视图解析与模板引擎
文章目录
视图解析:SpringBoot默认不支持 JSP,需要引入第三方模板引擎技术实现页面渲染。
一、视图解析
1、处理方式
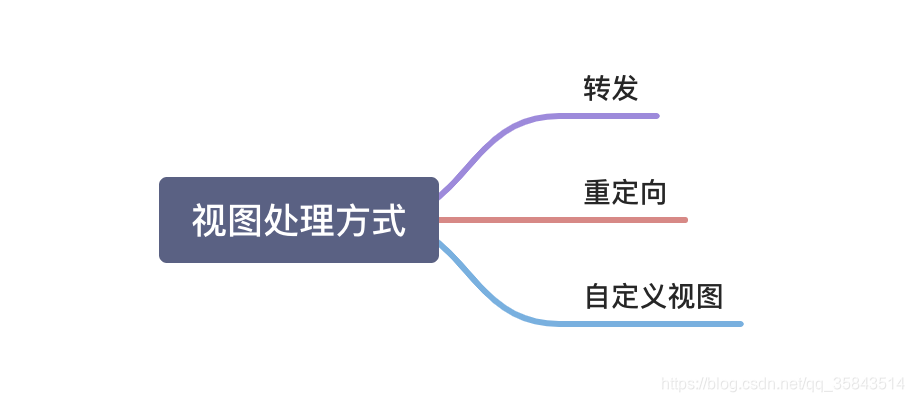
2、视图解析原理过程
(1)目标方法处理的过程中,所有数据都会被放在 ModelAndViewContainer 里面。包括数据和视图地址。
(2)方法的参数是一个自定义类型对象(从请求参数中确定的),把他重新放在 ModelAndViewContainer
(3)任何目标方法执行完成以后都会返回 ModelAndView(数据和视图地址)
(4)processDispatchResult 处理派发结果(页面该如何响应)
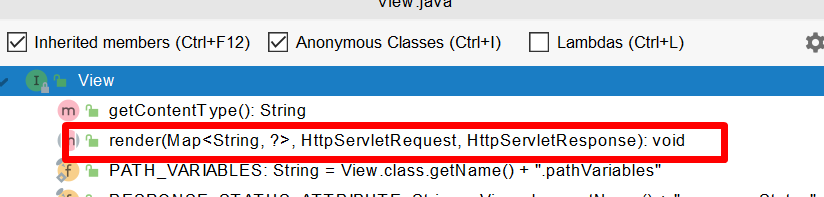
render(mv, request, response); 进行页面渲染逻辑
根据方法的String返回值得到 View 对象 [定义了页面的渲染逻辑]
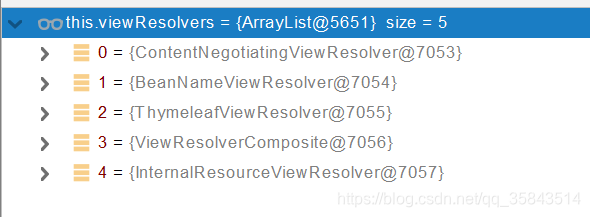
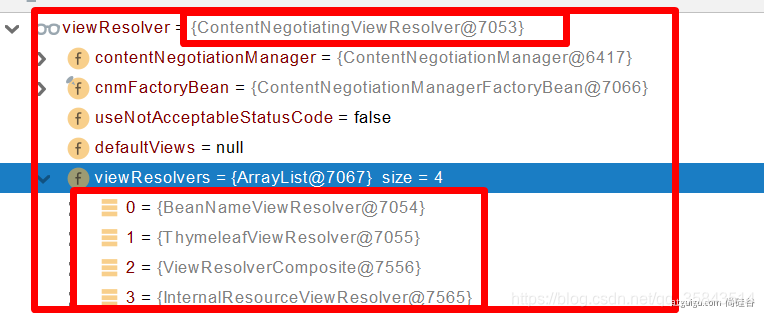
- 所有的视图解析器尝试是否能根据当前返回值得到View对象
- 得到了 redirect:/main.html --> Thymeleaf new RedirectView()
- ContentNegotiationViewResolver 里面包含了下面所有的视图解析器,内部还是利用下面所有视图解析器得到视图对象。
- view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); 视图对象调用自定义的render进行页面渲染工作
注:RedirectView 如何渲染 [重定向到一个页面] - (1)获取目标url地址
- (2)response.sendRedirect(encodedURL);
视图解析:
- 返回值以 forward: 开始:
new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl);--> 转发request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request, response); - 返回值以 redirect: 开始:
new RedirectView() --》 render就是重定向 - 返回值是普通字符串:
new ThymeleafView()--->
自定义视图解析器+自定义视图; 大厂学院。
二、模板引擎-Thymeleaf
1、thymeleaf简介
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments, capable of processing HTML, XML, JavaScript, CSS and even plain text.
现代化、服务端Java模板引擎
2、基本语法
(1)表达式

(2)字面量
文本值: ‘one text’ , ‘Another one!’ ,…
数字: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
布尔值: true , false
空值: null
变量: one,two,… 变量不能有空格
(3)文本操作
字符串拼接: +
变量替换: |The name is ${name}|
(4)数学运算
运算符: + , - , * , / , %
(5)布尔运算
运算符: and , or
一元运算: ! , not
(6)比较运算
比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )等式: == , != ( eq , ne )
(7)条件运算
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
(8)特殊操作
无操作: _
3、设置属性值-th:attr
设置单个值
<form action="subscribe.html" th:attr="action=@{/subscribe}">
<fieldset>
<input type="text" name="email" />
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:attr="value=#{subscribe.submit}"/>
</fieldset>
</form>
设置多个值:
<img src="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
以上两个的代替写法 th:xxxx:
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:value="#{subscribe.submit}"/>
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">
所有h5兼容的标签写法
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#setting-value-to-specific-attributes
4、迭代
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
5、条件运算
<a href="comments.html"
th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">view</a>
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
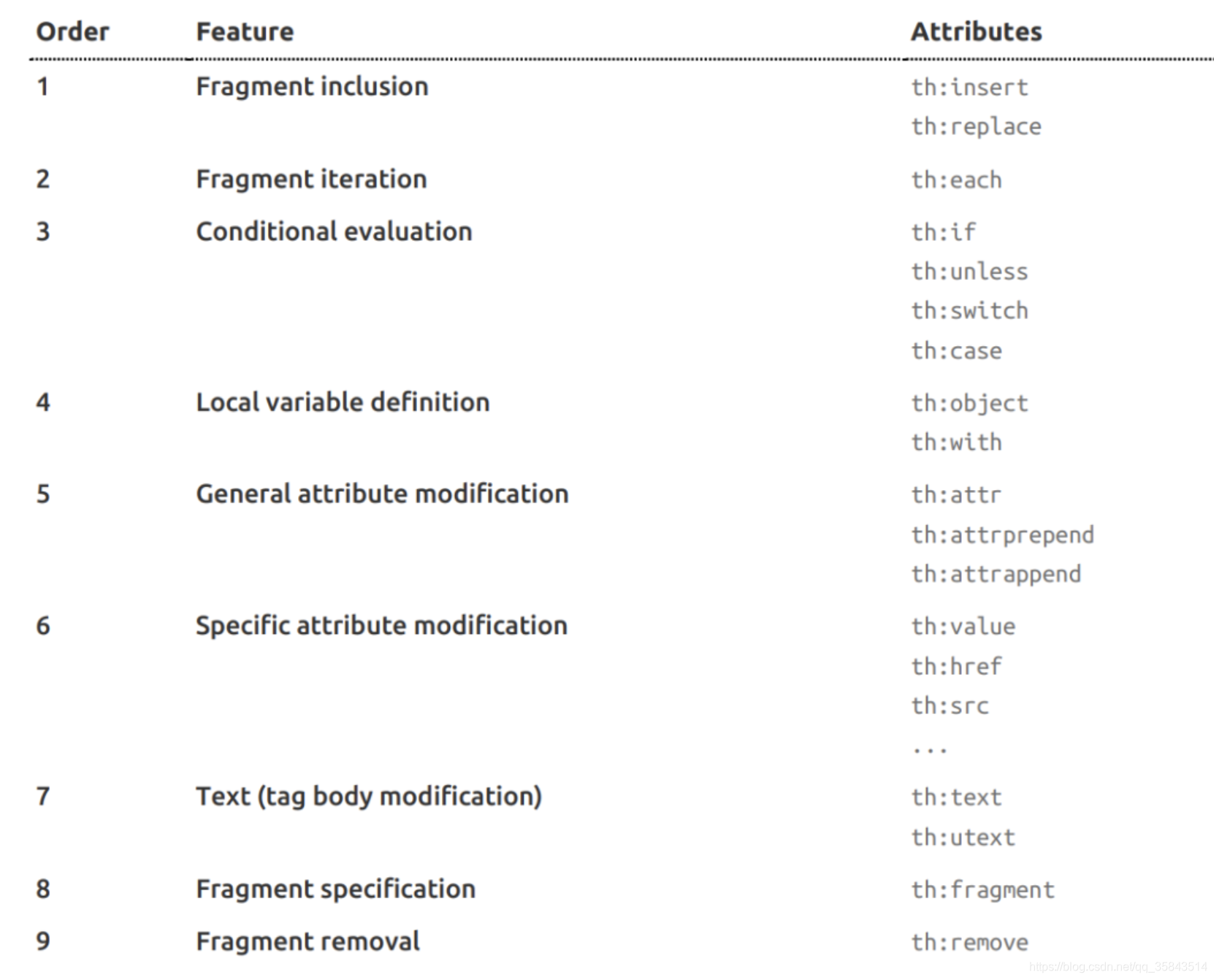
6、属性优先级
三、Thymeleaf的使用
1、引入Starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、自动配置好了thymeleaf
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThymeleafProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass({
TemplateMode.class, SpringTemplateEngine.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter({
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class })
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration {
}
自动配好的策略
- 所有thymeleaf的配置值都在 ThymeleafProperties
- 配置好了 SpringTemplateEngine
- 配好了 ThymeleafViewResolver
- 我们只需要直接开发页面
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; //xxx.html
3、页面开发
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${msg}">哈哈</h1>
<h2>
<a href="www.micah.com" th:href="${link}">去百度</a> <br/>
<a href="www.micah.com" th:href="@{link}">去百度2</a>
</h2>
</body>
</html>

四、构建后台管理系统
1、项目创建
thymeleaf、web-starter、devtools、lombok
2、静态资源处理
自动配置好,我们只需要把所有静态资源放到 static 文件夹下
3、路径构建
th:action="@{/login}"
4、模板抽取
th:insert/replace/include
5、页面跳转
@PostMapping("/login")
public String main(User user, HttpSession session, Model model){
if(StringUtils.hasLength(user.getUserName()) && "123456".equals(user.getPassword())){
//把登陆成功的用户保存起来
session.setAttribute("loginUser",user);
//登录成功重定向到main.html; 重定向防止表单重复提交
return "redirect:/main.html";
}else {
model.addAttribute("msg","账号密码错误");
//回到登录页面
return "login";
}
}
6、数据渲染
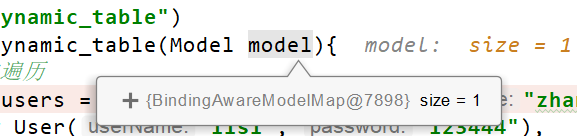
@GetMapping("/dynamic_table")
public String dynamic_table(Model model){
//表格内容的遍历
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("zhangsan", "123456"),
new User("lisi", "123444"),
new User("haha", "aaaaa"),
new User("hehe ", "aaddd"));
model.addAttribute("users",users);
return "table/dynamic_table";
}
<table class="display table table-bordered" id="hidden-table-info">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>用户名</th>
<th>密码</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr class="gradeX" th:each="user,stats:${users}">
<td th:text="${stats.count}">Trident</td>
<td th:text="${user.userName}">Internet</td>
<td >[[${
user.password}]]</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>