原题描述
废话不多说,这道题题目描述如下
/**
* Alipay.com Inc.
* Copyright (c) 2004-2021 All Rights Reserved.
*/
//对单链表表示的大数进行求和:1->2->3+4->5=1->6->8 (123+45=168)。
审题
这是我们这个系列第一篇文章,首先来分享一道阿里笔试题。阿里一般是面试官通过邮件发送过来,要求一个小时内完成。其实时间还是挺紧的,一般做题步骤是15-20分钟左右思考,然后30-40分钟编写代码。对于笔试经验少的童鞋,最好多拿几家笔试来练练手,否则容易一上来紧张后懵了。
为什么先选这道题来讲,目的就是给童鞋们敲一个警钟,很多童鞋一般喜欢买个刷题课程或者看别人文章,很多课程基本都是把一些代表性的LeetCode题目解法讲一遍。作为过来人可以很负责的告诉你。如果只靠这些就觉得自己已经掌握了LeetCode上的题目那就大错特错了。因为不经过平时自我严格的训练,很可能由于紧张现场翻车。
做题过程还原
刚拿到题目的时候千万不能慌,先多读读题。这道题的意思是两个非空单链表,并且每个节点只能存储一位数字。请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
思路
对于阿里好多笔试题并不是LeetCode原题,但是这个题其实和LeetCode的第2题两数相加非常像了。区别就是LeetCode的第2题中的题目已经把链表转置好了,结果不需要转置回去。
所以看到了吧,大家平时要刷题的话题目一定要首先自己做一做才能加深印象,笔试的时候才不会怕。这个题的思路如下
- 将两个链表进行转置;
- 创建新链表;
- 同时遍历两个链表,逐位计算它们的和,并与当前位置的进位值相加。假设当前两个链表处相应位置的数字为 n1,n2,假设进位值为 carry,则它们的和为 n1+n2+carry。每一位计算的同时需要考虑上一位的进位问题,而当前位计算结束后同样需要更新进位值
- 如果两个链表全部遍历完毕后,进位值为 1,则在新链表最前方添加节点 1。
- 对新链表进行转置
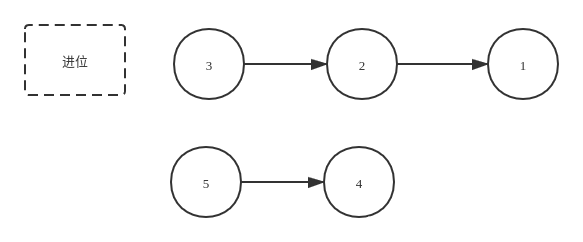
该题代码如下
public class BigSum {
static class ListNode {
private ListNode next;
private int value;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(ListNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static ListNode addTwoList(ListNode first, ListNode second) {
//必须合法
if (null == first || null == second) {
return null;
}
ListNode reverseFirst = reverseList(first);
ListNode reverseSend = reverseList(second);
ListNode temFirst = reverseFirst;
ListNode temSecond = reverseSend;
ListNode resultList = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = resultList;
int flag = 0;
while (temFirst != null || temSecond != null) {
int temp = flag;
if (temFirst != null) {
temp += temFirst.value;
temFirst = temFirst.next;
}
if (temSecond != null) {
temp += temSecond.value;
temSecond = temSecond.next;
}
if (temp > 9) {
temp -= 10;
flag = 1;
} else {
flag = 0;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(temp);
p.next = node;
p = p.next;
}
if (flag == 1) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(1);
p.next = node;
}
return reverseList(resultList.next);
}
//翻转链表
public static ListNode reverseList (ListNode targetList) {
ListNode newhead = null;
while (targetList != null) {
ListNode temp = targetList.next;
targetList.next = newhead;
newhead = targetList;
targetList = temp;
}
return newhead;
}
// 1->2->3+4->5=1->6->8 (123+45=168)
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode first = new ListNode(1);
ListNode two = new ListNode(2);
ListNode three = new ListNode(3);
first.setNext(two);
two.setNext(three);
ListNode second = new ListNode(4);
ListNode five = new ListNode(5);
second.setNext(five);
ListNode result = addTwoList(first,second);
}
}