基本概念
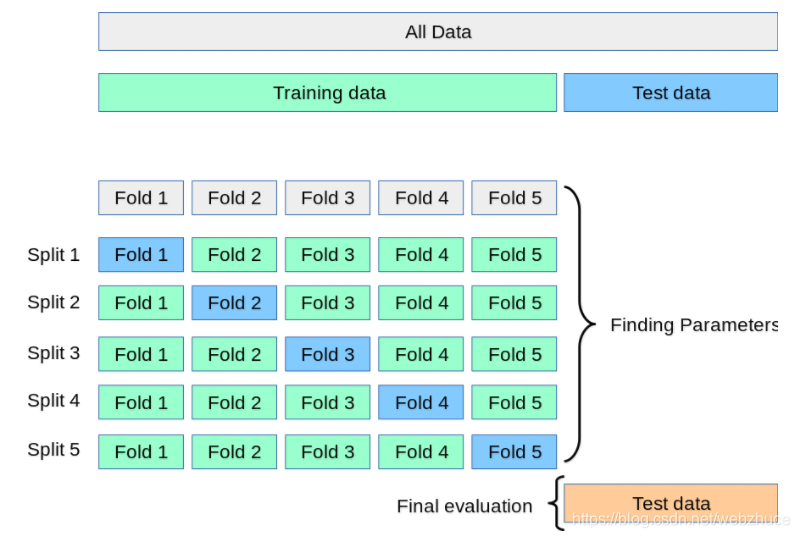
在构建模型时,调参(超参数)是极为重要的一个步骤,因为只有选择最佳的参数才能构建一个最优的模型。但是应该如何确定参数的值呢?一般可以通过交叉验证的方法。什么是交叉验证?我K-折交叉验证为例。当K=2时,就是我们说的2-折交叉验证;当K=5时,就是5折-交叉验证。5-折交叉验证的原理,如下图所示。
如何利用交叉验证来选择参数?我们利用循环不断改变参数,利用交叉验证法评估每个参数值的模型性能,最终选择性能最好的参数。
示例演示
sklearn库提供了GridSearchCV模块,用来对模型参数进行调优。grid search采用基于网格搜索的交叉验证法来选择模型参数,避免了参数选择的盲目性和随意性。这里给出sklearn的官方示例:
Parameter estimation using grid search with cross-validation。
"""
============================================================
Parameter estimation using grid search with cross-validation
============================================================
This examples shows how a classifier is optimized by cross-validation,
which is done using the :class:`sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV` object
on a development set that comprises only half of the available labeled data.
The performance of the selected hyper-parameters and trained model is
then measured on a dedicated evaluation set that was not used during
the model selection step.
More details on tools available for model selection can be found in the
sections on :ref:`cross_validation` and :ref:`grid_search`.
"""
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.svm import SVC
print(__doc__)
# Loading the Digits dataset
digits = datasets.load_digits()
# To apply an classifier on this data, we need to flatten the image, to
# turn the data in a (samples, feature) matrix:
n_samples = len(digits.images)
X = digits.images.reshape((n_samples, -1))
y = digits.target
# Split the dataset in two equal parts
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)
# Set the parameters by cross-validation
tuned_parameters = [{
'kernel': ['rbf'], 'gamma': [1e-3, 1e-4],
'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]},
{
'kernel': ['linear'], 'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]}]
scores = ['precision', 'recall']
for score in scores:
print("# Tuning hyper-parameters for %s" % score)
print()
clf = GridSearchCV(
SVC(), tuned_parameters, scoring='%s_macro' % score
)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
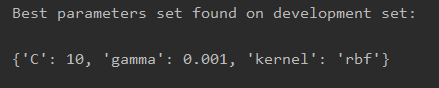
print("Best parameters set found on development set:")
print()
print(clf.best_params_)
print()
print("Grid scores on development set:")
print()
means = clf.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
stds = clf.cv_results_['std_test_score']
for mean, std, params in zip(means, stds, clf.cv_results_['params']):
print("%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r"
% (mean, std * 2, params))
print()
print("Detailed classification report:")
print()
print("The model is trained on the full development set.")
print("The scores are computed on the full evaluation set.")
print()
y_true, y_pred = y_test, clf.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))
print()
# Note the problem is too easy: the hyperparameter plateau is too flat and the
# output model is the same for precision and recall with ties in quality.
运行结果