文章目录
openmmlab教程3-MMSeg 使用
3. MMSeg 使用
需要基础,首先得跑过一个完整的语义分割的网络模型,这样子学起来比较轻松
- 准备数据集 dataset
- 数据增强
- 准备网络模型model
- 准备训练train
- 设置优化器sgd,adawm
- 设置学习策略poly,step,cosine
- 设置损失函数CrossEntropy
- 设置评价指标miou
3.1 运行demo
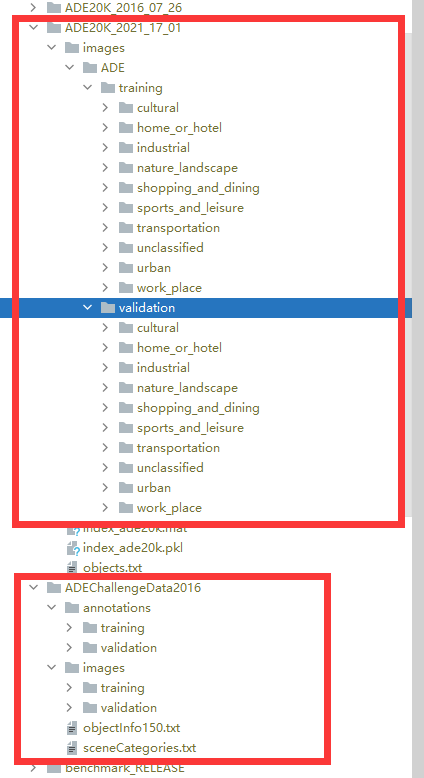
1) 准备数据集
首先下载ade20k。emmm,mmseg的ade20k和我平常用的数据长的不一样
2) 配置文件
就准备使用mmseg内置的deeplabv3plus模型来进行。
修改数据集路径
# 设置数据集的格式
# dataset的类的名称
dataset_type = 'ADE20KDataset'
# 数据集的地址
data_root = r'E:\note\cv\data\ADEChallengeData2016'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
# 裁剪大小
crop_size = (512, 512)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', reduce_zero_label=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(2048, 512), ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)),
dict(type='RandomCrop', crop_size=crop_size, cat_max_ratio=0.75),
dict(type='RandomFlip', prob=0.5),
dict(type='PhotoMetricDistortion'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size=crop_size, pad_val=0, seg_pad_val=255),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_semantic_seg']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(2048, 512),
# img_ratios=[0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75],
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
samples_per_gpu=2,
workers_per_gpu=2,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='images/training',
ann_dir='annotations/training',
pipeline=train_pipeline),
val=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='images/validation',
ann_dir='annotations/validation',
pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='images/validation',
ann_dir='annotations/validation',
pipeline=test_pipeline))
# 准备模型
# norm_cfg = dict(type='SyncBN', requires_grad=True)
# SyncBN 是多卡同步的BN,因为我是单卡,所以改成BN。
norm_cfg = dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
# 模型是预训练 好的
model = dict(
type='EncoderDecoder',
pretrained='open-mmlab://resnet50_v1c',
backbone=dict(
type='ResNetV1c',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
dilations=(1, 1, 2, 4),
strides=(1, 2, 1, 1),
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
norm_eval=False,
style='pytorch',
contract_dilation=True),
decode_head=dict(
type='ASPPHead',
in_channels=2048,
in_index=3,
channels=512,
dilations=(1, 12, 24, 36),
dropout_ratio=0.1,
num_classes=150,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
auxiliary_head=dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=1024,
in_index=2,
channels=256,
num_convs=1,
concat_input=False,
dropout_ratio=0.1,
num_classes=150,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=0.4)),
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg=dict(),
test_cfg=dict(mode='whole'))
# 准备训练各种参数
# yapf:disable
# 准备日志
log_config = dict(
interval=50,
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook', by_epoch=False),
# dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')
# dict(type='PaviLoggerHook') # for internal services
])
# yapf:enable
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
load_from = None
resume_from = None
workflow = [('train', 1)]
cudnn_benchmark = True
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0005)
optimizer_config = dict()
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(policy='poly', power=0.9, min_lr=1e-4, by_epoch=False)
# runtime settings
runner = dict(type='IterBasedRunner', max_iters=20000)
checkpoint_config = dict(by_epoch=False, interval=2000)
# 每2000次item迭代一次
evaluation = dict(interval=2000, metric='mIoU', pre_eval=True)
3) 训练
train.py。来自官方的tools/train.py
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
import argparse
import copy
import os
import os.path as osp
import time
import warnings
import mmcv
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
from mmcv.cnn.utils import revert_sync_batchnorm
from mmcv.runner import get_dist_info, init_dist
from mmcv.utils import Config, DictAction, get_git_hash
from mmseg import __version__
from mmseg.apis import init_random_seed, set_random_seed, train_segmentor
from mmseg.datasets import build_dataset
from mmseg.models import build_segmentor
from mmseg.utils import (collect_env, get_device, get_root_logger,
setup_multi_processes)
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Train a segmentor')
parser.add_argument('config', help='train config file path')
parser.add_argument('--work-dir', help='the dir to save logs and models')
parser.add_argument(
'--load-from', help='the checkpoint file to load weights from')
parser.add_argument(
'--resume-from', help='the checkpoint file to resume from')
parser.add_argument(
'--no-validate',
action='store_true',
help='whether not to evaluate the checkpoint during training')
group_gpus = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group()
group_gpus.add_argument(
'--gpus',
type=int,
help='(Deprecated, please use --gpu-id) number of gpus to use '
'(only applicable to non-distributed training)')
group_gpus.add_argument(
'--gpu-ids',
type=int,
nargs='+',
help='(Deprecated, please use --gpu-id) ids of gpus to use '
'(only applicable to non-distributed training)')
group_gpus.add_argument(
'--gpu-id',
type=int,
default=0,
help='id of gpu to use '
'(only applicable to non-distributed training)')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=None, help='random seed')
parser.add_argument(
'--diff_seed',
action='store_true',
help='Whether or not set different seeds for different ranks')
parser.add_argument(
'--deterministic',
action='store_true',
help='whether to set deterministic options for CUDNN backend.')
parser.add_argument(
'--options',
nargs='+',
action=DictAction,
help="--options is deprecated in favor of --cfg_options' and it will "
'not be supported in version v0.22.0. Override some settings in the '
'used config, the key-value pair in xxx=yyy format will be merged '
'into config file. If the value to be overwritten is a list, it '
'should be like key="[a,b]" or key=a,b It also allows nested '
'list/tuple values, e.g. key="[(a,b),(c,d)]" Note that the quotation '
'marks are necessary and that no white space is allowed.')
parser.add_argument(
'--cfg-options',
nargs='+',
action=DictAction,
help='override some settings in the used config, the key-value pair '
'in xxx=yyy format will be merged into config file. If the value to '
'be overwritten is a list, it should be like key="[a,b]" or key=a,b '
'It also allows nested list/tuple values, e.g. key="[(a,b),(c,d)]" '
'Note that the quotation marks are necessary and that no white space '
'is allowed.')
parser.add_argument(
'--launcher',
choices=['none', 'pytorch', 'slurm', 'mpi'],
default='none',
help='job launcher')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=0)
parser.add_argument(
'--auto-resume',
action='store_true',
help='resume from the latest checkpoint automatically.')
args = parser.parse_args()
if 'LOCAL_RANK' not in os.environ:
os.environ['LOCAL_RANK'] = str(args.local_rank)
if args.options and args.cfg_options:
raise ValueError(
'--options and --cfg-options cannot be both '
'specified, --options is deprecated in favor of --cfg-options. '
'--options will not be supported in version v0.22.0.')
if args.options:
warnings.warn('--options is deprecated in favor of --cfg-options. '
'--options will not be supported in version v0.22.0.')
args.cfg_options = args.options
return args
def main():
args = parse_args()
cfg = Config.fromfile(args.config)
if args.cfg_options is not None:
cfg.merge_from_dict(args.cfg_options)
# set cudnn_benchmark
if cfg.get('cudnn_benchmark', False):
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
# work_dir is determined in this priority: CLI > segment in file > filename
if args.work_dir is not None:
# update configs according to CLI args if args.work_dir is not None
cfg.work_dir = args.work_dir
elif cfg.get('work_dir', None) is None:
# use config filename as default work_dir if cfg.work_dir is None
cfg.work_dir = osp.join('./work_dirs',
osp.splitext(osp.basename(args.config))[0])
if args.load_from is not None:
cfg.load_from = args.load_from
if args.resume_from is not None:
cfg.resume_from = args.resume_from
if args.gpus is not None:
cfg.gpu_ids = range(1)
warnings.warn('`--gpus` is deprecated because we only support '
'single GPU mode in non-distributed training. '
'Use `gpus=1` now.')
if args.gpu_ids is not None:
cfg.gpu_ids = args.gpu_ids[0:1]
warnings.warn('`--gpu-ids` is deprecated, please use `--gpu-id`. '
'Because we only support single GPU mode in '
'non-distributed training. Use the first GPU '
'in `gpu_ids` now.')
if args.gpus is None and args.gpu_ids is None:
cfg.gpu_ids = [args.gpu_id]
cfg.auto_resume = args.auto_resume
# init distributed env first, since logger depends on the dist info.
if args.launcher == 'none':
distributed = False
else:
distributed = True
init_dist(args.launcher, **cfg.dist_params)
# gpu_ids is used to calculate iter when resuming checkpoint
_, world_size = get_dist_info()
cfg.gpu_ids = range(world_size)
# 创建日志文件夹
mmcv.mkdir_or_exist(osp.abspath(cfg.work_dir))
# dump config
cfg.dump(osp.join(cfg.work_dir, osp.basename(args.config)))
# 获取时间
timestamp = time.strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S', time.localtime())
log_file = osp.join(cfg.work_dir, f'{
timestamp}.log')
logger = get_root_logger(log_file=log_file, log_level=cfg.log_level)
# set multi-process settings
setup_multi_processes(cfg)
# init the meta dict to record some important information such as
# environment info and seed, which will be logged
meta = dict()
# log env info
env_info_dict = collect_env()
env_info = '\n'.join([f'{
k}: {
v}' for k, v in env_info_dict.items()])
dash_line = '-' * 60 + '\n'
logger.info('Environment info:\n' + dash_line + env_info + '\n' +
dash_line)
meta['env_info'] = env_info
# log some basic info
logger.info(f'Distributed training: {
distributed}')
logger.info(f'Config:\n{
cfg.pretty_text}')
# 设置随机种子
cfg.device = get_device()
seed = init_random_seed(args.seed, device=cfg.device)
seed = seed + dist.get_rank() if args.diff_seed else seed
logger.info(f'Set random seed to {
seed}, '
f'deterministic: {
args.deterministic}')
set_random_seed(seed, deterministic=args.deterministic)
cfg.seed = seed
meta['seed'] = seed
meta['exp_name'] = osp.basename(args.config)
# 创建 模型
model = build_segmentor(
cfg.model,
train_cfg=cfg.get('train_cfg'),
test_cfg=cfg.get('test_cfg'))
model.init_weights()
# SyncBN is not support for DP
if not distributed:
warnings.warn(
'SyncBN is only supported with DDP. To be compatible with DP, '
'we convert SyncBN to BN. Please use dist_train.sh which can '
'avoid this error.')
model = revert_sync_batchnorm(model)
logger.info(model)
# 构建数据集
datasets = [build_dataset(cfg.data.train)]
if len(cfg.workflow) == 2:
val_dataset = copy.deepcopy(cfg.data.val)
val_dataset.pipeline = cfg.data.train.pipeline
datasets.append(build_dataset(val_dataset))
if cfg.checkpoint_config is not None:
# save mmseg version, config file content and class names in
# checkpoints as meta data
cfg.checkpoint_config.meta = dict(
mmseg_version=f'{
__version__}+{
get_git_hash()[:7]}',
config=cfg.pretty_text,
CLASSES=datasets[0].CLASSES,
PALETTE=datasets[0].PALETTE)
# add an attribute for visualization convenience
# 模型的分类树
model.CLASSES = datasets[0].CLASSES
# passing checkpoint meta for saving best checkpoint
meta.update(cfg.checkpoint_config.meta)
train_segmentor(
model,
datasets,
cfg,
distributed=distributed,
validate=(not args.no_validate),
timestamp=timestamp,
meta=meta)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
开始训练
python .\train.py .\config.py --work-dir E:\note\openmmlab\log --seed 0
尴尬,说我 out memory,电脑配置不够
autodl上训练。使用autodl-tmp/autodl/openmmlab/
python /root/autodl-tmp/autodl/openmmlab/train.py /root/autodl-tmp/autodl/openmmlab/config.py --work-dir /root/autodl-tmp/autodl/openmmlab/log --seed 0
4) 测试
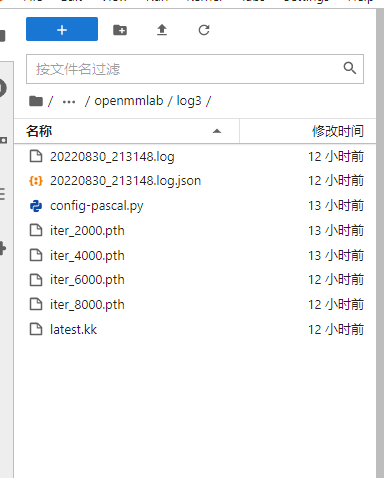
训练结束后,日志目录会出现,这么多的文件。加载你想训练的模型
然后cd到对应的目录 test.py是从tools/test.py复制粘贴过来的
python test.py config-pascal.py log3/iter_6000.pth --show-dir test_image
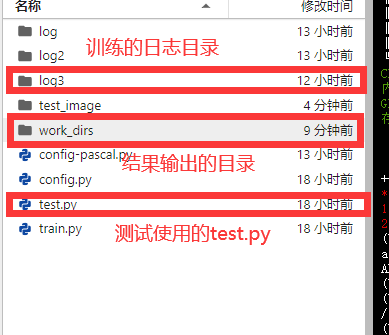
随便截取一张图片,效果还可以
终端结果显示

3.2 使用自己的网络 训练 公开数据集
1) 定义自己的网络 mysegformer
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from mmseg.models.builder import BACKBONES
from mmcv.runner import BaseModule
import torch
from torch import nn, Tensor
from typing import Tuple
from torch.nn import functional as F
import warnings
import math
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
Copied from timm
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
def __init__(self, p: float = None):
super().__init__()
self.p = p
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
if self.p == 0. or not self.training:
return x
kp = 1 - self.p
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = kp + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
return x.div(kp) * random_tensor
def _no_grad_trunc_normal_(tensor, mean, std, a, b):
# Cut & paste from PyTorch official master until it's in a few official releases - RW
# Method based on https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/presentations/truncated_normal.pdf
def norm_cdf(x):
# Computes standard normal cumulative distribution function
return (1. + math.erf(x / math.sqrt(2.))) / 2.
if (mean < a - 2 * std) or (mean > b + 2 * std):
warnings.warn("mean is more than 2 std from [a, b] in nn.init.trunc_normal_. "
"The distribution of values may be incorrect.",
stacklevel=2)
with torch.no_grad():
# Values are generated by using a truncated uniform distribution and
# then using the inverse CDF for the normal distribution.
# Get upper and lower cdf values
l = norm_cdf((a - mean) / std)
u = norm_cdf((b - mean) / std)
# Uniformly fill tensor with values from [l, u], then translate to
# [2l-1, 2u-1].
tensor.uniform_(2 * l - 1, 2 * u - 1)
# Use inverse cdf transform for normal distribution to get truncated
# standard normal
tensor.erfinv_()
# Transform to proper mean, std
tensor.mul_(std * math.sqrt(2.))
tensor.add_(mean)
# Clamp to ensure it's in the proper range
tensor.clamp_(min=a, max=b)
return tensor
def trunc_normal_(tensor, mean=0., std=1., a=-2., b=2.):
# type: (Tensor, float, float, float, float) -> Tensor
r"""Fills the input Tensor with values drawn from a truncated
normal distribution. The values are effectively drawn from the
normal distribution :math:`\mathcal{N}(\text{mean}, \text{std}^2)`
with values outside :math:`[a, b]` redrawn until they are within
the bounds. The method used for generating the random values works
best when :math:`a \leq \text{mean} \leq b`.
Args:
tensor: an n-dimensional `torch.Tensor`
mean: the mean of the normal distribution
std: the standard deviation of the normal distribution
a: the minimum cutoff value
b: the maximum cutoff value
Examples:
>>> w = torch.empty(3, 5)
>>> nn.init.trunc_normal_(w)
"""
return _no_grad_trunc_normal_(tensor, mean, std, a, b)
############################################
# backbone 部分
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, head, sr_ratio):
"""
注意力头
:param dim: 输入维度
:param head: 注意力头数目
:param sr_ratio: 缩放倍数
"""
super().__init__()
self.head = head
self.sr_ratio = sr_ratio
self.scale = (dim // head) ** -0.5
self.q = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.kv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 2)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
if sr_ratio > 1:
self.sr = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, sr_ratio, sr_ratio)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, H, W) -> Tensor:
B, N, C = x.shape
q = self.q(x).reshape(B, N, self.head, C // self.head).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
if self.sr_ratio > 1:
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1).reshape(B, C, H, W)
x = self.sr(x).reshape(B, C, -1).permute(0, 2, 1)
x = self.norm(x)
k, v = self.kv(x).reshape(B, -1, 2, self.head, C // self.head).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
return x
class DWConv(nn.Module):
"""
深度可分离卷积。
"""
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.dwconv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1, groups=dim)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, H, W) -> Tensor:
B, _, C = x.shape
x = x.transpose(1, 2).view(B, C, H, W)
x = self.dwconv(x)
return x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(c1, c2)
self.dwconv = DWConv(c2)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(c2, c1)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, H, W) -> Tensor:
return self.fc2(F.gelu(self.dwconv(self.fc1(x), H, W)))
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1=3, c2=32, patch_size=7, stride=4):
"""
下采样模块
:param c1: 输入通道数
:param c2: 输出通道数
:param patch_size: patch 大小
:param stride: 下采样倍数
"""
super().__init__()
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, patch_size, stride, patch_size // 2) # padding=(ps[0]//2, ps[1]//2)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(c2)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.proj(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, H, W
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, head, sr_ratio=1, dpr=0.):
"""
这是一个标准的transformer block。
:param dim: 输入维度
:param head: 注意力头的维度
:param sr_ratio:
:param dpr:
"""
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim, head, sr_ratio)
self.drop_path = DropPath(dpr) if dpr > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.mlp = MLP(dim, int(dim * 4))
def forward(self, x: Tensor, H, W) -> Tensor:
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x), H, W))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x), H, W))
return x
mit_settings = {
'B0': [[32, 64, 160, 256], [2, 2, 2, 2]], # [embed_dims, depths]
'B1': [[64, 128, 320, 512], [2, 2, 2, 2]],
'B2': [[64, 128, 320, 512], [3, 4, 6, 3]],
'B3': [[64, 128, 320, 512], [3, 4, 18, 3]],
'B4': [[64, 128, 320, 512], [3, 8, 27, 3]],
'B5': [[64, 128, 320, 512], [3, 6, 40, 3]]
}
@BACKBONES.register_module()
class my_MiT(BaseModule):
def __init__(self, model_name: str = 'B0'):
super(my_MiT, self).__init__()
assert model_name in mit_settings.keys(), f"MiT model name should be in {
list(mit_settings.keys())}"
embed_dims, depths = mit_settings[model_name]
drop_path_rate = 0.1
self.embed_dims = embed_dims
# patch_embed
self.patch_embed1 = PatchEmbed(3, embed_dims[0], 7, 4)
self.patch_embed2 = PatchEmbed(embed_dims[0], embed_dims[1], 3, 2)
self.patch_embed3 = PatchEmbed(embed_dims[1], embed_dims[2], 3, 2)
self.patch_embed4 = PatchEmbed(embed_dims[2], embed_dims[3], 3, 2)
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
cur = 0
self.block1 = nn.ModuleList([Block(embed_dims[0], 1, 8, dpr[cur + i]) for i in range(depths[0])])
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dims[0])
cur += depths[0]
self.block2 = nn.ModuleList([Block(embed_dims[1], 2, 4, dpr[cur + i]) for i in range(depths[1])])
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dims[1])
cur += depths[1]
self.block3 = nn.ModuleList([Block(embed_dims[2], 5, 2, dpr[cur + i]) for i in range(depths[2])])
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dims[2])
cur += depths[2]
self.block4 = nn.ModuleList([Block(embed_dims[3], 8, 1, dpr[cur + i]) for i in range(depths[3])])
self.norm4 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dims[3])
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
B = x.shape[0]
# stage 1
x, H, W = self.patch_embed1(x)
# torch.Size([1, 3136, 64])
for blk in self.block1:
x = blk(x, H, W)
# x= torch.Size([1, 3136, 64])
x1 = self.norm1(x).reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)# ([1, 64, 56, 56])
# stage 2
x, H, W = self.patch_embed2(x1)
for blk in self.block2:
x = blk(x, H, W)
x2 = self.norm2(x).reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# stage 3
x, H, W = self.patch_embed3(x2)
for blk in self.block3:
x = blk(x, H, W)
x3 = self.norm3(x).reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# stage 4
x, H, W = self.patch_embed4(x3)
for blk in self.block4:
x = blk(x, H, W)
x4 = self.norm4(x).reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return [x1, x2, x3, x4]
if __name__ == '__main__':
x=torch.randn(1,3,224,224)
model=my_MiT("B0")
y=model(x)
for temp in y:
print(temp.shape)
# backbone部分返回4个参数值
# torch.Size([1, 32, 56, 56])
# torch.Size([1, 64, 28, 28])
# torch.Size([1, 160, 14, 14])
# torch.Size([1, 256, 7, 7])
2) 修改模型配置文件
import mysegformer 一定要加,不然加载不成功,除非你是源码安装
# model settings
import mysegformer
norm_cfg = dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
model = dict(
type='EncoderDecoder',
pretrained=None,
backbone=dict(
# 自定义backbone的需要输入的3个参数
type='my_MiT',
# backbone需要的参数
model_name="B0"
),
# 设置辅助头
decode_head=dict(
type='UPerHead',
# 这里需要改一下,因为自定义的backbone ,输出的4层数据为
# torch.Size([1, 32, 56, 56])
# torch.Size([1, 64, 28, 28])
# torch.Size([1, 160, 14, 14])
# torch.Size([1, 256, 7, 7])
in_channels=[32, 64, 160, 256],
in_index=[0, 1, 2, 3],
pool_scales=(1, 2, 3, 6),
channels=512,
dropout_ratio=0.1,
# 使用的是 pascal voc 数据集,分类数目为21
num_classes=21,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg=dict(),
test_cfg=dict(mode='whole'))
3) 总体配置文件
# 加载模型配置文件
_base_ =[
'./config_mysegformer.py'
]
dataset_type = 'PascalVOCDataset'
data_root = r'E:\note\cv\data\VOCdevkit\VOC2012'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
crop_size = (512, 512)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations'),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(2048, 512), ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)),
dict(type='RandomCrop', crop_size=crop_size, cat_max_ratio=0.75),
dict(type='RandomFlip', prob=0.5),
dict(type='PhotoMetricDistortion'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size=crop_size, pad_val=0, seg_pad_val=255),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_semantic_seg']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(2048, 512),
# img_ratios=[0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75],
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
samples_per_gpu=4,
workers_per_gpu=4,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='JPEGImages',
ann_dir='SegmentationClass',
split='ImageSets/Segmentation/train.txt',
pipeline=train_pipeline),
val=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='JPEGImages',
ann_dir='SegmentationClass',
split='ImageSets/Segmentation/val.txt',
pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='JPEGImages',
ann_dir='SegmentationClass',
split='ImageSets/Segmentation/val.txt',
pipeline=test_pipeline))
# 准备训练各种参数
# yapf:disable
# 准备日志
log_config = dict(
interval=50,
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook', by_epoch=False),
# dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')
# dict(type='PaviLoggerHook') # for internal services
])
# yapf:enable
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
load_from = None
resume_from = None
workflow = [('train', 1)]
cudnn_benchmark = True
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0005)
optimizer_config = dict()
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(policy='poly', power=0.9, min_lr=1e-4, by_epoch=False)
# runtime settings
runner = dict(type='IterBasedRunner', max_iters=20000)
checkpoint_config = dict(by_epoch=False, interval=2000)
# 每2000次item迭代一次
evaluation = dict(interval=2000, metric='mIoU', pre_eval=True)
4) 训练
python train.py config.py --work-dir /root/autodl-tmp/autodl/test1/log --seed 0
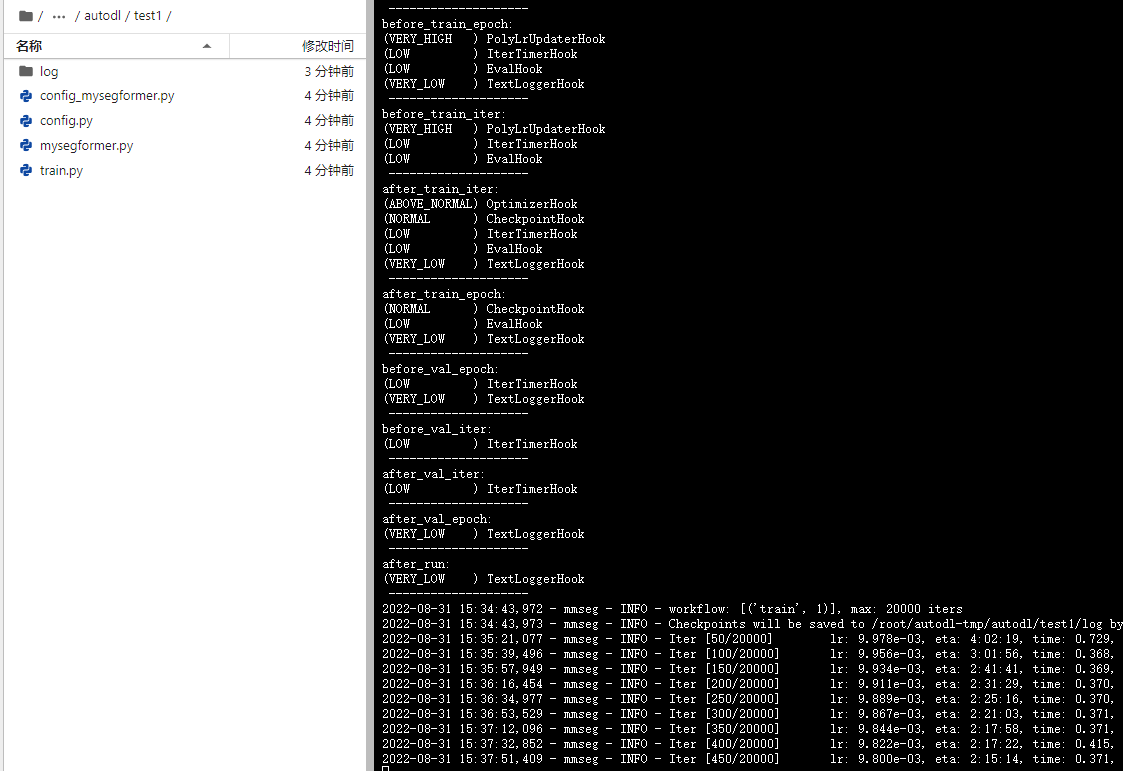
3.2 使用自己的网络 训练 自己的数据集CamVid
1) 准备自己的数据集
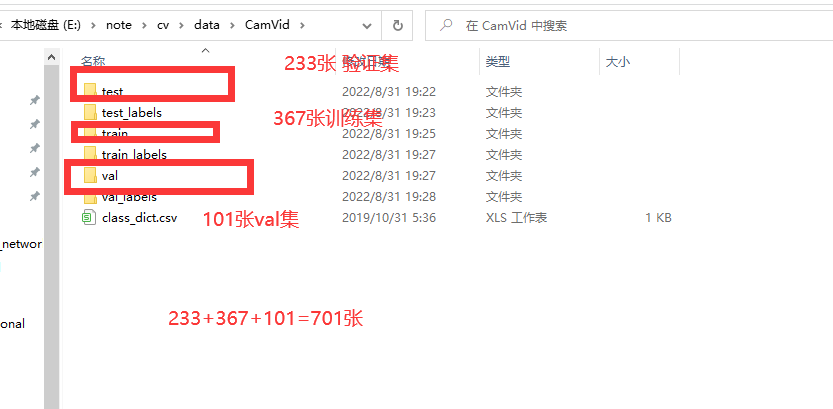
CamVid 数据集是由剑桥大学公开发布的城市道路场景的数据集。CamVid全称:The Cambridge-driving Labeled Video Database,它是第一个具有目标类别语义标签的视频集合。
数据集包 括 700 多张精准标注的图片用于强监督学习,可分为训练集、验证集、测试集。
同时, 在 CamVid 数据集中通常使用 11 种常用的类别来进行分割精度的评估,分别为:道路 (Road)、交通标志(Symbol)、汽车(Car)、天空(Sky)、行人道(Sidewalk)、电线杆 (Pole)、围墙(Fence)、行人(Pedestrian)、建筑物(Building)、自行车(Bicyclist)、 树木(Tree)。
图片呢,(3,720,960)大小,一共颜色有32种

| 名称 | 下载链接 |
|---|---|
| CamVid_32(原版) | |
| CamVid_12(处理后,8位图,才能符合MMSeg的格式) |
2) 准备自己数据集的配置文件
from mmseg.datasets.builder import DATASETS
from mmseg.datasets.custom import CustomDataset
@DATASETS.register_module()
class Camvid12(CustomDataset):
CLASSES =('Bicyclist','Building','Car','Column_Pole','Fence','Pedestrian','Road'
'Sidewalk','SignSymbol','Sky','Tree','backgroud')
PALETTE = [[0, 128, 192],[128, 0, 0],[64, 0, 128],[192, 192, 128],[64, 64, 128],[64, 64, 0],[128, 64, 128],
[0, 0, 192],[192, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128],[128, 128, 0],[0,0,0]]
# [[0, 128, 192], [128, 0, 0], [64, 0, 128], [192, 192, 128], [64, 64, 128], [64, 64, 0], [128, 64, 128],
# [0, 0, 192], [192, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128], [128, 128, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Camvid12, self).__init__(
img_suffix='.png',
seg_map_suffix='_L.png',
reduce_zero_label=True,
**kwargs)
CamVid32.py
from mmseg.datasets.builder import DATASETS
from mmseg.datasets.custom import CustomDataset
@DATASETS.register_module()
class Camvid32(CustomDataset):
CLASSES = (
'Animal', 'Archway', 'Bicyclist', 'Bridge', 'Building', 'Car', 'CartLuggagePram', 'Child', 'Column_Pole',
'Fence',
'LaneMkgsDriv', 'LaneMkgsNonDriv', 'Misc_Text', 'MotorcycleScooter', 'OtherMoving', 'ParkingBlock',
'Pedestrian',
'Road', 'RoadShoulder', 'Sidewalk', 'SignSymbol', 'Sky', 'SUVPickupTruck', 'TrafficCone', 'TrafficLight',
'Train',
'Tree', 'Truck_Bus', 'Tunnel', 'VegetationMisc', 'Void', 'Wall')
PALETTE = [[64, 128, 64], [192, 0, 128], [0, 128, 192], [0, 128, 64], [128, 0, 0], [64, 0, 128], [64, 0, 192],
[192, 128, 64],
[192, 192, 128], [64, 64, 128], [128, 0, 192], [192, 0, 64], [128, 128, 64], [192, 0, 192],
[128, 64, 64],
[64, 192, 128], [64, 64, 0], [128, 64, 128], [128, 128, 192], [0, 0, 192], [192, 128, 128],
[128, 128, 128],
[64, 128, 192], [0, 0, 64], [0, 64, 64], [192, 64, 128], [128, 128, 0], [192, 128, 192], [64, 0, 64],
[192, 192, 0], [0, 0, 0], [64, 192, 0]]
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Camvid32, self).__init__(
img_suffix='.png',
seg_map_suffix='.png',
reduce_zero_label=True,
**kwargs)
3) 配置文件
创建config_camvid.py
import camvid12
dataset_type = 'Camvid12'
# 数据集的地址
data_root = r'/root/autodl-tmp/camvid3/camvid3/CamVid_11'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
# 裁剪大小
crop_size = (512, 512)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', reduce_zero_label=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(720, 960), ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)),
dict(type='RandomCrop', crop_size=crop_size, cat_max_ratio=0.75),
dict(type='RandomFlip', prob=0.5),
dict(type='PhotoMetricDistortion'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size=crop_size, pad_val=0, seg_pad_val=255),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_semantic_seg']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(720, 960),
# img_ratios=[0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75],
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
samples_per_gpu=4,
workers_per_gpu=4,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir=['train'],
ann_dir=['train_labels'],
pipeline=train_pipeline),
# val=,
# 测试集
val=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='test',
ann_dir='test_labels',
pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
img_dir='test',
ann_dir='test_labels',
pipeline=test_pipeline))
4) 准备模型的配置文件 BiSeNetV2训练
_base_ = [
'./config_camvid.py',
]
# model settings
norm_cfg = dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
model = dict(
type='EncoderDecoder',
pretrained=None,
backbone=dict(
type='BiSeNetV2',
detail_channels=(64, 64, 128),
semantic_channels=(16, 32, 64, 128),
semantic_expansion_ratio=6,
bga_channels=128,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
init_cfg=None,
align_corners=False),
decode_head=dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=128,
in_index=0,
channels=1024,
num_convs=1,
concat_input=False,
dropout_ratio=0.1,
num_classes=12,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
auxiliary_head=[
dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=16,
channels=16,
num_convs=2,
num_classes=12,
in_index=1,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
concat_input=False,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=32,
channels=64,
num_convs=2,
num_classes=12,
in_index=2,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
concat_input=False,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=64,
channels=256,
num_convs=2,
num_classes=12,
in_index=3,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
concat_input=False,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='FCNHead',
in_channels=128,
channels=1024,
num_convs=2,
num_classes=19,
in_index=4,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
concat_input=False,
align_corners=False,
loss_decode=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0)),
],
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg=dict(),
test_cfg=dict(mode='whole'))
# yapf:disable
log_config = dict(
interval=50,
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook', by_epoch=False),
# dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')
# dict(type='PaviLoggerHook') # for internal services
])
# yapf:enable
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
load_from = None
resume_from = None
workflow = [('train', 1)]
cudnn_benchmark = True
# optimizer
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.05, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0005)
optimizer_config = dict()
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(policy='poly', power=0.9, min_lr=1e-4, by_epoch=False,warmup='linear', warmup_iters=1000)
# runtime settings
runner = dict(type='IterBasedRunner', max_iters=160000)
checkpoint_config = dict(by_epoch=False, interval=16000)
evaluation = dict(interval=16000, metric='mIoU', pre_eval=True)
5) 训练
python train.py config.py --work-dir /root/openmmlab/9-1log/ --seed 0
