目录
1.移除链表元素
题目要求

分析一下
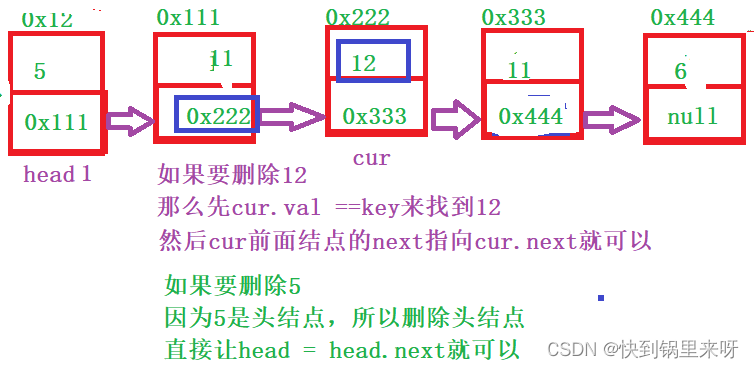
上代码
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == val) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (head.val == val) {
head= head.next;
}
return head;
}
}2.反转链表
题目要求
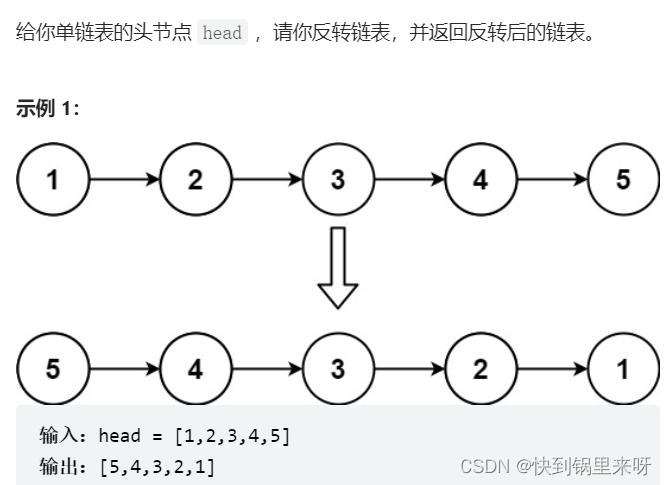
分析一下
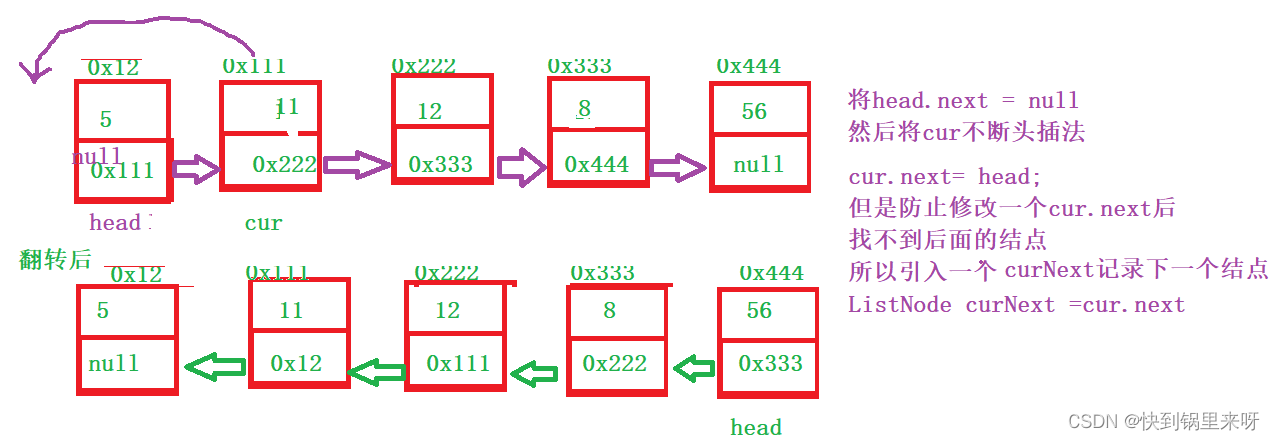
上代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;//说明链表为空
if(head.next == null) return head;//说明只有一个节点
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext= cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head =cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}
}3.链表的中间结点
链接 876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目要求

分析一下
上代码
4.链表中倒数第k个结点
链接 链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
题目要求

分析一下
上代码
5.合并两个有序链表
链接 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目要求
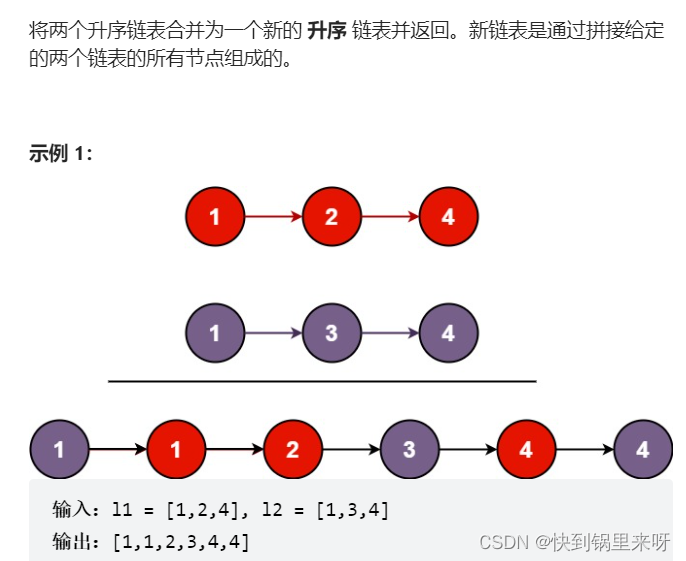
分析一下
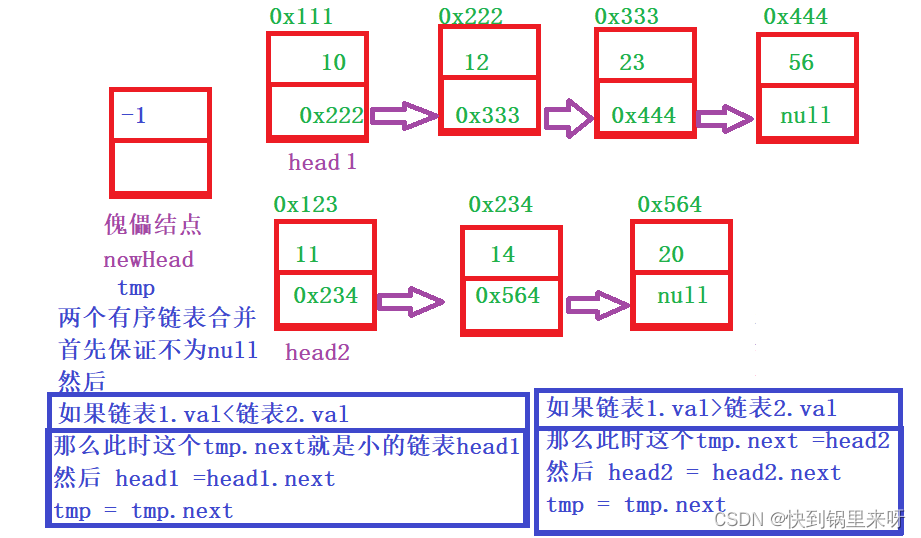

上代码
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);//傀儡节点 虚拟结点
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if(list1.val < list2.val) {
tmp.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
} else {
tmp.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if(list1 != null) {
tmp.next = list1;
}
if(list2 != null) {
tmp.next = list2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}6.链表分割
链接 链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
题目要求

分析一下
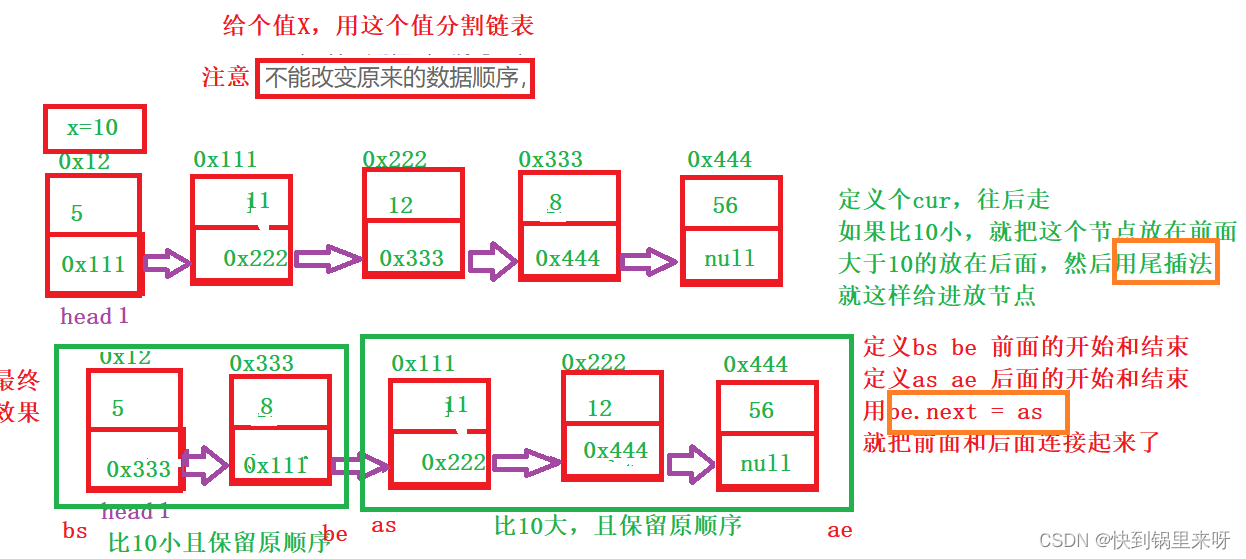
上代码
import java.util.*;
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
ListNode bs = null;
ListNode be = null;
ListNode as = null;
ListNode ae = null;
ListNode cur = pHead;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val < x) {
//插入到第一个段
if(bs == null) {
//这是第一次插入元素
bs = cur;
be = cur;
}else {
be.next =cur;
be = be.next;
}
} else {
//插入到第二个段
if(as == null) {
as =cur;
ae =cur;
}else {
ae.next =cur;
ae = ae.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(bs == null) {
return as;
}
be.next =as;
if(as != null) {
ae.next = null;
}
return bs;
}
}7.链表的回文结构
链接 链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
题目要求

分析一下

上代码
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
// write code here
if(A == null || A.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode fast = A;
ListNode slow = A;
//找中点
while(fast!= null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//翻转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//对比
while(A != slow) {
if(A.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
//偶数情况下
if(A.next != slow) {
return true;
}
A = A.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}8.相交链表
题目要求
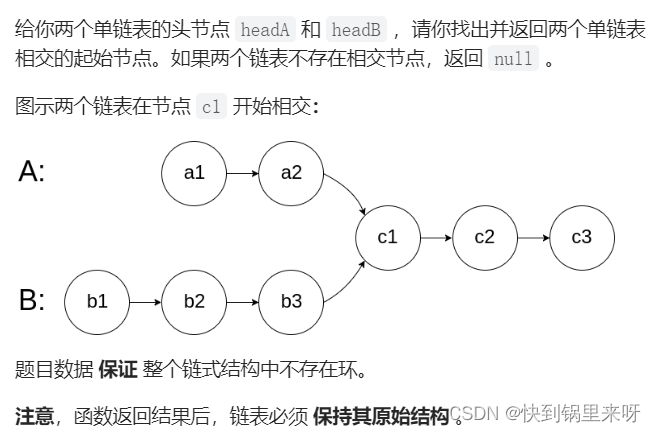
分析一下
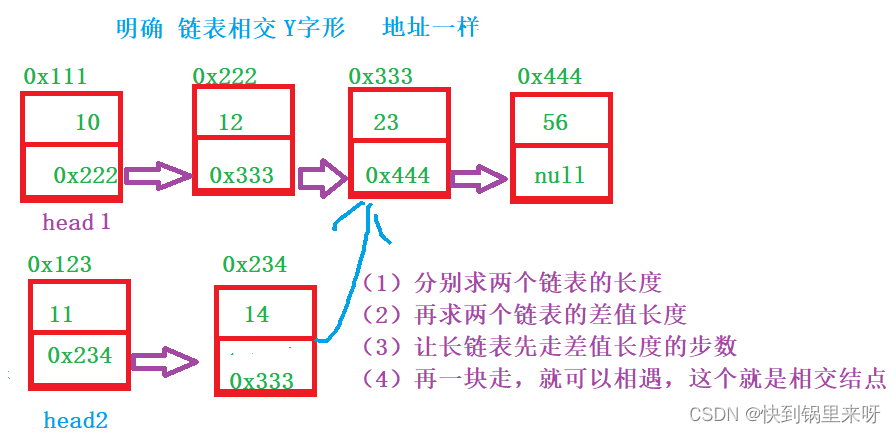
上代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//1.分别求两个链表的长度
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
ListNode pl = headA;//pl代表永远指向长的链表
ListNode ps = headB;//ps代表永远指向短的链表
while(pl != null) {
lenA++;
pl = pl.next;
}
while(ps != null) {
lenB++;
ps = ps.next;
}
pl = headA;
ps = headB;
//2,求两个链表的差值长度 len一定是一个正数
int len = lenA -lenB;
if(len < 0) {
pl = headB;
ps = headA;
len = lenB - lenA;
}
//3.让长链表先走差值长度
while(len != 0) {
pl = pl.next;
len--;
}
//4.再一块走,相遇
while(pl != ps && pl != null) {
pl = pl.next;
ps = ps.next;
}
if(pl == null) {
return null;
}
return pl;
}
}9.环形链表
题目要求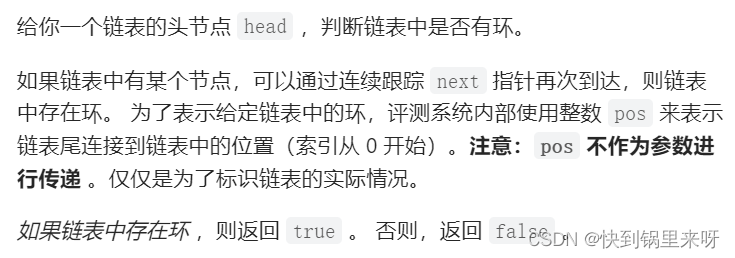
分析一下
首先,明白什么叫链表带环,
由链表中的某一个节点,一直找next指针,一定会再次到达这个节点,这样的链表就说是有环的,并且带环的链表每个节点的next 指针,都不为null。
其次,这道题如果继续考虑使用快慢指针来做,那么快指针fast每次走几步,
(1)如果快指针fast每次都两步,慢指针slow每次走一步,一定可以相遇
 (2)如果快指针fast每次都走3步,走4步...走n步,不一定可以相遇
(2)如果快指针fast每次都走3步,走4步...走n步,不一定可以相遇

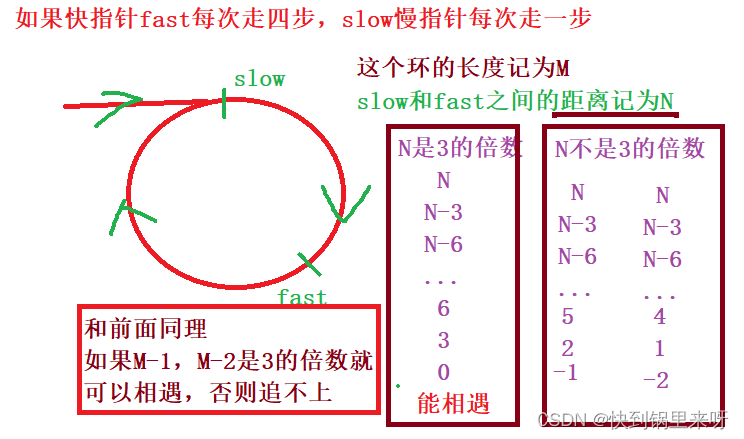 所以只要快指针fast每次走2步,慢指针每次走1步,就一定可以追上,这道题就按这个思路走
所以只要快指针fast每次走2步,慢指针每次走1步,就一定可以追上,这道题就按这个思路走
上代码
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}10.环形链表II
链接 142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目要求

分析一下
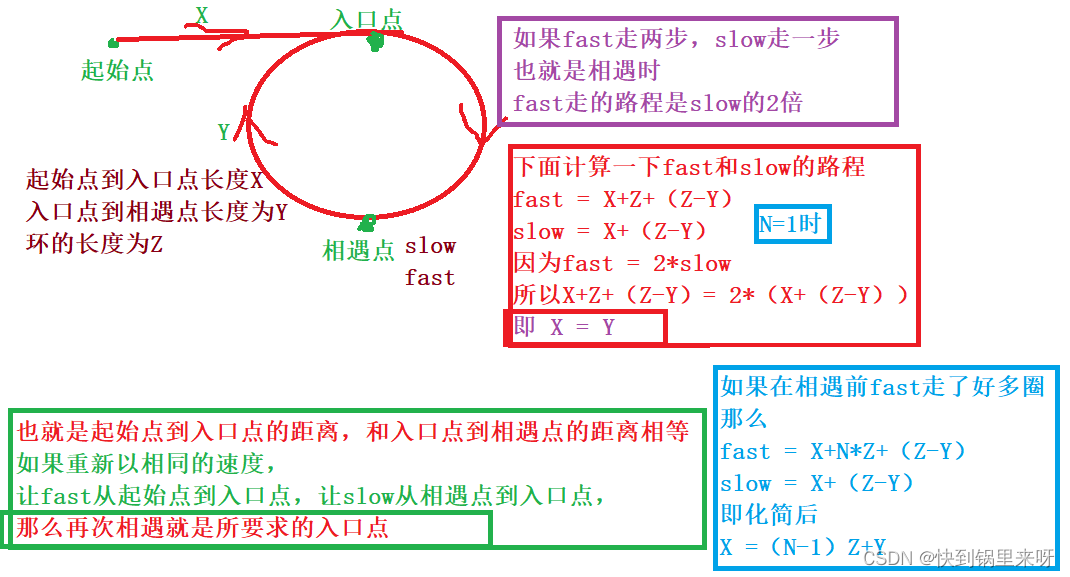 上代码
上代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
slow = head;
while(slow != fast) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}