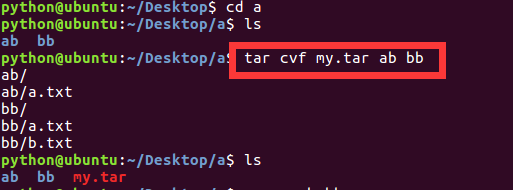
1、切换目录(cd)
-bash: cd: --: invalid option
cd: usage: cd [-L|-P] [dir]
2、查看文件(cat)
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output.
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Examples:
cat f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat Copy standard input to standard output.
3、查看文件的最后几行(tail)
Usage: tail [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Print the last 10 lines of each FILE to standard output.
With more than one FILE, precede each with a header giving the file name.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-c, --bytes=K output the last K bytes; alternatively, use -c +K
to output bytes starting with the Kth of each file
-f, --follow[={name|descriptor}]
output appended data as the file grows;
-f, --follow, and --follow=descriptor are
equivalent
-F same as --follow=name --retry
-n, --lines=K output the last K lines, instead of the last 10;
or use -n +K to output lines starting with the Kth
--max-unchanged-stats=N
with --follow=name, reopen a FILE which has not
changed size after N (default 5) iterations
to see if it has been unlinked or renamed
(this is the usual case of rotated log files).
With inotify, this option is rarely useful.
--pid=PID with -f, terminate after process ID, PID dies
-q, --quiet, --silent never output headers giving file names
--retry keep trying to open a file even when it is or
becomes inaccessible; useful when following by
name, i.e., with --follow=name
-s, --sleep-interval=N with -f, sleep for approximately N seconds
(default 1.0) between iterations.
With inotify and --pid=P, check process P at
least once every N seconds.
-v, --verbose always output headers giving file names
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
4、编辑文件(vi)
usage: vim [arguments] [file ..] edit specified file(s)
or: vim [arguments] - read text from stdin
or: vim [arguments] -t tag edit file where tag is defined
Arguments:
-- Only file names after this
-v Vi mode (like "vi")
-e Ex mode (like "ex")
-E Improved Ex mode
-s Silent (batch) mode (only for "ex")
-y Easy mode (like "evim", modeless)
-R Readonly mode (like "view")
-Z Restricted mode (like "rvim")
-m Modifications (writing files) not allowed
-M Modifications in text not allowed
-b Binary mode
-C Compatible with Vi: 'compatible'
-N Not fully Vi compatible: 'nocompatible'
-V[N][fname] Be verbose [level N] [log messages to fname]
-n No swap file, use memory only
-r List swap files and exit
-r (with file name) Recover crashed session
-L Same as -r
-T <terminal> Set terminal type to <terminal>
-u <vimrc> Use <vimrc> instead of any .vimrc
--noplugin Don't load plugin scripts
-p[N] Open N tab pages (default: one for each file)
-o[N] Open N windows (default: one for each file)
-O[N] Like -o but split vertically
+ Start at end of file
+<lnum> Start at line <lnum>
--cmd <command> Execute <command> before loading any vimrc file
-c <command> Execute <command> after loading the first file
-S <session> Source file <session> after loading the first file
-s <scriptin> Read Normal mode commands from file <scriptin>
-w <scriptout> Append all typed commands to file <scriptout>
-W <scriptout> Write all typed commands to file <scriptout>
-h or --help Print Help (this message) and exit
--version Print version information and exit
5、查看进进程(ps)
********* simple selection ********* ********* selection by list *********
-A all processes -C by command name
-N negate selection -G by real group ID (supports names)
-a all w/ tty except session leaders -U by real user ID (supports names)
-d all except session leaders -g by session OR by effective group name
-e all processes -p by process ID
-q by process ID (unsorted & quick)
T all processes on this terminal -s processes in the sessions given
a all w/ tty, including other users -t by tty
g OBSOLETE -- DO NOT USE -u by effective user ID (supports names)
r only running processes U processes for specified users
x processes w/o controlling ttys t by tty
*********** output format ********** *********** long options ***********
-o,o user-defined -f full --Group --User --pid --cols --ppid
-j,j job control s signal --group --user --sid --rows --info
-O,O preloaded -o v virtual memory --cumulative --format --deselect
-l,l long u user-oriented --sort --tty --forest --version
-F extra full X registers --heading --no-heading --context
--quick-pid
********* misc options *********
-V,V show version L list format codes f ASCII art forest
-m,m,-L,-T,H threads S children in sum -y change -l format
-M,Z security data c true command name -c scheduling class
-w,w wide output n numeric WCHAN,UID -H process hierarchy
6、杀死进程(kill)
kill: usage: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec ... or kill -l [sigspec]
7、tomcat启动命令
cd (tomcat目录)/bin
sh startup.sh8、tomcat停止命令
cd (tomcat目录)/bin
sh shutdown.sh9、打压包,解包命令
注:本部分参考文章(linux打包,压缩,解压的几种方式用法)
| 方式 | 打包命令 | 解包命令 |
| tar | tar -cvf 压缩包名.tar (需要压缩的文件名,多个文件时,中间用空格分开)
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
13010233 查看本文章

|
tar -xvf 压缩包名.tar
|
| gzip |  |
 |
| tar + gzip |  |
 |
| tar + bzip2 |  |
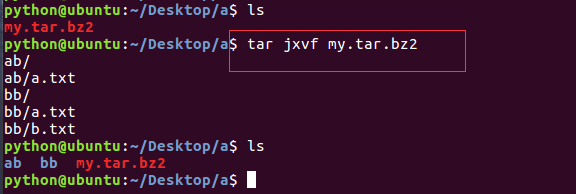 |
| zip | 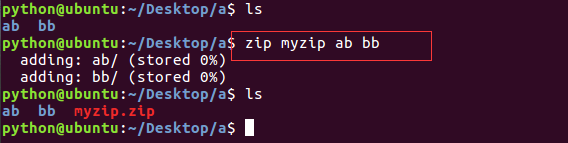 |
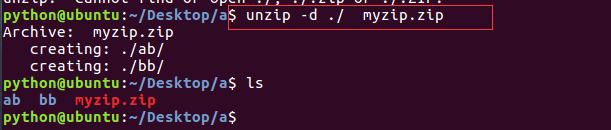 |