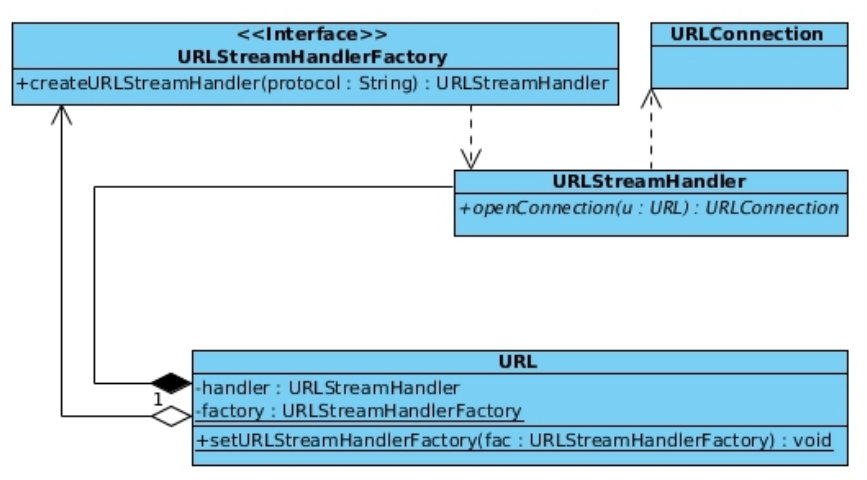
java.net.URL中定义了一个静态变量factory:
static URLStreamHandlerFactory factory;
public static void setURLStreamHandlerFactory(URLStreamHandlerFactory fac) {
synchronized (streamHandlerLock) {
if (factory != null) {
// 只能设置一次
throw new Error("factory already defined");
}
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkSetFactory();
}
handlers.clear();
factory = fac;
}
}
基于 java.net.URLStreamHandler
基于 java.net.URLStreamHandler 扩展协议(JDK 1.8 內建协议实现):
| 协议 | 实现类 |
|---|---|
| file | sun.net.www.protocol.file.Handler |
| ftp | sun.net.www.protocol.ftp.Handler |
| http | sun.net.www.protocol.http.Handler |
| https | sun.net.www.protocol.https.Handler |
| jar | sun.net.www.protocol.jar.Handler |
| mailto | sun.net.www.protocol.mailto.Handler |
| netdoc | sun.net.www.protocol.netdoc.Handler |
实现类名必须为 “Handler”:
| 实现类命名规则 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 默认 | sun.net.www.protocol.${protocol}.Handler |
| 自定义 | 通过 Java Properties java.protocol.handler.pkgs 指定实现类包名,实现类名必须为“Handler”。如果存在多包名指定,通过分隔符 “|” |
java.net.URL中定义protocolPathProp:
private static final String protocolPathProp = "java.protocol.handler.pkgs";
static URLStreamHandler getURLStreamHandler(String protocol) {
URLStreamHandler handler = handlers.get(protocol);
if (handler == null) {
boolean checkedWithFactory = false;
// Use the factory (if any)
if (factory != null) {
handler = factory.createURLStreamHandler(protocol);
checkedWithFactory = true;
}
// Try java protocol handler
if (handler == null) {
// 对protocolPathProp 的处理
String packagePrefixList = null;
packagePrefixList
= java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction(
protocolPathProp,""));
if (packagePrefixList != "") {
packagePrefixList += "|";
}
// REMIND: decide whether to allow the "null" class prefix
// or not.
packagePrefixList += "sun.net.www.protocol";
StringTokenizer packagePrefixIter =
new StringTokenizer(packagePrefixList, "|");
3、Java 标准资源管理扩展的步骤
(1)简易实现
实现 URLStreamHandler 并放置在 sun.net.www.protocol.${protocol}.Handler 包下
(2)自定义实现
• 实现 URLStreamHandler
• 添加 -Djava.protocol.handler.pkgs 启动参数,指向 URLStreamHandler 实现类的包下
(3)高级实现
• 实现 URLStreamHandlerFactory 并传递到 URL 之中
4、Spring为什么不用Java标准的资源管理
Java 标准资源管理强大,然而扩展复杂,资源存储方式并不统一。
而使用Java开发的程序员,基本也都离不开Spring,作为Java届的龙头老大,Spring的很多东西都要试图与Java比一比,很多东西都完全独立于jdk自己重新弄了一套。
这个操作,Spring似乎实现的很成功,甚至隐隐超过jdk默认的很多实现,有一种引领java开发的潮流的意思。
二、Spring资源接口与实现
1、Spring基本资源接口
资源接口:
| 类型 | 接口 |
|---|---|
| 输入流 | org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource |
| 只读资源 | org.springframework.core.io.Resource |
| 可写资源 | org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource |
| 编码资源 | org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource |
| 上下文资源 | org.springframework.core.io.ContextResource |
InputStreamSource接口
InputStreamSource接口只有一个方法,getInputStream获取输入流。
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
Resource接口
Resource只读资源,继承了InputStreamSource接口,也具有获取输入流功能。同时具有getURL、getURI、getFile等功能,对资源只提供读取功能的接口。
WritableResource接口
WritableResource可写资源,继承Resource,有isWritable来判断资源是否可写,同时可以getOutputStream获取输出流。
EncodedResource类
EncodedResource类用于编码,继承InputStreamSource,针对需要指定资源编码如UTF-8这种的资源。属性有Resource对象,主要通过getInputStreamReader来实现编码。
ContextResource接口
ContextResource接口继承了Resource接口,ContextResource应用较少,上下文资源,一般给Servlet引擎使用。。
2、Spring 内建 Resource 实现
| 资源来源 | 资源协议 | 实现类 |
|---|---|---|
| Bean 定义 | 无 | org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionResource |
| 数组 | 无 org.springframework.core.io.ByteArrayResource | |
| 类路径 | classpath:/ | org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource |
| 文件系统 | file:/ | org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource |
| URL | URL 支持的协议 | org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource |
| ServletContext | 无 | org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextResource |
BeanDefinitionResource
实际上这个类很少用到。
它是不可读的,主要用于描述。
ByteArrayResource
内存型的资源流,同java.io.ByteArrayInputStream
ClassPathResource
它是用class、classLoader进行资源的读取的。
FileSystemResource
3、Spring Resource 接口扩展
可写资源接口
org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource
- org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource
- org.springframework.core.io.FileUrlResource(@since 5.0.2)
- org.springframework.core.io.PathResource(@since 4.0 & @Deprecated)
编码资源接口
org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource
// 代码实例
String currentJavaFilePath = "D:\\test.text";
File currentJavaFile = new File(currentJavaFilePath);
// FileSystemResource => WritableResource => Resource
FileSystemResource fileSystemResource = new FileSystemResource(currentJavaFilePath);
EncodedResource encodedResource = new EncodedResource(fileSystemResource, "UTF-8");
// 字符输入流
try (Reader reader = encodedResource.getReader()) {
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(reader));
}
4、Spring 资源加载器
org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader
- org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader
- org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResourceLoader
- org.springframework.core.io.ClassRelativeResourceLoader
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext是应用上下文的实现,所以说spring应用上下文也是一种资源加载器。
String currentJavaFilePath = "/D:\\test.text"; // 以 / 开头
// 新建一个 FileSystemResourceLoader 对象
FileSystemResourceLoader resourceLoader = new FileSystemResourceLoader();
// FileSystemResource => WritableResource => Resource
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(currentJavaFilePath);
EncodedResource encodedResource = new EncodedResource(resource, "UTF-8");
// 字符输入流
try (Reader reader = encodedResource.getReader()) {
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(reader));
}
5、Spring 通配路径资源加载器
通配路径 ResourceLoader:
- org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
- org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
路径匹配器:
- org.springframework.util.PathMatcher
- Ant 模式匹配实现 - org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher
Spring 通配路径资源扩展
public interface ResourceUtils {
static String getContent(Resource resource) {
try {
return getContent(resource, "UTF-8");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
static String getContent(Resource resource, String encoding) throws IOException {
EncodedResource encodedResource = new EncodedResource(resource, encoding);
// 字符输入流
try (Reader reader = encodedResource.getReader()) {
return IOUtils.toString(reader); // org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils
}
}
}
(1)实现 org.springframework.util.PathMatcher
(2)重置 PathMatcher:PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#setPathMatcher
public class CustomizedResourcePatternResolverDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 读取当前 package 对应的所有的 .java 文件
// *.java
String currentPackagePath = "/D:\\";
String locationPattern = currentPackagePath + "*.java";
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(new FileSystemResourceLoader());
resourcePatternResolver.setPathMatcher(new JavaFilePathMatcher());
Resource[] resources = resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern);
Stream.of(resources).map(ResourceUtils::getContent).forEach(System.out::println);
}
static class JavaFilePathMatcher implements PathMatcher {
@Override
public boolean isPattern(String path) {
return path.endsWith(".java");
}
@Override
public boolean match(String pattern, String path) {
return path.endsWith(".java");
}
@Override
public boolean matchStart(String pattern, String path) {
return false;
}
@Override
public String extractPathWithinPattern(String pattern, String path) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> extractUriTemplateVariables(String pattern, String path) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Comparator<String> getPatternComparator(String path) {
return null;
}
@Override
public String combine(String pattern1, String pattern2) {
return null;
}
}
}
三、依赖注入Spring Resource
基于 @Value 实现,如:
@Value(“classpath:/...”)
private Resource resource;
通常 Resource 无法通过依赖查找,可以通过@Value来配合依赖注入,它们属于内部依赖对象,非常规的 Bean 生命周期管理。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 注入 {@link Resource} 对象示例,ResourceUtils在上面有
*
* @see Resource
* @see Value
* @see AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
* @since
*/
public class InjectingResourceDemo {
// 注入default.properties资源
@Value("classpath:/META-INF/default.properties")
private Resource defaultPropertiesResource;
// 注入所有的properties资源
// classpath*:/ 表示所有 ClassPath 下的资源,相当于 ClassLoader#getResources 方法
// classpath:/ 表示当前 ClassPath 下的资源,相当于 ClassLoader#getResource 方法
@Value("classpath*:/META-INF/*.properties")
private Resource[] propertiesResources;
// 获取Environment参数
@Value("${user.dir}")
private String currentProjectRootPath;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println(ResourceUtils.getContent(defaultPropertiesResource));
System.out.println("================");
Stream.of(propertiesResources).map(ResourceUtils::getContent).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("================");
System.out.println(currentProjectRootPath);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 注册当前类作为 Configuration Class
context.register(InjectingResourceDemo.class);
// 启动 Spring 应用上下文
context.refresh();
// 关闭 Spring 应用上下文
context.close();
}
}
四、依赖注入 ResourceLoader
方法一:实现 ResourceLoaderAware 回调
方法二:@Autowired 注入 ResourceLoader
方法三:注入 ApplicationContext 作为 ResourceLoader
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 注入 {@link ResourceLoader} 对象示例
*
* @see ResourceLoader
* @see Resource
* @see Value
* @see AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
* @since
*/
public class InjectingResourceLoaderDemo implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; // 方法一
@Autowired
private ResourceLoader autowiredResourceLoader; // 方法二
@Autowired
private AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext; // 方法三
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("resourceLoader == autowiredResourceLoader : " + (resourceLoader == autowiredResourceLoader));// true
System.out.println("resourceLoader == applicationContext : " + (resourceLoader == applicationContext)); // true
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 注册当前类作为 Configuration Class
context.register(InjectingResourceLoaderDemo.class);
// 启动 Spring 应用上下文
context.refresh();
// 关闭 Spring 应用上下文
context.close();
}
}
参考资料
极客时间-《小马哥讲 Spring 核心编程思想》