一、搭建环境
环境是:一人一狗
狗类:
package com.wzq.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public class Dog {
private String name;
public void shout(){
System.out.println("汪汪汪~");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
人有一只狗,人的实体类:
package com.wzq.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private Dog dog;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}
二、使用JavaConfig实现配置
Spring可以完全使用Java来代替xml
在JavaConfig中有几个重要的注解,分别是:
-
@Configuration:指定这个类为配置类 -
@ComponentScan("包"):扫描指定包下的类全都注册到Ioc容器中等价于
.xml中的:<!-- 指定扫描包,这个包下的注解就会生效 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.wzq.pojo" /> -
@Import(某配置类.class):导入其他配置类扫描二维码关注公众号,回复: 13123202 查看本文章
等价于
.xml的:<import resource="xxxx.xml" /> -
@Bean:把具体的某个类注册为Bean等价于
.xml的:<bean id="" class="" > </bean>
下面开始演示:
新建包,随后新建一个BeansConfig.class类,这个类是配置类,它的任务是把人和狗注册为Bean:
package com.wzq.config;
import com.wzq.pojo.Dog;
import com.wzq.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
//指定这个类为配置类
@Configuration
//扫描包
@ComponentScan("com.wzq.pojo")
public class BeansConfig {
//把某个类注册
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@Bean
public Dog dog(){
return new Dog();
}
}
三、使用注解开发
注意:以下操作在被注册为bean的类中操作
| 注解 | 说明 | 等价于 |
|---|---|---|
@Component |
注册某个类为bean与上面提到的 @Bean作用一致 |
<bean id="" class=""></bean> |
@Value("值") |
用于给基本数据类型注入值 | <property name="" value=""/> |
@Autowired |
在上篇博客已经提及 | |
@Scope("作用域名称") |
指定这个类的作用域 | <bean scope="singleton" /> |
在web开发中,会按照MVC三层架构分层,为了更好的区分,Spring 多出了几个衍生注解,他们的作用与@Component一致:
| 注解 | 层 |
|---|---|
@Repository |
dao层 |
@Service |
service层 |
@Controller |
controller层 |
下面实现一下:
人类:
package com.wzq.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component(value = "user111")
@Scope("singleton")
public class User {
@Value("1")
private int id;
@Value("wzq")
private String name;
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}
狗类:
package com.wzq.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("singleton")
public class Dog {
@Value("wzq's dog")
private String name;
public void shout(){
System.out.println("汪汪汪~");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
四、测试
import com.wzq.config.BeansConfig;
import com.wzq.pojo.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
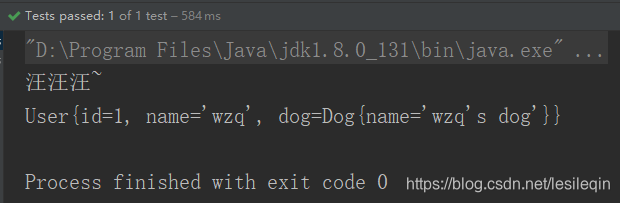
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void Test(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeansConfig.class);
User user = context.getBean("user111", User.class);
user.getDog().shout();
System.out.println(user);
}
}