RunLoop的定义
当有持续的异步任务需求时,我们会创建一个独立的生命周期可控的线程。RunLoop就是控制线程生命周期并接收事件进行处理的机制。
RunLoop是iOS事件响应与任务处理最核心的机制,它贯穿iOS整个系统。
Foundation: NSRunLoop
Core Foundation: CFRunLoop 核心部分,代码开源,C 语言编写,跨平台
RunLoop特性
- 主线程的RunLoop在应用启动的时候就会自动创建
- 其他线程则需要在该线程下自己启动
- 不能自己创建RunLoop
- RunLoop并不是线程安全的,所以需要避免在其他线程上调用当前线程的RunLoop
- RunLoop负责管理autorelease pools
- RunLoop负责处理消息事件,即输入源事件和计时器事件
RunLoop数据结构
runloop数据结构
//线程-》runloop-》内存 dict
//pthread getter runloop
//runloop:items->mode->run->thread
struct __CFRunLoop {
CFRuntimeBase _base;
pthread_mutex_t _lock; /* locked for accessing mode list */
__CFPort _wakeUpPort; // used for CFRunLoopWakeUp
Boolean _unused;
volatile _per_run_data *_perRunData; // reset for runs of the run loop
pthread_t _pthread;//对应线程
uint32_t _winthread;
CFMutableSetRef _commonModes;//模型集合
CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems;//任务
CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode;//当前mode,可以切换,timer UI
CFMutableSetRef _modes;//
struct _block_item *_blocks_head;
struct _block_item *_blocks_tail;
CFAbsoluteTime _runTime;
CFAbsoluteTime _sleepTime;
CFTypeRef _counterpart;
};Runloop与线程,Mode对应关系
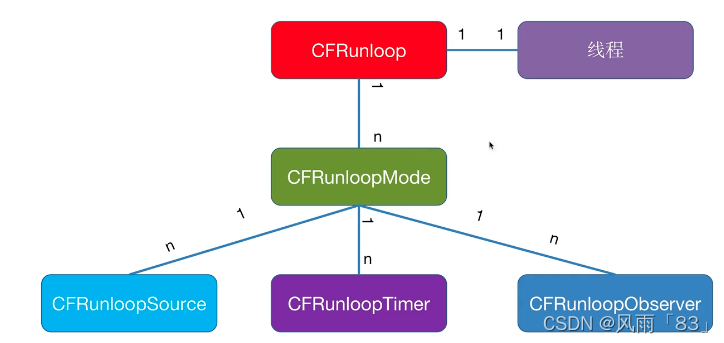
NSRunLoop(Foundation)是CFRunLoop(CoreFoundation)的封装,提供了面向对象的API
RunLoop 相关的主要涉及五个类:
- CFRunLoop:RunLoop对象
- CFRunLoopMode:运行模式
- CFRunLoopSource:输入源/事件源
- CFRunLoopTimer:定时源
- CFRunLoopObserver:观察者
1、CFRunLoop
由pthread(线程对象,说明RunLoop和线程是一一对应的)、currentMode(当前所处的运行模式)、modes(多个运行模式的集合)、commonModes(模式名称字符串集合)、commonModelItems(Observer,Timer,Source集合)构成
2、CFRunLoopMode
由name、source0、source1、observers、timers构成
3、分为source0和source1两种
-
source0:
即非基于port的,也就是用户触发的事件。需要手动唤醒线程,将当前线程从内核态切换到用户态 -
source1:
基于port的,包含一个 mach_port 和一个回调,可监听系统端口和通过内核和其他线程发送的消息,能主动唤醒RunLoop,接收分发系统事件,具备唤醒线程的能力。
4、CFRunLoopTimer
于时间的触发器,基本上说的就是NSTimer。在预设的时间点唤醒RunLoop执行回调。因为它是基于RunLoop的,因此它不是实时的(就是NSTimer 是不准确的。 因为RunLoop只负责分发源的消息。如果线程当前正在处理繁重的任务,就有可能导致Timer本次延时,或者少执行一次)
5、CFRunLoopObserver
监听以下时间点:CFRunLoopActivity
RunLoop机制
主线程 (有 RunLoop 的线程) 几乎所有函数都从以下六个之一的函数调起:
-
CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION
CFRunloop is calling out to an abserver callback function
用于向外部报告 RunLoop 当前状态的更改,框架中很多机制都由 RunLoopObserver 触发,如 CAAnimation -
CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK
CFRunloop is calling out to a block
消息通知、非延迟的perform、dispatch调用、block回调、KVO -
CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE
CFRunloop is servicing the main desipatch queue -
CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_TIMER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION
CFRunloop is calling out to a timer callback function
延迟的perform, 延迟dispatch调用 -
CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION
CFRunloop is calling out to a source 0 perform function
处理App内部事件、App自己负责管理(触发),如UIEvent、CFSocket。普通函数调用,系统调用 -
CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE1_PERFORM_FUNCTION
CFRunloop is calling out to a source 1 perform function
由RunLoop和内核管理,Mach port驱动,如CFMachPort、CFMessagePort

NSTimer,延迟的perform, 延迟dispatch调用
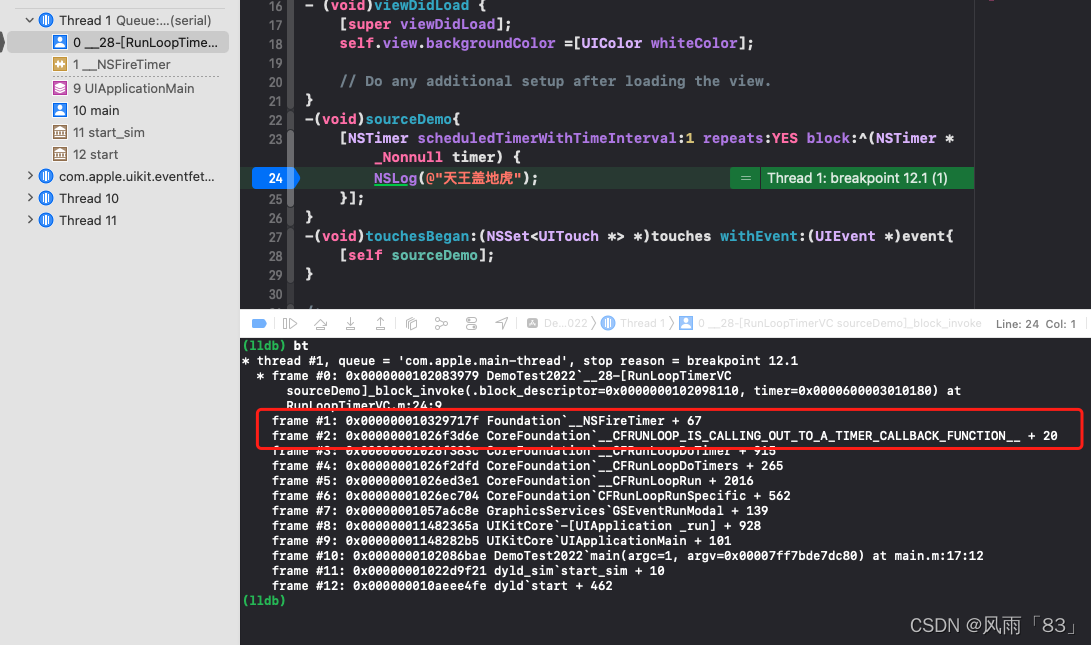
 处理App内部事件、App自己负责管理(触发),如UIEvent、CFSocket。普通函数调用,系统调用
处理App内部事件、App自己负责管理(触发),如UIEvent、CFSocket。普通函数调用,系统调用
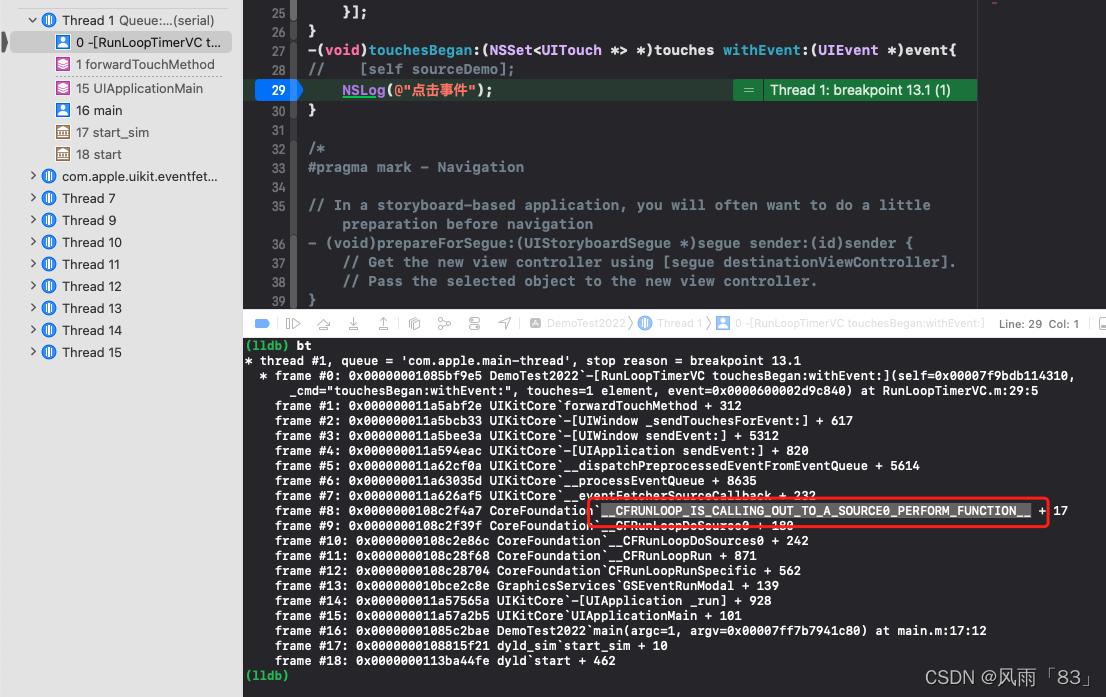
RunLoop 架构
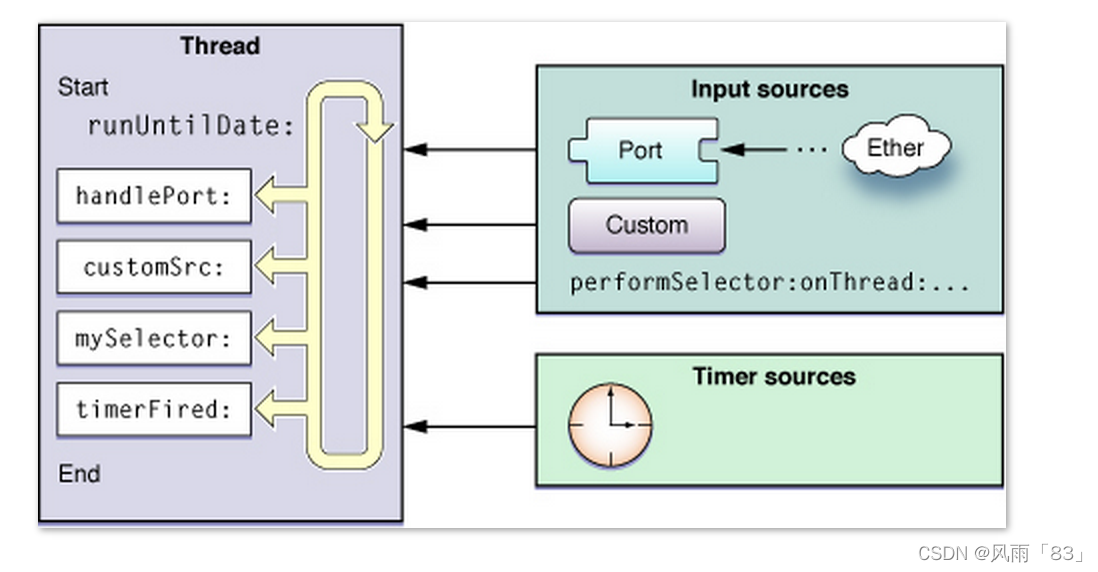
runloop运行时
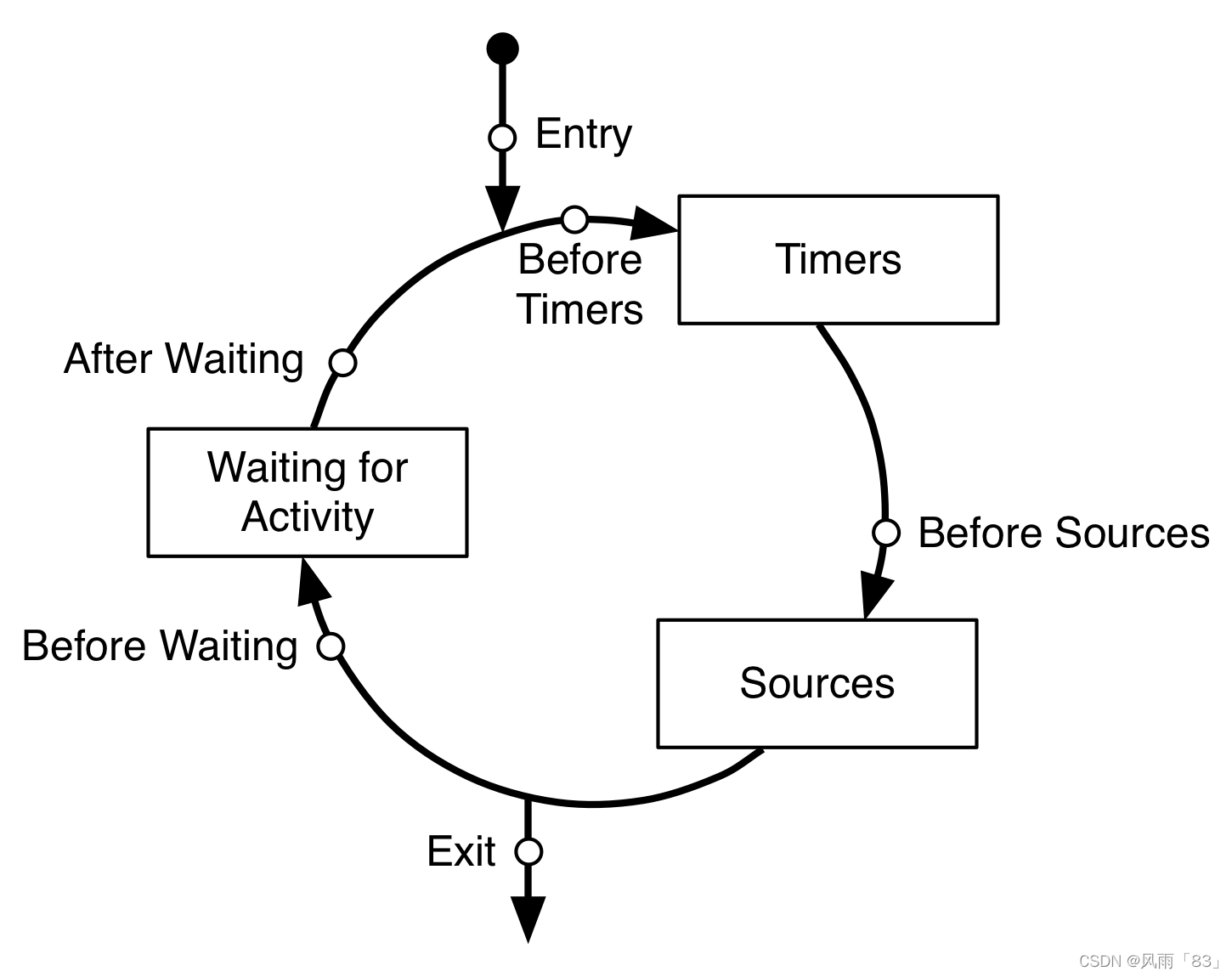
主要有以下六种状态:
- kCFRunLoopEntry -- 进入runloop循环
- kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers -- 处理定时调用前回调
- kCFRunLoopBeforeSources -- 处理input sources的事件
- kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting -- runloop睡眠前调用
- kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting -- runloop唤醒后调用
- kCFRunLoopExit -- 退出runloop
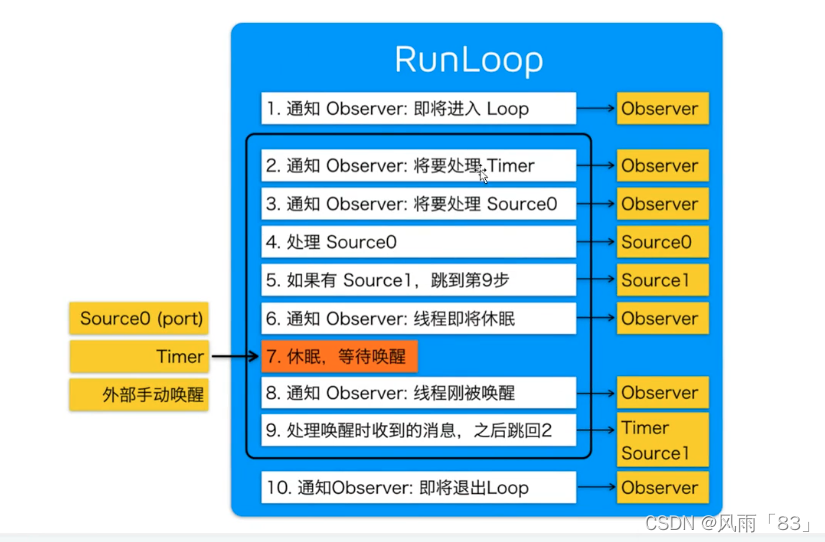
RunLoop的内部逻辑
//用DefaultMode启动
void CFRunLoopRun(void) {
CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
}
//用指定的Mode启动,允许设置RunLoop的超时时间
int CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle) {
return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);
}
//RunLoop的实现
int CFRunLoopRunSpecific(runloop, modeName, seconds, stopAfterHandle) {
//首先根据modeName找到对应的mode
CFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(runloop, modeName, false);
//如果mode中没有source/timer/observer,直接返回
if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(currentMode)) return;
//1.通知Observers:RunLoop即将进入loop
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);
//调用函数__CFRunLoopRun 进入loop
__CFRunLoopRun(runloop, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled) {
Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = NO;
int retVal = 0;
do {
//2.通知Observers:RunLoop即将触发Timer回调
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
//3.通知Observers:RunLoop即将触发Source0(非port)回调
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
///执行被加入的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
//4.RunLoop触发Source0(非port)回调
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(runloop, currentMode, stopAfterHandle);
//执行被加入的Block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
//5.如果有Source1(基于port)处于ready状态,直接处理这个Source1然后跳转去处理消息
if (__Source0DidDispatchPortLastTime) {
Boolean hasMsg = __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg)
if (hasMsg) goto handle_msg;
}
//6.通知Observers:RunLoop的线程即将进入休眠
if (!sourceHandledThisLoop) {
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
}
//7.调用mach_msg等待接收mach_port的消息。线程将进入休眠,直到被下面某个事件唤醒
// 一个基于port的Source的事件
//一个Timer时间到了
//RunLoop自身的超时时间到了
//被其他什么调用者手动唤醒
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort) {
mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG, port); // thread wait for receive msg
}
//8.通知Observers:RunLoop的线程刚刚被唤醒
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
//收到消息,处理消息
handle_msg:
//9.1 如果一个Timer时间到了,触发这个timer的回调
if (msg_is_timer) {
__CFRunLoopDoTimers(runloop, currentMode, mach_absolute_time())
}
//9.2 如果有dispatch到main_queue的block,执行block
else if (msg_is_dispatch) {
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);
}
//9.3 如果一个Source1(基于port)发出事件了,处理这个事件
else {
CFRunLoopSourceRef source1 = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(runloop, currentMode, livePort);
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(runloop, currentMode, source1, msg);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {
mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply);
}
}
//执行加入到loop的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {
/// 进入loop时参数说处理完事件就返回。
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;
} else if (timeout) {
/// 超出传入参数标记的超时时间了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;
} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(runloop)) {
/// 被外部调用者强制停止了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(runloop, currentMode)) {
/// source/timer/observer一个都没有了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
// 如果没超时,mode里没空,loop也没被停止,那继续loop。
} while (retVal == 0);
}
//10. 通知Observers:RunLoop即将退出
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);
}
RunLoop在实际开发中的应用
- 控制线程生命周期(线程保活)
- 解决NSTimer在滑动时停止工作的问题
- 监控应用卡顿
- 性能优化
1、线程保活
平时创建子线程时,线程上的任务执行完这个线程就会销毁掉。
有时我们会需要经常在一个子线程中执行任务,频繁的创建和销毁线程就会造成很多的开销,这时我们可以通过runloop来控制线程的生命周期
RunLoop启动方法
三种启动RunLoop的方法
- run,无条件
- runUntilDate, 设置时间限制
- runMode:before:Date:,在特定模式下
self.stopped = NO;
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
self.thread = [[MyThread alloc] initWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"新线程");
CFRunLoopObserverRef observer = CFRunLoopObserverCreateWithHandler(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), kCFRunLoopAllActivities, YES, 0, ^(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity) {
switch (activity) {
case kCFRunLoopEntry:
NSLog(@"即将进入RunLoop");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers:
NSLog(@"即将处理Timer");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeSources:
NSLog(@"即将处理Sources");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting:
NSLog(@"即将进入休眠");
break;
case kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting:
NSLog(@"从休眠中唤醒");
break;
case kCFRunLoopExit:
NSLog(@"即将退出RunLoop");
break;
default:
break;
}
});
// 监听RunLoop的状态变化
CFRunLoopAddObserver(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), observer, kCFRunLoopDefaultMode);
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addPort:[[NSPort alloc]init] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
while (!weakSelf.stopped) {
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]];
NSLog(@"-----------while---");
}
NSLog(@"end");
}];
self.thread.name=@"mytestthread";
[self.thread start];常驻线程停止的方式
- (void)pressStop {
//子线程中调用stop
if (_stopped == NO ) {
[self performSelector:@selector(stop) onThread:_thread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:YES];
}
}
//停止子线程的runloop
- (void)stop {
//设置标记yes
self.stopped = YES;
//停止runloop
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
NSLog(@"%s, %@", __func__, [NSThread currentThread]);
//解除引用, 停止runloop这个子线程就会dealloc
self.thread = nil;
}2、NSTimer相关问题
创建timer使用了带有scheduledTimer的方法,创建的timer是在runloop默认模式下,也就是NSDefaultRunLoopMode。
当拖动模拟机上的scrollView时,定时器就会失效,停止拖动,定时器恢复。说明定时器并不在UITrackingRunLoopMode模式(mode)下。只需要将这个timer也添加到UITrackingRunLoopMode模式下就可以正常工作
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
或者
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:UITrackingRunLoopMode];3、监控应用卡顿
iOS之卡顿检测_风雨「83」的博客-CSDN博客_ios 卡顿检测
//
// RunloopViewController.m
// DemoTest2022
//
// Created by wangyun on 2022/6/21.
//
#import "RunloopViewController.h"
#import "MyThread.h"
#import "TestObject.h"
@interface RunloopViewController ()
@property(nonatomic,strong) MyThread *thread;
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL stopped;
@end
@implementation RunloopViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
UIButton *button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
[self.view addSubview:button];
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(pressPrint) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[button setTitle:@"执行任务" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
button.frame = CGRectMake(100, 200, 100, 20);
UIButton *stopButton = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
[self.view addSubview:stopButton];
[stopButton addTarget:self action:@selector(pressStop) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[stopButton setTitle:@"停止RunLoop" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
stopButton.frame = CGRectMake(100, 400, 100, 20);
self.stopped = NO;
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
self.thread = [[MyThread alloc] initWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"新线程");
CFRunLoopObserverRef observer = CFRunLoopObserverCreateWithHandler(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), kCFRunLoopAllActivities, YES, 0, ^(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity) {
switch (activity) {
case kCFRunLoopEntry:
NSLog(@"即将进入RunLoop");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers:
NSLog(@"即将处理Timer");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeSources:
NSLog(@"即将处理Sources");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting:
NSLog(@"即将进入休眠");
break;
case kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting:
NSLog(@"从休眠中唤醒");
break;
case kCFRunLoopExit:
NSLog(@"即将退出RunLoop");
break;
default:
break;
}
});
// 监听RunLoop的状态变化
CFRunLoopAddObserver(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), observer, kCFRunLoopDefaultMode);
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addPort:[[NSPort alloc]init] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
while (!weakSelf.stopped) {
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]];
NSLog(@"-----------while---");
}
NSLog(@"end");
}];
self.thread.name=@"mytestthread";
[self.thread start];
}
- (void)pressPrint {
//子线程中调用print
[self performSelector:@selector(print) onThread:_thread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO];
}
//子线程需要执行的任务
- (void)print {
NSLog(@"%s, %@", __func__, [NSThread currentThread]);
__autoreleasing TestObject *model = [[TestObject alloc] init];
NSLog(@"%@",model);
}
- (void)pressStop {
//子线程中调用stop
if (_stopped == NO ) {
[self performSelector:@selector(stop) onThread:_thread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:YES];
}
}
//停止子线程的runloop
- (void)stop {
//设置标记yes
self.stopped = YES;
//停止runloop
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
NSLog(@"%s, %@", __func__, [NSThread currentThread]);
//解除引用, 停止runloop这个子线程就会dealloc
self.thread = nil;
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {
//退出当前页面
//保证这个vc销毁时,子线程也要销毁
[self pressStop];
[self.navigationController popViewControllerAnimated:YES];
}
- (void)dealloc {
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
/*
#pragma mark - Navigation
// In a storyboard-based application, you will often want to do a little preparation before navigation
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
// Get the new view controller using [segue destinationViewController].
// Pass the selected object to the new view controller.
}
*/
@end
进入vc log:
2022-07-17 11:37:43.352422+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 新线程
2022-07-17 11:37:43.352952+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将进入RunLoop
2022-07-17 11:37:43.353264+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Timer
2022-07-17 11:37:43.353542+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Sources
2022-07-17 11:37:43.353801+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将进入休眠
点击执行任务 log:
2022-07-17 11:38:42.157601+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 从休眠中唤醒
2022-07-17 11:38:42.157805+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Timer
2022-07-17 11:38:42.158081+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Sources
2022-07-17 11:38:42.158376+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -[RunloopViewController print], <MyThread: 0x600002832c00>{number = 8, name = mytestthread}
2022-07-17 11:38:42.158572+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] <TestObject: 0x600003f642a0>
2022-07-17 11:38:42.158790+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -[TestObject dealloc]
2022-07-17 11:38:42.159116+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将退出RunLoop
2022-07-17 11:38:42.159287+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -----------while---
2022-07-17 11:38:42.159494+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将进入RunLoop
2022-07-17 11:38:42.159817+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Timer
2022-07-17 11:38:42.160106+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Sources
2022-07-17 11:38:42.160390+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将进入休眠
点击屏幕log:
2022-07-17 11:39:53.883534+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 从休眠中唤醒
2022-07-17 11:39:53.883898+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Timer
2022-07-17 11:39:53.884167+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将处理Sources
2022-07-17 11:39:53.884552+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -[RunloopViewController stop], <MyThread: 0x600002832c00>{number = 8, name = mytestthread}
2022-07-17 11:39:53.884873+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] 即将退出RunLoop
2022-07-17 11:39:53.885192+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -----------while---
2022-07-17 11:39:53.885500+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] end
2022-07-17 11:39:53.886056+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753494] -[MyThread dealloc]
2022-07-17 11:39:54.399634+0800 DemoTest2022[49641:753178] -[RunloopViewController dealloc]
总结
RunLoop是维护其内部事件循环的一个对象,它在程序运行过程中重复的做着一些事情,例如接收消息、处理消息、休眠等等。
所谓的事件循环,就是对事件/消息进行管理,没有消息时,休眠线程以避免资源消耗,从用户态切换到内核态。
有事件/消息需要进行处理时,立即唤醒线程,回到用户态进行处理。