说明
1、手眼标定实际上是求解矩阵方程:AX = XB ; A是摄像机(单目或双目)前后两次空间变换的齐次矩阵 ; B是机械臂末端坐标系前后两次变换的齐次矩阵 ; X为待求解的手眼矩阵;通过多次求解该方程,即可解出X(A 、B矩阵求法如下)

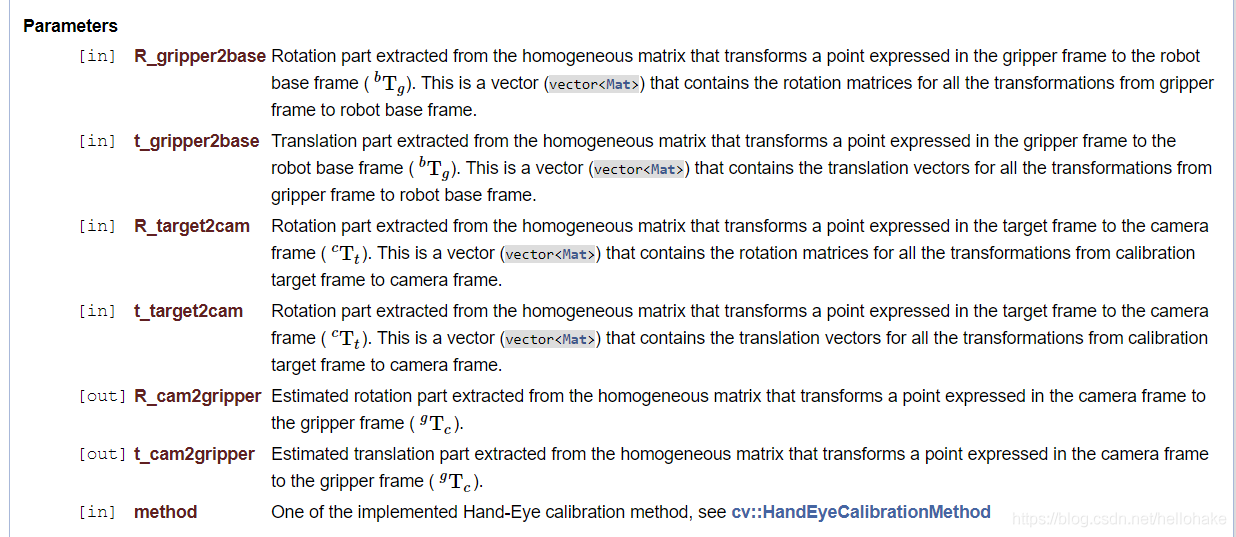
2、calibrateHandeye() 参数描述如下:R_gripper2base,t_gripper2base是机械臂抓手相对于机器人基坐标系的旋转矩阵与平移向量,需要通过机器人运动控制器或示教器读取相关参数转换计算得到;R_target2cam , t_target2cam 是标定板相对于双目相机的齐次矩阵,在进行相机标定时可以求取得到(calibrateCamera()得到), 也可以通过solvePnP()单独求取相机外参数获得 ; R_cam2gripper , t_cam2gripper是求解的手眼矩阵分解得到的旋转矩阵与平移矩阵;OpenCV实现了5种方法求取手眼矩阵 , Tsai两步法速度最快。
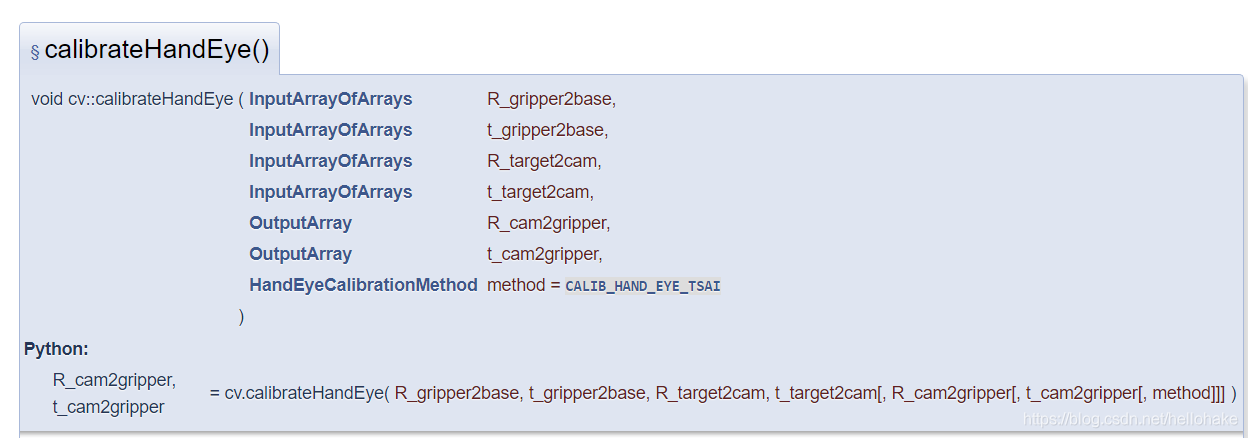
OpenCV实现的5种方法:

3、计算步骤:

4、原理:
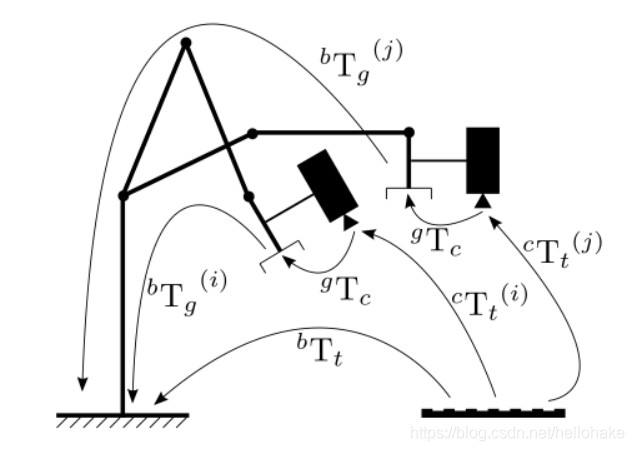

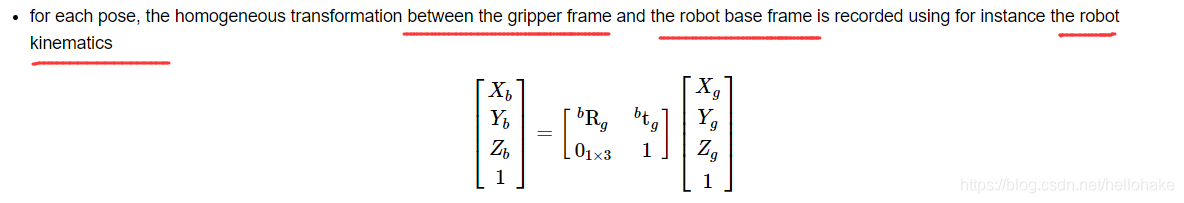
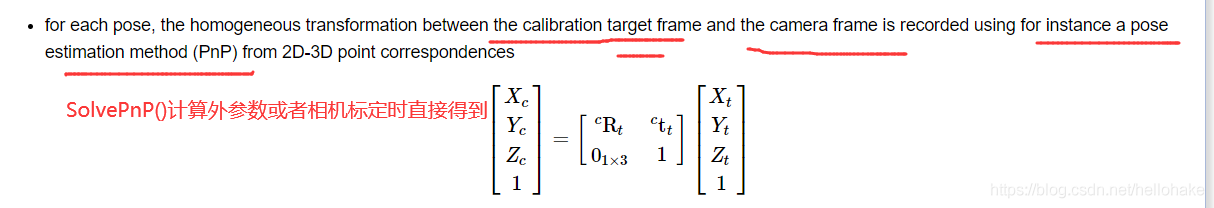

5、坐标转换关系:一般是获得摄像机坐标系中点在机器人坐标系下的点的空间位置的描述;



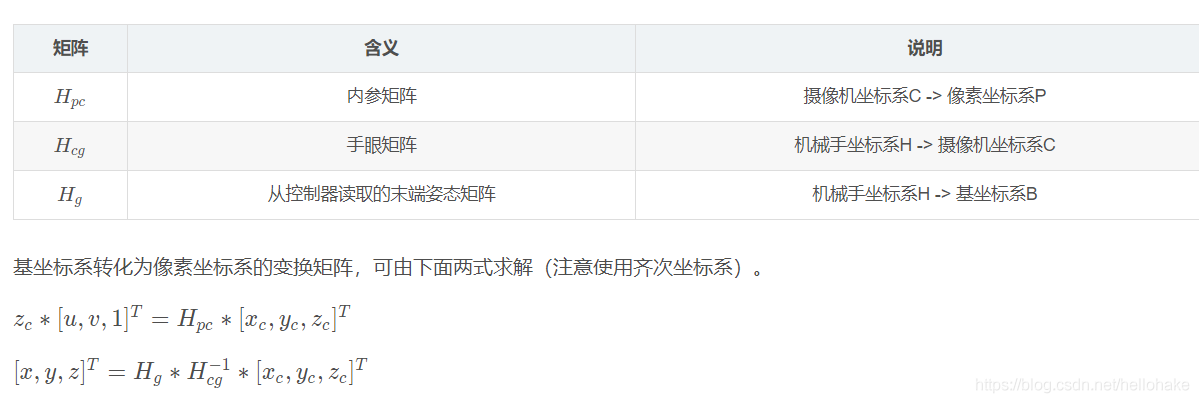
6、手眼方程:
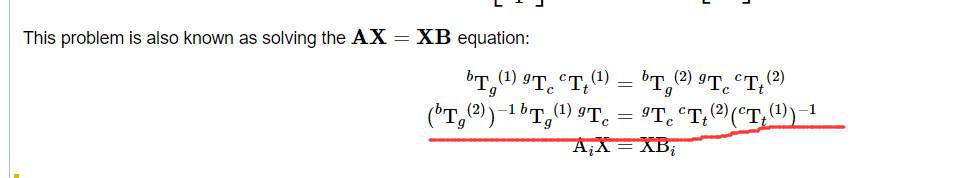

Code
1、思路:编写一些函数:实现四元数、欧拉角到旋转矩阵的转换,实现齐次矩阵的分解与合成,然后处理数据,提供给calibrateHandeye()使用,计算出手眼矩阵。
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
Mat R_T2HomogeneousMatrix(const Mat& R, const Mat& T);
void HomogeneousMtr2RT(Mat& HomoMtr, Mat& R, Mat& T);
bool isRotatedMatrix(Mat& R);
Mat eulerAngleToRotateMatrix(const Mat& eulerAngle, const std::string& seq);
Mat quaternionToRotatedMatrix(const Vec4d& q);
Mat attitudeVectorToMatrix(const Mat& m, bool useQuaternion, const string& seq);
//数据使用的已有的值
//相机中13组标定板的位姿,x,y,z,rx,ry,rz,
Mat_<double> CalPose = (cv::Mat_<double>(13, 6) <<
-0.072944147641399, -0.06687830562048944, 0.4340418493881254, -0.2207496117519063, 0.0256862005614321, 0.1926014162476009,
-0.01969337858360518, -0.05095294728651902, 0.3671266719105768, 0.1552099329677287, -0.5763323472739464, 0.09956130526058841,
0.1358164536530692, -0.1110802522656379, 0.4001396735998251, -0.04486168331242635, -0.004268942058870162, 0.05290073845562016,
0.1360676260120161, -0.002373036366121294, 0.3951670952829301, -0.4359637938379769, 0.00807193982932386, 0.06162504121755787,
-0.1047666520352697, -0.01377729010376614, 0.4570029374109721, -0.612072103513551, -0.04939465180949879, -0.1075464055169537,
0.02866460103085085, -0.1043911269729344, 0.3879127305077527, 0.3137563103168434, -0.02113958397023016, 0.1311397970432597,
0.1122741829392126, 0.001044006395747612, 0.3686697279333643, 0.1607160803445018, 0.2468677059920437, 0.1035103912091547,
-0.06079521129779342, -0.02815190820828123, 0.4451740202390909, 0.1280935541917056, -0.2674407142401368, 0.1633865613363686,
-0.02475533256363622, -0.06950841248698086, 0.2939836207787282, 0.1260629671933584, -0.2637748974005461, 0.1634102148863728,
0.1128618887222624, 0.00117877722121125, 0.3362496409334229, 0.1049541359309871, -0.2754352318773509, 0.4251492928748009,
0.1510545750008333, -0.0725019944548204, 0.3369908269102371, 0.2615745097093249, -0.1295598776133405, 0.6974394284203849,
0.04885313290076512, -0.06488755216394324, 0.2441532410787161, 0.1998243391807502, -0.04919417529483511, -0.05133193756053007,
0.08816140480523708, -0.05549965109057759, 0.3164905645998022, 0.164693654482863, 0.1153894876338608, 0.01455551646362294);
//机械臂末端13组位姿,x,y,z,rx,ry,rz
Mat_<double> ToolPose = (cv::Mat_<double>(13, 6) <<
-0.3969707, -0.460018, 0.3899877, 90.2261, -168.2015, 89.7748,
-0.1870185, -0.6207147, 0.2851157, 57.2636, -190.2034, 80.7958,
-0.1569776, -0.510021, 0.3899923, 90.225, -178.2038, 81.7772,
-0.1569787, -0.5100215, 0.3299975, 90.2252, -156.205, 81.7762,
-0.3369613, -0.4100348, 0.3299969, 90.2264, -146.2071, 71.778,
-0.2869552, -0.6100449, 0.4299998, 90.2271, -199.2048, 86.7806,
-0.2869478, -0.6600489, 0.4299948, 105.2274, -189.2053, 86.7814,
-0.286938, -0.6300559, 0.4299997, 75.2279, -189.2056, 86.783,
-0.2869343, -0.5700635, 0.2800084, 75.2291, -189.2055, 86.7835,
-0.1669241, -0.5700796, 0.280015, 75.2292, -189.205, 101.7845,
-0.236909, -0.4700997, 0.3600046, 87.2295, -196.2063, 118.7868,
-0.2369118, -0.6201035, 0.2600001, 87.2297, -192.2087, 75.7896,
-0.2468983, -0.620112, 0.359992, 97.2299, -190.2082, 80.7908);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//数据声明
vector<Mat> R_gripper2base;
vector<Mat> T_gripper2base;
vector<Mat> R_target2cam;
vector<Mat> T_target2cam;
Mat R_cam2gripper = Mat(3,3,CV_64FC1); //相机与机械臂末端坐标系的旋转矩阵与平移矩阵
Mat T_cam2gripper = Mat(3,1,CV_64FC1);
Mat Homo_cam2gripper = Mat(4,4,CV_64FC1);
vector<Mat> Homo_target2cam;
vector<Mat> Homo_gripper2base;
Mat tempR, tempT, temp;
for (int i = 0; i < CalPose.rows; i++) //计算标定板与相机间的齐次矩阵(旋转矩阵与平移向量)
{
temp = attitudeVectorToMatrix(CalPose.row(i), false, ""); //注意seq为空,相机与标定板间的为旋转向量
Homo_target2cam.push_back(temp);
HomogeneousMtr2RT(temp, tempR, tempT);
/*cout << i << "::" << temp << endl; cout << i << "::" << tempR << endl; cout << i << "::" << tempT << endl;*/
R_target2cam.push_back(tempR);
T_target2cam.push_back(tempT);
}
for (int j = 0; j < ToolPose.rows; j++) //计算机械臂末端坐标系与机器人基坐标系之间的齐次矩阵
{
temp = attitudeVectorToMatrix(ToolPose.row(j), false, "xyz"); //注意seq不是空,机械臂末端坐标系与机器人基坐标系之间的为欧拉角
Homo_gripper2base.push_back(temp);
HomogeneousMtr2RT(temp, tempR,tempT);
/*cout << j << "::" << temp << endl; cout << j << "::" << tempR << endl; cout << j << "::" << tempT << endl;*/
R_gripper2base.push_back(tempR);
T_gripper2base.push_back(tempT);
}
//TSAI计算速度最快
calibrateHandEye(R_gripper2base,T_gripper2base,R_target2cam,T_target2cam,R_cam2gripper,T_cam2gripper,CALIB_HAND_EYE_TSAI);
Homo_cam2gripper = R_T2HomogeneousMatrix(R_cam2gripper, T_cam2gripper);
cout << Homo_cam2gripper << endl;
cout << "Homo_cam2gripper 是否包含旋转矩阵:" << isRotatedMatrix(Homo_cam2gripper) << endl;
///
/************************************************** * @note 手眼系统精度测试,原理是标定板在机器人基坐标系中位姿固定不变, * 可以根据这一点进行演算 **************************************************/
//使用1,2组数据验证 标定板在机器人基坐标系中位姿固定不变
cout << "1 : " << Homo_gripper2base[0] * Homo_cam2gripper * Homo_target2cam[0] << endl;
cout << "2 : " << Homo_gripper2base[1] * Homo_cam2gripper * Homo_target2cam[1] << endl;
//标定板在相机中的位姿
cout << "3 : " << Homo_target2cam[1] << endl;
cout << "4 : " << Homo_cam2gripper.inv() * Homo_gripper2base[1].inv() * Homo_gripper2base[0] * Homo_cam2gripper * Homo_target2cam[0] << endl;
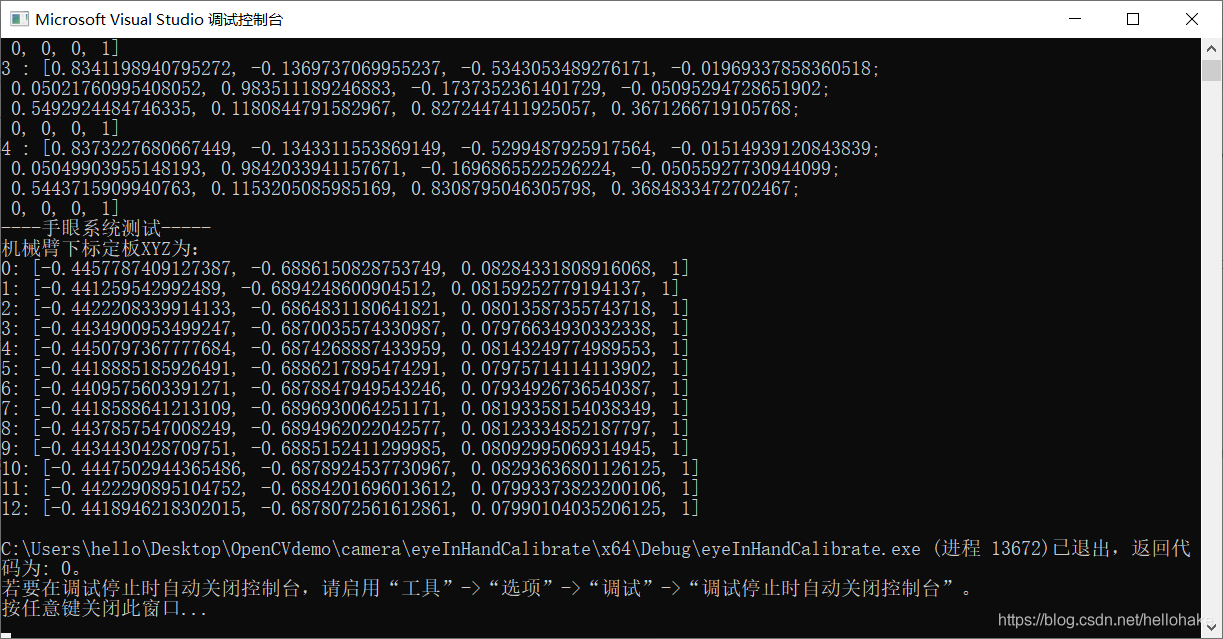
cout << "----手眼系统测试-----" << endl;
cout << "机械臂下标定板XYZ为:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < Homo_target2cam.size(); i++)
{
Mat chessPos{
0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0 }; //4*1矩阵,单独求机械臂坐标系下,标定板XYZ
Mat worldPos = Homo_gripper2base[i] * Homo_cam2gripper * Homo_target2cam[i] * chessPos;
cout << i << ": " << worldPos.t() << endl;
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
/************************************************** * @brief 将旋转矩阵与平移向量合成为齐次矩阵 * @note * @param Mat& R 3*3旋转矩阵 * @param Mat& T 3*1平移矩阵 * @return Mat 4*4齐次矩阵 **************************************************/
Mat R_T2HomogeneousMatrix(const Mat& R,const Mat& T)
{
Mat HomoMtr;
Mat_<double> R1 = (Mat_<double>(4, 3) <<
R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2),
R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2),
R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2),
0, 0, 0);
Mat_<double> T1 = (Mat_<double>(4, 1) <<
T.at<double>(0,0),
T.at<double>(1,0),
T.at<double>(2,0),
1);
cv::hconcat(R1, T1, HomoMtr); //矩阵拼接
return HomoMtr;
}
/************************************************** * @brief 齐次矩阵分解为旋转矩阵与平移矩阵 * @note * @param const Mat& HomoMtr 4*4齐次矩阵 * @param Mat& R 输出旋转矩阵 * @param Mat& T 输出平移矩阵 * @return **************************************************/
void HomogeneousMtr2RT(Mat& HomoMtr, Mat& R, Mat& T)
{
//Mat R_HomoMtr = HomoMtr(Rect(0, 0, 3, 3)); //注意Rect取值
//Mat T_HomoMtr = HomoMtr(Rect(3, 0, 1, 3));
//R_HomoMtr.copyTo(R);
//T_HomoMtr.copyTo(T);
/*HomoMtr(Rect(0, 0, 3, 3)).copyTo(R); HomoMtr(Rect(3, 0, 1, 3)).copyTo(T);*/
Rect R_rect(0, 0, 3, 3);
Rect T_rect(3, 0, 1, 3);
R = HomoMtr(R_rect);
T = HomoMtr(T_rect);
}
/************************************************** * @brief 检查是否是旋转矩阵 * @note * @param * @param * @param * @return true : 是旋转矩阵, false : 不是旋转矩阵 **************************************************/
bool isRotatedMatrix(Mat& R) //旋转矩阵的转置矩阵是它的逆矩阵,逆矩阵 * 矩阵 = 单位矩阵
{
Mat temp33 = R({
0,0,3,3 }); //无论输入是几阶矩阵,均提取它的三阶矩阵
Mat Rt;
transpose(temp33, Rt); //转置矩阵
Mat shouldBeIdentity = Rt * temp33;//是旋转矩阵则乘积为单位矩阵
Mat I = Mat::eye(3, 3, shouldBeIdentity.type());
return cv::norm(I, shouldBeIdentity) < 1e-6;
}
/************************************************** * @brief 欧拉角转换为旋转矩阵 * @note * @param const std::string& seq 指定欧拉角的排列顺序;(机械臂的位姿类型有xyz,zyx,zyz几种,需要区分) * @param const Mat& eulerAngle 欧拉角(1*3矩阵), 角度值 * @param * @return 返回3*3旋转矩阵 **************************************************/
Mat eulerAngleToRotateMatrix(const Mat& eulerAngle, const std::string& seq)
{
CV_Assert(eulerAngle.rows == 1 && eulerAngle.cols == 3);//检查参数是否正确
eulerAngle /= (180 / CV_PI); //度转弧度
Matx13d m(eulerAngle); //<double, 1, 3>
auto rx = m(0, 0), ry = m(0, 1), rz = m(0, 2);
auto rxs = sin(rx), rxc = cos(rx);
auto rys = sin(ry), ryc = cos(ry);
auto rzs = sin(rz), rzc = cos(rz);
//XYZ方向的旋转矩阵
Mat RotX = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1, 0, 0,
0, rxc, -rxs,
0, rxs, rxc);
Mat RotY = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << ryc, 0, rys,
0, 1, 0,
-rys, 0, ryc);
Mat RotZ = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << rzc, -rzs, 0,
rzs, rzc, 0,
0, 0, 1);
//按顺序合成后的旋转矩阵
cv::Mat rotMat;
if (seq == "zyx") rotMat = RotX * RotY * RotZ;
else if (seq == "yzx") rotMat = RotX * RotZ * RotY;
else if (seq == "zxy") rotMat = RotY * RotX * RotZ;
else if (seq == "yxz") rotMat = RotZ * RotX * RotY;
else if (seq == "xyz") rotMat = RotZ * RotY * RotX;
else if (seq == "xzy") rotMat = RotY * RotZ * RotX;
else
{
cout << "Euler Angle Sequence string is wrong...";
}
if (!isRotatedMatrix(rotMat)) //欧拉角特殊情况下会出现死锁
{
cout << "Euler Angle convert to RotatedMatrix failed..." << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return rotMat;
}
/************************************************** * @brief 将四元数转换为旋转矩阵 * @note * @param const Vec4d& q 归一化的四元数: q = q0 + q1 * i + q2 * j + q3 * k; * @return 返回3*3旋转矩阵R **************************************************/
Mat quaternionToRotatedMatrix(const Vec4d& q)
{
double q0 = q[0], q1 = q[1], q2 = q[2], q3 = q[3];
double q0q0 = q0 * q0 , q1q1 = q1 * q1 , q2q2 = q2 * q2, q3q3 = q3 * q3;
double q0q1 = q0 * q1 , q0q2 = q0 * q2 , q0q3 = q0 * q3;
double q1q2 = q1 * q2, q1q3 = q1 * q3;
double q2q3 = q2 * q3;
//根据公式得来
Mat RotMtr = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << (q0q0 + q1q1 - q2q2 - q3q3), 2 * (q1q2 + q0q3), 2 * (q1q3 - q0q2),
2 * (q1q2 - q0q3), (q0q0 - q1q1 + q2q2 - q3q3), 2 * (q2q3 + q0q1),
2 * (q1q3 + q0q2), 2 * (q2q3 - q0q1), (q0q0 - q1q1 - q2q2 + q3q3));
//这种形式等价
/*Mat RotMtr = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << (1 - 2 * (q2q2 + q3q3)), 2 * (q1q2 - q0q3), 2 * (q1q3 + q0q2), 2 * (q1q2 + q0q3), 1 - 2 * (q1q1 + q3q3), 2 * (q2q3 - q0q1), 2 * (q1q3 - q0q2), 2 * (q2q3 + q0q1), (1 - 2 * (q1q1 + q2q2)));*/
return RotMtr;
}
/************************************************** * @brief 将采集的原始数据转换为齐次矩阵(从机器人控制器中获得的) * @note * @param Mat& m 1*6//1*10矩阵 , 元素为: x,y,z,rx,ry,rz or x,y,z, q0,q1,q2,q3,rx,ry,rz * @param bool useQuaternion 原始数据是否使用四元数表示 * @param string& seq 原始数据使用欧拉角表示时,坐标系的旋转顺序 * @return 返回转换完的齐次矩阵 **************************************************/
Mat attitudeVectorToMatrix(const Mat& m, bool useQuaternion, const string& seq)
{
CV_Assert(m.total() == 6 || m.total() == 10);
//if (m.cols == 1) //转置矩阵为行矩阵
// m = m.t();
Mat temp = Mat::eye(4, 4, CV_64FC1);
if (useQuaternion)
{
Vec4d quaternionVec = m({
3,0,4,1 }); //读取存储的四元数
quaternionToRotatedMatrix(quaternionVec).copyTo(temp({
0,0,3,3}));
}
else
{
Mat rotVec;
if (m.total() == 6)
{
rotVec = m({
3,0,3,1 }); //读取存储的欧拉角
}
if (m.total() == 10)
{
rotVec = m({
7,0,3,1 });
}
//如果seq为空,表示传入的是3*1旋转向量,否则,传入的是欧拉角
if (0 == seq.compare(""))
{
Rodrigues(rotVec, temp({
0,0,3,3 })); //罗德利斯转换
}
else
{
eulerAngleToRotateMatrix(rotVec, seq).copyTo(temp({
0,0,3,3 }));
}
}
//存入平移矩阵
temp({
3,0,1,3 }) = m({
0,0,3,1 }).t();
return temp; //返回转换结束的齐次矩阵
}
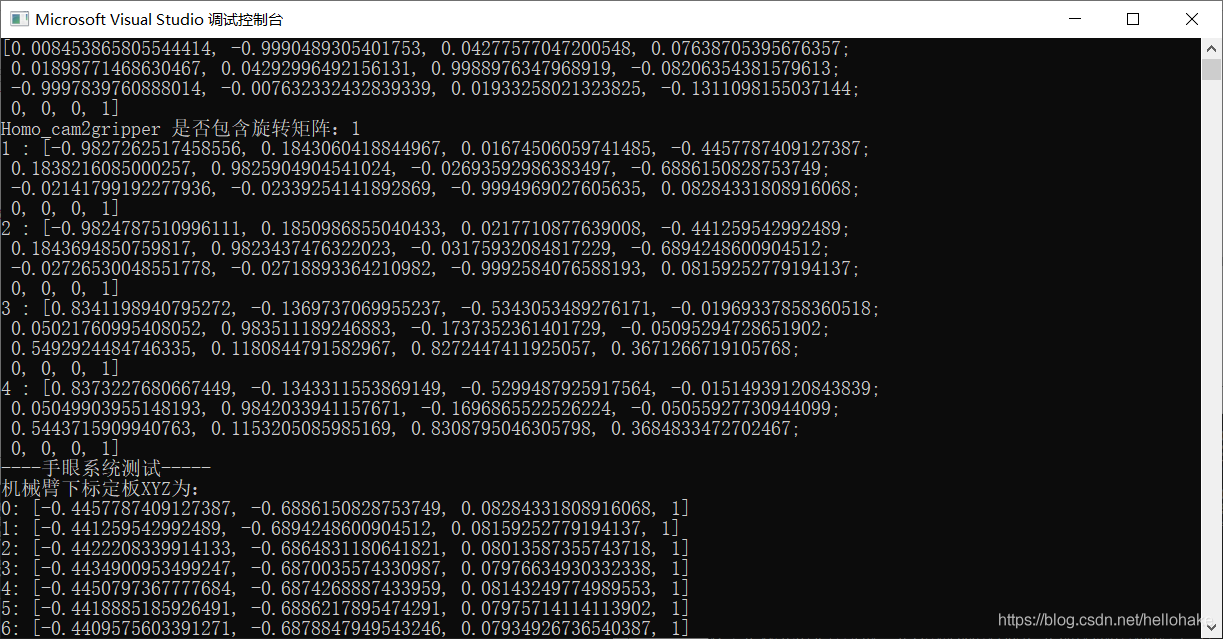
实验效果
参考博客
1、https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42203839/article/details/103882739
2、https://blog.csdn.net/wanggao_1990/article/details/81435660