这里简单分析一下java.lang包下面的部分类。
1.Object
Object类比较简单,大部分基本方法是native方法。
需要注意的就是equals()默认以'=='方法判断,getClass<T>返回其运行时的Class对象,wait()不释放锁且抛出InterruptedException异常,notify()唤醒以本对象为锁且等待中的线程(仅让他加入竞争池),clone()默认仅浅拷贝且调用时检查是否实现Cloneable接口。
public class Object {
//初始化java方法映射到C
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
//返回Class对象,注意返回的是运行时类型的Class对象
//A a = new B();
//a.getClass()结果为B
public final native Class<?> getClass();
//返回对象hash值
public native int hashCode();
//比较
//默认是比较引用对象地址
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
//克隆
//默认浅拷贝(引用类型的成员不会内存复制)
//这个方法通常由子类覆盖,先super.clone()浅拷贝,在扩展实现深拷贝
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
//唤醒一个在当前对象监视器上等待的线程
public final native void notify();
//唤醒所有在当前对象监视器上等待的线程
public final native void notifyAll();
//无用对象被清理时调用
//jvm不保证此方法会走完
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
//将当前线程停止一段时间,不释放锁
//这个方法会抛出异常
public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (timeout < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos > 0) {
timeout++;
}
wait(timeout);
}
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
wait(0);
}
}
2.String
String类是不可变类,持有一个不可变的字符数组的引用来保存整个字符串。equals()方法比较数组长度和每个元素。compareTo(anotherString)方法先比较共同长度部分,返回第一个不同字符的asci码减法结果,如果前面都相同则返回数组长度相减的结果。trim()方法去掉字符串两端Unicode编码小于等于32(\u0020)的所有字符(包括空格)。intern()方法用equals()去常量池中查找本字符串,如果找不到则加入方法区的常量池。
源码去掉注释还有3000多行比较长。工具类型的方法都比较简单,都是基于字符数组来操作数组元素。这里分析一下部分方法,源码如下:
public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
//不可变字符数组
private final char value[];
//保存hash值,默认0
private int hash;
//构造器:无参数、或者调用Arrays工具类阶段字符数组或者byte数组
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
//返回字符数组长度
public int length() {
return value.length;
}
//比较是否相等
//挨个比较字符数组中的每个元素和数组长度
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//与equals()类似,但是这里要求比较对象是CharSequence子类
public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs) {
if (cs instanceof AbstractStringBuilder) {
if (cs instanceof StringBuffer) {
synchronized(cs) {
return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
}
} else {
return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
}
}
if (cs instanceof String) {
return equals(cs);
}
char v1[] = value;
int n = v1.length;
if (n != cs.length()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (v1[i] != cs.charAt(i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) {
return (this == anotherString) ? true
: (anotherString != null)
&& (anotherString.value.length == value.length)
&& regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length);
}
//比较大小
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
//取长度最小值lim
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
//从0到lim有不同的字符
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
//ASCI码相减作为返回结果
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
//从0到lim字符均相同
//长度相减并返回
return len1 - len2;
}
//计算hash值
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
//hash值默认为0,等于0说明还没计算过
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
//计算过程
//s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
//按指定字符串分割为数组
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
char ch = 0;
//regex指定正则表达式
if (((regex.value.length == 1 &&
".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
(regex.length() == 2 &&
regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
(((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
(ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE))
{
int off = 0;
int next = 0;
boolean limited = limit > 0;
//先按指定字符分割后加入ArrayList中
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
list.add(substring(off, next));
off = next + 1;
} else { // last one
//assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
off = value.length;
break;
}
}
if (off == 0)
return new String[]{this};
if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
//从这里开始构造结果
int resultSize = list.size();
if (limit == 0) {
//找到n个ArrayList中长度为0的元素,则size-n
while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) {
resultSize--;
}
}
String[] result = new String[resultSize];
//截取最终长度的子集,所有这里去掉了尾部的长度为0的元素
return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
}
//去掉字符串两端Unicode编码小于等于32(\u0020)的所有字符(包括空格)
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
st++;
}
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}
//将该字符串加入方法区的常量池
//加入的条件是equasl()池中已有字符串均返回false
public native String intern();
}
3.AbstractStringBuilder
由于String的value域不可变造成字符串的值不能修改,所以产生了value域可变的字符串构建器,用来对不能修改的字符串提供修改的功能。
为什么字符串不能修改,为什么字符串拼接会产生新的字符串对象:
字符串拼接、修改使得字符数组长度改变,比如数组扩容需要创建新的更长的字符数组,由于String的字符数组value域是final的,其字符数组不允许扩容成新的长数组,所以一个字符串对象所表示的字符串就不能修改。
而字符构建器的字符数组引用不是final的,允许指向新的长数组。所以字符串拼接通常是利用字符构建器拼接成新的字符数组(当然会先到方法区常量池中找一下),再toString返回一个新的字符串,这也是编译器对字符串加操作的执行过程,原来的字符串引用指向上一步得到的新字符串。
所以这里说的字符串不可变并不是指String的引用不可变,而是指String.value的引用不可变。
AbstractStringBuilder 是字符构建器的抽象类,提供了对可变字符数组的一系列操作用于操作字符串,源码如下:
//给出了一系列的字符数组的操作方法用于字符串构建
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
//存储字符串(可变的)
char[] value;
//记录存储了多少个字符
int count;
//下面两方法用于判断数组扩容
public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(minimumCapacity);
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
}
//数组扩容
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
//2倍+2
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity < 0) {
if (minimumCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
//创建新数组
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}
//去掉数组尾部未使用的容量
public void trimToSize() {
if (count < value.length) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, count);
}
}
//强制增大count
//会触发数组扩容函数
//比原来count多出来的部分用null来初始化
public void setLength(int newLength) {
if (newLength < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(newLength);
ensureCapacityInternal(newLength);
//从count~newCount用null来初始化数组元素
if (count < newLength) {
Arrays.fill(value, count, newLength, '\0');
}
count = newLength;
}
//将字符数组value倒叙
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse() {
boolean hasSurrogates = false;
int n = count - 1;
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = n - j;
char cj = value[j];
char ck = value[k];
value[j] = ck;
value[k] = cj;
if (Character.isSurrogate(cj) ||
Character.isSurrogate(ck)) {
hasSurrogates = true;
}
}
if (hasSurrogates) {
reverseAllValidSurrogatePairs();
}
return this;
}
//倒叙帮助方法
private void reverseAllValidSurrogatePairs() {
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) {
char c2 = value[i];
if (Character.isLowSurrogate(c2)) {
char c1 = value[i + 1];
if (Character.isHighSurrogate(c1)) {
value[i++] = c1;
value[i] = c2;
}
}
}
}
//将子字符数组复制到另外一个字符数组的dstBegin位置
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
{
if (srcBegin < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
if ((srcEnd < 0) || (srcEnd > count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
if (srcBegin > srcEnd)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("srcBegin > srcEnd");
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
//指定下标范围的子字符数组,用另一个String替换
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
//end开始的后半部分后移,腾出空位
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
//将str的字符数组复制到另一个字符数组value中,且第一个字符保存到value的start位置
//其实就是将str的字符数组填充到value在上一步腾出的空位上
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
//获得指定下标范围的子字符数组
@Override
public CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end) {
return substring(start, end);
}
public String substring(int start) {
return substring(start, count);
}
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
return new String(value, start, end - start);
}
//删除指定下标范围的子数组
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
//删除,后半部分前移
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
//下面是一系列字符串拼接,
//提供多种重载,但是底层还是操作其字符数组,实现方式比较简单,其他省略
public AbstractStringBuilder append(StringBuffer sb) {
if (sb == null)
return appendNull();
int len = sb.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//下面是一系列的插入子字符数组的方法
//提供多种重载,但是底层还是操作其字符数组,实现方式比较简单,其他省略
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
if ((index < 0) || (index > length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
if ((offset < 0) || (len < 0) || (offset > str.length - len))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"offset " + offset + ", len " + len + ", str.length "
+ str.length);
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(value, index, value, index + len, count - index);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, index, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
//下面是子字符数组下标获取相关方法,实现比较简单,省略
}
4.StringBuilder
StringBuilder 覆盖了父类的一些字符数组操作的常用方法,基本上都依赖于父类实现。值的注意的就是toString()方法将字符数组返回一个新的String对象,且方法均非线程安全。
public final class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence
{
//构造器
public StringBuilder() {
super(16);
}
public StringBuilder(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
public StringBuilder(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
public StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) {
this(seq.length() + 16);
append(seq);
}
//拼接字符串
//有多个重载,均是调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的实现,省略
@Override
public StringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));
}
@Override
public StringBuilder appendCodePoint(int codePoint) {
super.appendCodePoint(codePoint);
return this;
}
//删除字符
@Override
public StringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index) {
super.deleteCharAt(index);
return this;
}
//替换字符
@Override
public StringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
super.replace(start, end, str);
return this;
}
//插入字符
//有多个重载,均是调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的实现,省略
@Override
public StringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
super.insert(index, str, offset, len);
return this;
}
//下标相关
//有多个重载,均是调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的实现,省略
@Override
public int indexOf(String str) {
return super.indexOf(str);
}
//字符数组反序
@Override
public StringBuilder reverse() {
super.reverse();
return this;
}
//返回修改后的字符串对象
@Override
public String toString() {
//这里创建了新的字符串
return new String(value, 0, count);
}
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
s.defaultWriteObject();
s.writeInt(count);
s.writeObject(value);
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
count = s.readInt();
value = (char[]) s.readObject();
}
}
5.StringBuffer
StringBuffer 如同StringBuilder 一样,覆盖了父类一系列字符数组的相关操作方法,底层也都是调用父类实现但是外层方法加了同步关键字保证线程安全。
public final class StringBuffer extends AbstractStringBuilder implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence
{
//字符数组,可变,不可序列化
private transient char[] toStringCache;
//构造器
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
public StringBuffer(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
public StringBuffer(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
public StringBuffer(CharSequence seq) {
this(seq.length() + 16);
append(seq);
}
//拼接字符串
//有一系列重载这里省略,均是利用父类实现,仅仅是添加了同步关键字
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer append(Object obj) {
toStringCache = null;
super.append(String.valueOf(obj));
return this;
}
//获取字符
@Override
public synchronized void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst,
int dstBegin)
{
super.getChars(srcBegin, srcEnd, dst, dstBegin);
}
//修改字符
@Override
public synchronized void setCharAt(int index, char ch) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
toStringCache = null;
value[index] = ch;
}
//删除字符
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) {
toStringCache = null;
super.deleteCharAt(index);
return this;
}
//替换字符
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) {
toStringCache = null;
super.replace(start, end, str);
return this;
}
//返回子字符数组得到的字符串
@Override
public synchronized String substring(int start) {
return substring(start, count);
}
//插入字符串
//有一系列重载这里省略,均是利用父类实现,仅仅是添加了同步关键字
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
toStringCache = null;
super.insert(index, str, offset, len);
return this;
}
//非线程安全的insert方法
//包含多个重载
//由insert(int, String)调用实现同步
@Override
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, long l) {
super.insert(offset, l);
return this;
}
//数组下标相关
//有一系列重载这里省略,均是利用父类实现,仅仅是添加了同步关键字
@Override
public int indexOf(String str) {
return super.indexOf(str);
}
//字符数组反序
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer reverse() {
toStringCache = null;
super.reverse();
return this;
}
//用字符数组返回字符串
@Override
public synchronized String toString() {
if (toStringCache == null) {
toStringCache = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, 0, count);
}
//这里创建了新的字符串
return new String(toStringCache, true);
}
//序列化相关
private static final java.io.ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
{
new java.io.ObjectStreamField("value", char[].class),
new java.io.ObjectStreamField("count", Integer.TYPE),
new java.io.ObjectStreamField("shared", Boolean.TYPE),
};
private synchronized void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
java.io.ObjectOutputStream.PutField fields = s.putFields();
fields.put("value", value);
fields.put("count", count);
fields.put("shared", false);
s.writeFields();
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
java.io.ObjectInputStream.GetField fields = s.readFields();
value = (char[])fields.get("value", null);
count = fields.get("count", 0);
}
}
6.基本类型包装类
基本类型的包装类均继承了Number接口。用于将基本类型到引用类型的转换,下面给出部分分析。
Byte:
不可变成员value保存实际值,在-128~127之间。
hashCode()返回的就是value。equals()比较的就是value。
n转为无符号的int值或者long值时,与0xff做&操作,n为正返回n,n为负返回256+n。
申明静态成员内部类BateCache,使用数组缓存-128~127的Byte对象,自动装箱会调用valueOf(),从数组缓存中找到并返回缓存对象,如果使用构造函数创建则不会用到缓存对象。
源码如下:
public final class Byte extends Number implements Comparable<Byte> {
//保存byte值
private final byte value;
//-128~127
public static final byte MIN_VALUE = -128;
public static final byte MAX_VALUE = 127;
//返回其泛型化的Class对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static final Class<Byte> TYPE = (Class<Byte>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("byte");
//hashCode
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Byte.hashCode(value);
}
public static int hashCode(byte value) {
//哈希值就是int类型的value值
return (int)value;
}
//equals
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Byte) {
//比较的是value,即基本类型的实际值
return value == ((Byte)obj).byteValue();
}
return false;
}
//转为无符号int
public static int toUnsignedInt(byte x) {
//0xff就是11111111
//x为正,结果为x
//x为负,结果为256+n
return ((int) x) & 0xff;
}
//转为无符号long
public static long toUnsignedLong(byte x) {
//0xffL就是11111111
return ((long) x) & 0xffL;
}
//缓存静态成员内部类
private static class ByteCache {
private ByteCache(){}
//类加载时将-128~127的Byte对象缓存到数组中,整个数组放在方法区的常量池
static final Byte cache[] = new Byte[-(-128) + 127 + 1];
static {
for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++)
cache[i] = new Byte((byte)(i - 128));
}
}
//自动装箱会调用这个方法,下面两者在-128~127之间等价
//Byte a = 20;
//Byte a = Byte.valueOf(20)
public static Byte valueOf(byte b) {
final int offset = 128;
//从缓存中获取
//下面两个引用在-128~127之间==返回true
//Byte a = 20;
//Byte b = 20;
return ByteCache.cache[(int)b + offset];
}
}
Integer也类似,用不可变私有域value保存值,值的范围在-(2^31)到(2^32)-1之间,同样申明静态成员内部类使用数组缓存-128到127之间的Integer对象,用这个范围之间的基本数值使用自动装箱创建Integer对象会先调用valueOf从缓存中查找。
7.Thread
Thread实现了Runnable接口用来操作线程。提供了一系列基本native用来控制线程状态,然后封装了导出方法给客户端使用,源码较长且部分并没有看懂,以后再改。
Thread类构造方法均调用了init()用来创建线程,线程优先级1~10默认5,使用枚举申明六个线程状态。
持有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap对象引用用来保存线程本地变量(这个Map每个Thread对象都有一个,使用ThreadLocal的弱引用作为key来保存变量值)
重要的公共导出方法包括:
yield()放弃cpu资源,sleep()使线程休眠但是不释放锁,start()调用native方法start0()开始运行线程,run()执行Runnable对象的run()也就是执行任务方法,interrupt()设置中断标志注意此方法与线程状态无关仅设置标志,interrupted()检查是否设置过标志且可以清除标志,setPriority()更改优先级,join()等待子线程终止,setDaemon()设置为守护线程,holdsLock()检查是否持有指定锁。上述公有方法均是封装了一系列私有或者native方法,已废弃方法省略,源码如下:
//函数式接口:允许使用lambda表达式(而非匿名类)方式给出方法实现
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
public class Thread implements Runnable {
//确保此方法最先调用,做一些准备工作
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
//name
private volatile char name[];
//优先级
private int priority;
//是否守护线程
private boolean daemon = false;
//虚拟机状态
private boolean stillborn = false;
//线程实际任务
private Runnable target;
//当前线程所属线程组
private ThreadGroup group;
//线程类加载器
private ClassLoader contextClassLoader;
//断阻塞器:当线程发生IO中断时,需要在线程被设置为中断状态后调用该对象的interrupt方法
volatile Object parkBlocker;
//阻塞器锁:主要用于处理阻塞情况
private volatile Interruptible blocker;
//interrupt()使用它做锁对象
private final Object blockerLock = new Object();
//保存线程本地变量的一个Map
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
//保存可继承的线程本地变量的一个Map
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
//指定线程栈大小,一般默认为0并由jvm指定,且某些jvm不支持此属性
private long stackSize;
//线程id
private long tid;
//线程状态
private volatile int threadStatus = 0;
//线程状态枚举类
public enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
}
//线程优先级1~10,默认5
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
//构造器
//利用init()进行一系列重载,这里省略
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize) {
// 分配新的 Thread 对象,以便将 target 作为其运行对象,将指定的 name 作为其名称,作为 group 所引用的线程组的一员,并具有指定的堆栈大小。
init(group, target, name, stackSize);
}
//init
//用于创建线程,构造器会用到
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name.toCharArray();
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
g.checkAccess();
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
this.stackSize = stackSize;
tid = nextThreadID();
}
//返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。
public static native Thread currentThread();
//暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程。
public static native void yield();
//线程休眠
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
//克隆
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//直接抛出异常
throw new CloneNotSupportedException();
}
//开始运行线程
public synchronized void start() {
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
//调用start0(),由jvm调用其run()
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
}
}
}
private native void start0();
//任务方法
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
//退出
private void exit() {
if (group != null) {
group.threadTerminated(this);
group = null;
}
target = null;
threadLocals = null;
inheritableThreadLocals = null;
inheritedAccessControlContext = null;
blocker = null;
uncaughtExceptionHandler = null;
}
//通知线程可以退出了,设置标志位,注意此方法与线程状态无关系,仅仅设置标志位
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
interrupt0();
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}
private native void interrupt0();
//interrupted():返回是否被通知退出过,此方法调用后会清除标志位,即消除通知,通常结合while实现线程的安全中断
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}
public boolean isInterrupted() {
return isInterrupted(false);
}
void blockedOn(Interruptible b) {
synchronized (blockerLock) {
blocker = b;
}
}
private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted);
//测试线程是否处于活动状态
public final native boolean isAlive();
//更改线程的优先级
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
ThreadGroup g;
checkAccess();
if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) {
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
setPriority0(priority = newPriority);
}
}
//等待该线程终止
public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
join(millis);
}
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
//标记为守护线程或用户线程
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) {
checkAccess();
if (isAlive()) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
daemon = on;
}
//检查可访问性
public final void checkAccess() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkAccess(this);
}
}
//是否持锁:obj为指定的监视器对象
public static native boolean holdsLock(Object obj);
//返回该线程的状态
public State getState() {
// get current thread state
return sun.misc.VM.toThreadState(threadStatus);
}
//以下代码还不知道是干嘛的
private long eetop;
private boolean single_step;
private AccessControlContext inheritedAccessControlContext;
private static int threadInitNumber;
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {
return threadInitNumber++;
}
private static long threadSeqNumber;
private static synchronized long nextThreadID() {
return ++threadSeqNumber;
}
private long nativeParkEventPointer;
private static final RuntimePermission SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION =
new RuntimePermission("enableContextClassLoaderOverride");
private static class Caches {
static final ConcurrentMap<WeakClassKey,Boolean> subclassAudits =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static final ReferenceQueue<Class<?>> subclassAuditsQueue =
new ReferenceQueue<>();
}
private static boolean isCCLOverridden(Class<?> cl) {
if (cl == Thread.class)
return false;
processQueue(Caches.subclassAuditsQueue, Caches.subclassAudits);
WeakClassKey key = new WeakClassKey(cl, Caches.subclassAuditsQueue);
Boolean result = Caches.subclassAudits.get(key);
if (result == null) {
result = Boolean.valueOf(auditSubclass(cl));
Caches.subclassAudits.putIfAbsent(key, result);
}
return result.booleanValue();
}
private static boolean auditSubclass(final Class<?> subcl) {
Boolean result = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
public Boolean run() {
for (Class<?> cl = subcl;
cl != Thread.class;
cl = cl.getSuperclass())
{
try {
cl.getDeclaredMethod("getContextClassLoader", new Class<?>[0]);
return Boolean.TRUE;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
}
try {
Class<?>[] params = {ClassLoader.class};
cl.getDeclaredMethod("setContextClassLoader", params);
return Boolean.TRUE;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
}
}
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
}
);
return result.booleanValue();
}
static void processQueue(ReferenceQueue<Class<?>> queue,ConcurrentMap<? extends WeakReference<Class<?>>, ?> map)
{
Reference<? extends Class<?>> ref;
while((ref = queue.poll()) != null) {
map.remove(ref);
}
}
static class WeakClassKey extends WeakReference<Class<?>> {
private final int hash;
WeakClassKey(Class<?> cl, ReferenceQueue<Class<?>> refQueue) {
super(cl, refQueue);
hash = System.identityHashCode(cl);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == this)
return true;
if (obj instanceof WeakClassKey) {
Object referent = get();
return (referent != null) &&
(referent == ((WeakClassKey) obj).get());
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
/** The current seed for a ThreadLocalRandom */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
long threadLocalRandomSeed;
/** Probe hash value; nonzero if threadLocalRandomSeed initialized */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
int threadLocalRandomProbe;
/** Secondary seed isolated from public ThreadLocalRandom sequence */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
int threadLocalRandomSecondarySeed;
}
8.ThreadLocal
首先来说下线程隔离变量实现方式:Thread持有一个ThreadLocalMap的引用,key是申明变量时的ThreadLocal对象,value是要保存的数据对象。所以真正保存的数据在线程对象里。
ThreadLocalMap:
是ThreadLocal的静态成员内部类,实现了一个map,嵌套实现了一个Entry节点类(key为ThreadLocal对象的弱引用,value保存数据对象)。这个map使用Entry循环数组组成一张table,首先计算key的hash值找到数组下标,然后利用线性探测法寻找临近的空位。数组容量为2的幂次方(方便与hash值求模得到均匀的数组下标),扩容阈值为长度的三分之二。提供了系列操作节点的方法。
弱引用:
Entry节点类继承自WeakReference<T>,接口方法get()返回T对象的引用,这里T类型ThreadLocal的对象引用变为弱引用。因为ThreadLocal对象如果使用强引用会造成生命周期与线程绑定,而现在线程通常需要复用会造成ThreadLocal对象一直可达而不被GC。ThreadLocal对象使用弱引用的话,在没有强引用它时通常其对象会在下一次GC被清理掉而使得key为null,我们可以手动设置value为null断开数据对象的强引用。
ThreadLocal:
除实现了静态成员内部类ThreadLocalMap之外,仅包含几个方法用于操作Thread的ThreadLocalMap成员来保存数据对象。值的注意的是他计算hash从id累加魔数而来,这样得到的hash值可以与数组长度求模,均匀映射到长度为2的幂次方的数组下标上。
先查看ThreadLocalMap,源码如下:
//Map:环形的键值对数组
static class ThreadLocalMap {
//初始容量
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
//节点数组
private Entry[] table;
//容量实际使用值
private int size = 0;
//扩容阈值,容量的2/3
private int threshold;
//Entry节点类
//通常线程需要复用而生命周期长,Entry键值对与线程之间的引用关系使得Entry难以被回收
//对象强引用链不可达通常活不过下一次GC,实现这个接口的对象就复合这种要求
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
//需要保存的值
Object value;
//key:ThreadLocal对象的引用,value:需要保存的值
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
//构造器
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
//创建节点数组ThreadLocal引用作为键,hash值来计算数组下标
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
//计算数组下标
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
//添加元素
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
//改变size
size = 1;
//计算扩容阈值
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();
if (key != null) {
Object value = key.childValue(e.value);
Entry c = new Entry(key, value);
int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
while (table[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
table[h] = c;
size++;
}
}
}
}
//计算扩容阈值
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
//环形数组下标移动:用于线性探测法寻找临近的空位
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
//重新计算hash值
private void rehash() {
//清理数组上无效key引用映射的value
expungeStaleEntries();
//可能使得容量实际使用小很多,所以将扩容阈值调低,然后在判断是否需要扩容
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
//扩容
resize();
}
//数组扩容
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
//获取节点
//会被ThreadLocal的get方法直接调用,用于获取map中某个ThreadLocal存放的值
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//ThreadLocal为键
//使用键的hash值计算数组下标
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
//因为是线性探测法,一个key的hash值会映射到多个数组下标,首先正向映射找到节点,再反向映射判断是否是我们查找的节点
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//未直接命中,向后寻找
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
//未直接命中,向后寻找
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
//保存变量
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//ThreadLocal为key,通过key的hash值找到数组下标
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
//该位置不为空,看下一个位置是否为空
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
//覆盖原有value
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
//删除变量
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
//同样,没找到继续向后找
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
//清理
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {//挨个向后
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
//找到某个有效Entry(Enter不为空或者threadLocal也还没被GC掉)
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
//从这个位置开始清理一个连续段
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
//清理节点
//key是弱引用被GC掉,那么value由我们显示断开强引用
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//显示断开value的强引用
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
Entry e;
int i;
//向后遍历,遍历连续段的有Entry对象的数组位置
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//Entry不为空,但是key(ThreadLocal)为空(已经被GC掉),则将value置空
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
//清理数组
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
}
查看外层的ThreadLocal类,源码如下:
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
//hash值:这个值与2的幂次方取模(数组长度)可以得到一个均匀的结果
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static int nextHashCode() {
//id累加魔数,得到一个hash值
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
//id
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();
//魔数
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
//构造器
public ThreadLocal() {
}
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) {
return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);
}
//get
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
//set
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
//remove
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
//返回Map
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
//创建Map
//第一次保存数据的时候调用
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier;
SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) {
this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);
}
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return supplier.get();
}
}
}
9.Enum
枚举类特点:
枚举可以实现接口
包含成员变量和方法
默认继承 java.lang.Enum 类所以不能继承其他父类
默认使用 final 修饰
因此不能派生子类
枚举类所有枚举对象必须在第一行给出,默认添加 public static final 修饰
values()返回枚举值的数组,valueOf返回枚举类中指定name的枚举值
jdk1.5后支持switch和case
枚举的使用:
enum Gender {
MALE("男"){
@Override
public void info() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
},FEMALE("女"){
@Override
public void info() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
private final String name;
private Gender(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
//抽象方法
public abstract void info();
}
Enum是所有枚举类的超类,包含name和ordinal两个成员,方法均比较简单,源码如下:
public abstract class Enum<E extends Enum<E>> implements Comparable<E>, Serializable ,Cloneable{
//对象名
private final String name;
public final String name() {
return name;
}
//下标(从0开始按照申明顺序排序)
private final int ordinal;
public final int ordinal() {
return ordinal;
}
//构造器(用户不能自己调用,会编译失败)
protected Enum(String name, int ordinal) {
this.name = name;
this.ordinal = ordinal;
}
//toString
public String toString() {
return name;
}
//equals
public final boolean equals(Object other) {
//使用==判断地址
return this==other;
}
//hashCode
public final int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
//clone
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//并没有克隆相关逻辑,直接抛出异常
throw new CloneNotSupportedException();
}
//compareTo
public final int compareTo(E o) {
Enum<?> other = (Enum<?>)o;
Enum<E> self = this;
if (self.getClass() != other.getClass() && self.getDeclaringClass() != other.getDeclaringClass())
throw new ClassCastException();
//返回下标差值
return self.ordinal - other.ordinal;
}
//返回申明的枚举类
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public final Class<E> getDeclaringClass() {
//enum关键字申明的枚举类对象的Class对象
Class<?> clazz = getClass();
//超类Enum
Class<?> zuper = clazz.getSuperclass();
return (zuper == Enum.class) ? (Class<E>)clazz : (Class<E>)zuper;
}
//返回枚举类中指定name的枚举值
public static <T extends Enum<T>> T valueOf(Class<T> enumType,String name) {
T result = enumType.enumConstantDirectory().get(name);
if (result != null)
return result;
if (name == null)
throw new NullPointerException("Name is null");
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No enum constant " + enumType.getCanonicalName() + "." + name);
}
protected final void finalize() { }
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException {
throw new InvalidObjectException("can't deserialize enum");
}
private void readObjectNoData() throws ObjectStreamException {
throw new InvalidObjectException("can't deserialize enum");
}
}
10.Throwable
首先,StackTraceElement是一个工具类,封装了被调用方法的申明类、方法名称、行数等等,源码如下:
public final class StackTraceElement implements java.io.Serializable {
//方法所在申明类
private String declaringClass;
//方法名称
private String methodName;
//文件名称
private String fileName;
//行数
private int lineNumber;
//一系列成员get方法
//构造器
public StackTraceElement(String declaringClass, String methodName,String fileName, int lineNumber) {
this.declaringClass = Objects.requireNonNull(declaringClass, "Declaring class is null");
this.methodName = Objects.requireNonNull(methodName, "Method name is null");
this.fileName = fileName;
this.lineNumber = lineNumber;
}
//打印成员信息
public String toString() {
return getClassName() + "." + methodName +
(isNativeMethod() ? "(Native Method)" :
(fileName != null && lineNumber >= 0 ?
"(" + fileName + ":" + lineNumber + ")" :
(fileName != null ? "("+fileName+")" : "(Unknown Source)")));
}
//equals
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj==this)
return true;
if (!(obj instanceof StackTraceElement))
return false;
StackTraceElement e = (StackTraceElement)obj;
//短路与方式比较上诉所有成员
return e.declaringClass.equals(declaringClass) &&
e.lineNumber == lineNumber &&
Objects.equals(methodName, e.methodName) &&
Objects.equals(fileName, e.fileName);
}
public int hashCode() {
int result = 31*declaringClass.hashCode() + methodName.hashCode();
result = 31*result + Objects.hashCode(fileName);
result = 31*result + lineNumber;
return result;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6992337162326171013L;
}
给出该类的一个测试类,帮助理解Throwable中StackTraceElement数组的使用,测试代码如下:
public class test {
//方法A
private void methodA() {
//调用B
methodB();
}
//方法B
private void methodB() {
//调用C
methodC();
}
//方法C
private void methodC() {
//回溯此方法调用链,输出相关信息
StackTraceElement elements[] = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
for (int i = 0; i < elements.length; i++) {
System.out.print("类名:"+elements[i].getClassName()+" ");
System.out.print("方法名:"+elements[i].getMethodName()+" ");
System.out.print("文件名:"+elements[i].getFileName()+" ");
System.out.print("行数:"+elements[i].getLineNumber()+" ");
System.out.println("Class对象:"+elements[i].getClass()+" ");
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
new test().methodA();
//结果:
//类名:java.lang.Thread 方法名:getStackTrace 文件名:null 行数:-1 Class对象:class java.lang.StackTraceElement
//类名:com.tyf.www.test 方法名:methodC 文件名:test.java 行数:23 Class对象:class java.lang.StackTraceElement
//类名:com.tyf.www.test 方法名:methodB 文件名:test.java 行数:18 Class对象:class java.lang.StackTraceElement
//类名:com.tyf.www.test 方法名:methodA 文件名:test.java 行数:12 Class对象:class java.lang.StackTraceElement
//类名:com.tyf.www.test 方法名:main 文件名:test.java 行数:6 Class对象:class java.lang.StackTraceElement
}
}
Throwable 是所有异常的顶层父类,最重要的成员是StackTrace,他是一个StackTraceElement数组,用来保存方法调用栈。重要的方法就是打印异常信息等一系列方法它们都是通过上面数组实现的。一般我们使用异常都是自定义异常,无非就是重写异常名称、异常信息等等相关方法。源码如下:
public class Throwable implements Serializable {
private transient Object backtrace;
//存放异常详细信息
private String detailMessage;
//哨兵提供
private static class SentinelHolder {
public static final StackTraceElement STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement("", "", null, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
public static final StackTraceElement[] STACK_TRACE_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement[] {STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL};
}
//异常原因
private Throwable cause = this;
//方法调用栈
private StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;//StackTraceElement封装了被调用方法的申明类、方法名称、文件名称、报错行数
private static final StackTraceElement[] UNASSIGNED_STACK = new StackTraceElement[0];
//存放try中的异常对象
private List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL;
private static final List<Throwable> SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<Throwable>(0));
//通用字符串
private static final String NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE = "Cannot suppress a null exception.";
private static final String SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE = "Self-suppression not permitted";
private static final String CAUSE_CAPTION = "Caused by: ";
private static final String SUPPRESSED_CAPTION = "Suppressed: ";
//构造器
public Throwable() {
fillInStackTrace();
}
public Throwable(String message) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
}
public Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
}
public Throwable(Throwable cause) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = (cause==null ? null : cause.toString());
this.cause = cause;
}
protected Throwable(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {
if (writableStackTrace) {
fillInStackTrace();
} else {
stackTrace = null;
}
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
if (!enableSuppression)
suppressedExceptions = null;
}
//返回详细异常信息
public String getMessage() {
return detailMessage;
}
//返回详细异常信息
public String getLocalizedMessage() {
return getMessage();
}
//返回异常的引用
public synchronized Throwable getCause() {
return (cause==this ? null : cause);
}
//异常初始化
public synchronized Throwable initCause(Throwable cause) {
//异常不是默认值,说明已经初始化过,也说明异常只能初始化一次
if (this.cause != this)
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't overwrite cause with " +
Objects.toString(cause, "a null"), this);
//若使用自己来初始化cause域,直接抛出方法参数不合法异常
if (cause == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self-causation not permitted", this);
this.cause = cause;
return this;
}
//打印异常栈
public void printStackTrace(PrintWriter s) {
printStackTrace(new WrappedPrintWriter(s));
}
public void printStackTrace() {
printStackTrace(System.err);
}
public void printStackTrace(PrintStream s) {
printStackTrace(new WrappedPrintStream(s));
}
private void printStackTrace(PrintStreamOrWriter s) {
Set<Throwable> dejaVu =Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<Throwable, Boolean>());
dejaVu.add(this);
//同步
synchronized (s.lock()) {
s.println(this);
StackTraceElement[] trace = getOurStackTrace();
//遍历方法调用栈,打印方法调用链
for (StackTraceElement traceElement : trace)
s.println("\tat " + traceElement);
//
for (Throwable se : getSuppressed())
se.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, SUPPRESSED_CAPTION, "\t", dejaVu);
Throwable ourCause = getCause();
if (ourCause != null)
ourCause.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, CAUSE_CAPTION, "", dejaVu);
}
}
private void printEnclosedStackTrace(PrintStreamOrWriter s,
StackTraceElement[] enclosingTrace,
String caption,
String prefix,
Set<Throwable> dejaVu) {
assert Thread.holdsLock(s.lock());
if (dejaVu.contains(this)) {
s.println("\t[CIRCULAR REFERENCE:" + this + "]");
} else {
dejaVu.add(this);
StackTraceElement[] trace = getOurStackTrace();
int m = trace.length - 1;
int n = enclosingTrace.length - 1;
while (m >= 0 && n >=0 && trace[m].equals(enclosingTrace[n])) {
m--; n--;
}
int framesInCommon = trace.length - 1 - m;
//打印异常栈
s.println(prefix + caption + this);
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
s.println(prefix + "\tat " + trace[i]);
if (framesInCommon != 0)
s.println(prefix + "\t... " + framesInCommon + " more");
//打印trt中异常对象
for (Throwable se : getSuppressed())
se.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, SUPPRESSED_CAPTION,
prefix +"\t", dejaVu);
//打印异常原因
Throwable ourCause = getCause();
if (ourCause != null)
//递归
ourCause.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, CAUSE_CAPTION, prefix, dejaVu);
}
}
//记录异常栈
public synchronized Throwable fillInStackTrace() {
if (stackTrace != null ||
backtrace != null /* Out of protocol state */ ) {
fillInStackTrace(0);
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;
}
return this;
}
private native Throwable fillInStackTrace(int dummy);//这里调用native,记录调用链
//返回方法栈
public StackTraceElement[] getStackTrace() {
return getOurStackTrace().clone();
}
private synchronized StackTraceElement[] getOurStackTrace() {
if (stackTrace == UNASSIGNED_STACK ||
(stackTrace == null && backtrace != null)) {
int depth = getStackTraceDepth();
stackTrace = new StackTraceElement[depth];
for (int i=0; i < depth; i++)
stackTrace[i] = getStackTraceElement(i);
} else if (stackTrace == null) {
return UNASSIGNED_STACK;
}
return stackTrace;
}
//添加方法栈
public void setStackTrace(StackTraceElement[] stackTrace) {
StackTraceElement[] defensiveCopy = stackTrace.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < defensiveCopy.length; i++) {
if (defensiveCopy[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException("stackTrace[" + i + "]");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (this.stackTrace == null && backtrace == null)
return;
this.stackTrace = defensiveCopy;
}
}
//返回异常深度
native int getStackTraceDepth();
//返回指定层的异常
native StackTraceElement getStackTraceElement(int index);
//搜集try中的异常对象
public final synchronized void addSuppressed(Throwable exception) {
if (exception == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE, exception);
if (exception == null)
throw new NullPointerException(NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE);
if (suppressedExceptions == null)
return;
if (suppressedExceptions == SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL)
suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<>(1);
//添加
suppressedExceptions.add(exception);
}
private static final Throwable[] EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY = new Throwable[0];
//返回try中的所有异常对象
public final synchronized Throwable[] getSuppressed() {
if (suppressedExceptions == SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL ||suppressedExceptions == null)
return EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY;
else
return suppressedExceptions.toArray(EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY);
}
//读写对象
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
if (suppressedExceptions != null) {
List<Throwable> suppressed = null;
if (suppressedExceptions.isEmpty()) {
suppressed = SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL;
} else {
suppressed = new ArrayList<>(1);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
if (t == null)
throw new NullPointerException(NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE);
if (t == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE);
suppressed.add(t);
}
}
suppressedExceptions = suppressed;
}
if (stackTrace != null) {
if (stackTrace.length == 0) {
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK.clone();
} else if (stackTrace.length == 1 &&
SentinelHolder.STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL.equals(stackTrace[0])) {
stackTrace = null;
} else {
for(StackTraceElement ste : stackTrace) {
if (ste == null)
throw new NullPointerException("null StackTraceElement in serial stream. ");
}
}
} else {
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK.clone();
}
}
private synchronized void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException {
getOurStackTrace();
StackTraceElement[] oldStackTrace = stackTrace;
try {
if (stackTrace == null)
stackTrace = SentinelHolder.STACK_TRACE_SENTINEL;
s.defaultWriteObject();
} finally {
stackTrace = oldStackTrace;
}
}
//输出流成员内部类
private abstract static class PrintStreamOrWriter {
abstract Object lock();
abstract void println(Object o);
}
private static class WrappedPrintStream extends PrintStreamOrWriter {
private final PrintStream printStream;
WrappedPrintStream(PrintStream printStream) {
this.printStream = printStream;
}
Object lock() {
return printStream;
}
void println(Object o) {
printStream.println(o);
}
}
private static class WrappedPrintWriter extends PrintStreamOrWriter {
private final PrintWriter printWriter;
WrappedPrintWriter(PrintWriter printWriter) {
this.printWriter = printWriter;
}
Object lock() {
return printWriter;
}
void println(Object o) {
printWriter.println(o);
}
}
}
11.Error和Exception
Error :系统错误,不应该被捕获而是直接停止应用程序。
Exception :jdk已经为我们实现了完善的一系列子类,从它继承而来的所有异常均可以catch可以错误恢复。包含运行时异常(不用捕获,方法也不用throws来申明),受检异常(需要显示catch,方法必须用throws来申明)。
这两个类均继承自Throwable。均只是重写了四个构造器,代码短短30行不到。源码如下:
//Error
public class Error extends Throwable {
static final long serialVersionUID = 4980196508277280342L;
//构造器
public Error() {
super();
}
public Error(String message) {
super(message);
}
public Error(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public Error(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected Error(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
//Exception
public class Exception extends Throwable {
static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L;
//构造器
public Exception() {
super();
}
public Exception(String message) {
super(message);
}
public Exception(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public Exception(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected Exception(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
下面给出jdk已经实现的Exception子类,分为运行时异常和受检查异常,代码如下:
//运行时异常(非受检异常):无需捕获和抛出 Java.lang.ArithmeticException Java.lang.ArrayStoreExcetpion Java.lang.ClassCastException Java.lang.EnumConstantNotPresentException Java.lang.IllegalArgumentException Java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException Java.lang.NumberFormatException Java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException Java.lang.IllegalStateException Java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException Java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException Java.lang.NegativeArraySizeException’ Java.lang.NullPointerException Java.lang.SecurityException Java.lang.TypeNotPresentException Java.lang.UnsupprotedOperationException //受检异常:需要显式catch和throws抛出 Java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException Java.lang.IllegalAccessException Java.lang.InterruptedException Java.lang.NoSuchFieldException Java.lang.NoSuchMetodException
12.Class
我们申明的所有的类都有一些共同点:有一系列成员方法、属性、构造器、直接实现多个接口、直接继承某个父类、泛型的参数化类型信息、注解、全路径等等。我们把所有信息都封装到一个Class类中,我们申明的所有类都有一个Class类对象用来描述该类的上述所有信息。Class类文件源码很长,这里分析部分常用方法。
Class类申明,源码如下:
public final class Class<T> implements java.io.Serializable,GenericDeclaration,Type,AnnotatedElement {
//GenericDeclaration接口:获取泛型申明
//Type:一个空接口,用于表示所有类型(原始类型、泛型参数化类型、数组等)
//AnnotatedElement:提供方法用于反射地读取注释信息
}
包含私有构造器,仅由jvm调用,源码如下:
//构造器
//私有,不允许客户端调用
private Class(ClassLoader loader) {
classLoader = loader;
}
常用的基本方法,大部分封装native方法。源码如下:
//强制转换为本类一个指定子类的Class对象
public <U> Class<? extends U> asSubclass(Class<U> clazz) {
if (clazz.isAssignableFrom(this))
return (Class<? extends U>) this;
else
throw new ClassCastException(this.toString());
}
//将obj转为本类的实例
public T cast(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && !isInstance(obj))
throw new ClassCastException(cannotCastMsg(obj));
//这里直接使用了强制类型转换
return (T) obj;
}
//判断是否是本类实例
public native boolean isInstance(Object obj);
//判断是否是调用者同类型
public native boolean isAssignableFrom(Class<?> cls);
//判断本类是否是接口
public native boolean isInterface();
//判断本类是否是数组
public native boolean isArray();
//判断本类是否是基本类型
public native boolean isPrimitive();
//判断本类是否是注释类型
public boolean isAnnotation() {
return (getModifiers() & ANNOTATION) != 0;
}
//判断本类是否是合成类型
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return (getModifiers() & SYNTHETIC) != 0;
}
//获得本类的包路径
public Package getPackage() {
return Package.getPackage(this);
}
//全限定名(包+类)
private transient String name;
public String getName() {
String name = this.name;
if (name == null)
this.name = name = getName0();
return name;
}
private native String getName0();
反射相关的方法,源码如下:
//注解相关
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return (A) annotationData().annotations.get(annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getAnnotations() {
return AnnotationParser.toArray(annotationData().annotations);
}
//属性相关
public Field[] getFields() throws SecurityException {//返回本类所有公有属性
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyFields(privateGetPublicFields(null));
}
public Field getField(String name)
throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException {//返回本类指定名称的公有属性
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Field field = getField0(name);
if (field == null) {
throw new NoSuchFieldException(name);
}
return field;
}
//方法相关
public Method[] getMethods() throws SecurityException {//返回本类所有公有方法
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyMethods(privateGetPublicMethods());
}
public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {//返回本类指定名称、参数的公有方法
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Method method = getMethod0(name, parameterTypes, true);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes));
}
return method;
}
//构造器相关
public Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() throws SecurityException {//返回本类所有公有构造器
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return copyConstructors(privateGetDeclaredConstructors(true));
}
public Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {//返回本类指定参数的公有构造器
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
return getConstructor0(parameterTypes, Member.PUBLIC);
}
//接口相关
public Class<?>[] getInterfaces() {//获取本类直接实现的所有接口
ReflectionData<T> rd = reflectionData();
if (rd == null) {
return getInterfaces0();
} else {
Class<?>[] interfaces = rd.interfaces;
if (interfaces == null) {
interfaces = getInterfaces0();
rd.interfaces = interfaces;
}
return interfaces.clone();
}
}
private native Class<?>[] getInterfaces0();
public Type[] getGenericInterfaces() {//获取本类直接实现的所有接口,返回这些接口的类型数组
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
return (info == null) ? getInterfaces() : info.getSuperInterfaces();
}
//返回本类申明的变量类型的数组
public TypeVariable<Class<T>>[] getTypeParameters() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
if (info != null)
return (TypeVariable<Class<T>>[])info.getTypeParameters();
else
return (TypeVariable<Class<T>>[])new TypeVariable<?>[0];
}
//获得本类的直接父类的Class对象
public native Class<? super T> getSuperclass();
//获得本类的直接父类的Class对象(带参数化类型)
public Type getGenericSuperclass() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
if (info == null) {
return getSuperclass();
}
if (isInterface()) {
return null;
}
return info.getSuperclass();
}
//如果本类是在某方法中定义的,返回这个方法对象
@CallerSensitive
public Method getEnclosingMethod() throws SecurityException {
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
if (!enclosingInfo.isMethod())
return null;
MethodRepository typeInfo = MethodRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(),getFactory());
Class<?> returnType = toClass(typeInfo.getReturnType());
Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes();
Class<?>[] parameterClasses = new Class<?>[parameterTypes.length];
for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++)
parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]);
Class<?> enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED,
Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
for(Method m: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredMethods()) {
if (m.getName().equals(enclosingInfo.getName()) ) {
Class<?>[] candidateParamClasses = m.getParameterTypes();
if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) {
boolean matches = true;
for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) {
if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) {
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches) {
if (m.getReturnType().equals(returnType) )
return m;
}
}
}
}
throw new InternalError("Enclosing method not found");
}
}
private native Object[] getEnclosingMethod0();
private EnclosingMethodInfo getEnclosingMethodInfo() {
Object[] enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethod0();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
return new EnclosingMethodInfo(enclosingInfo);
}
}
//如果是在方法中定义本类,封装这个放的相关信息到一个成员内部类中
private final static class EnclosingMethodInfo {
private Class<?> enclosingClass;
private String name;
private String descriptor;
private EnclosingMethodInfo(Object[] enclosingInfo) {
if (enclosingInfo.length != 3)
throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information");
try {
enclosingClass = (Class<?>) enclosingInfo[0];
assert(enclosingClass != null);
name = (String) enclosingInfo[1];
descriptor = (String) enclosingInfo[2];
assert((name != null && descriptor != null) || name == descriptor);
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new InternalError("Invalid type in enclosing method information", cce);
}
}
boolean isPartial() {
return enclosingClass == null || name == null || descriptor == null;
}
boolean isConstructor() { return !isPartial() && "<init>".equals(name); }
boolean isMethod() { return !isPartial() && !isConstructor() && !"<clinit>".equals(name); }
Class<?> getEnclosingClass() { return enclosingClass; }
String getName() { return name; }
String getDescriptor() { return descriptor; }
}
private static Class<?> toClass(Type o) {
if (o instanceof GenericArrayType)
return Array.newInstance(toClass(((GenericArrayType)o).getGenericComponentType()),0)
.getClass();
return (Class<?>)o;
}
//如果本来是在某构造器中定义的,返回这个构造器对象
@CallerSensitive
public Constructor<?> getEnclosingConstructor() throws SecurityException {
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
if (enclosingInfo == null)
return null;
else {
if (!enclosingInfo.isConstructor())
return null;
ConstructorRepository typeInfo = ConstructorRepository.make(enclosingInfo.getDescriptor(),
getFactory());
Type [] parameterTypes = typeInfo.getParameterTypes();
Class<?>[] parameterClasses = new Class<?>[parameterTypes.length];
for(int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++)
parameterClasses[i] = toClass(parameterTypes[i]);
Class<?> enclosingCandidate = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
enclosingCandidate.checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED,
Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
for(Constructor<?> c: enclosingCandidate.getDeclaredConstructors()) {
Class<?>[] candidateParamClasses = c.getParameterTypes();
if (candidateParamClasses.length == parameterClasses.length) {
boolean matches = true;
for(int i = 0; i < candidateParamClasses.length; i++) {
if (!candidateParamClasses[i].equals(parameterClasses[i])) {
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches)
return c;
}
}
throw new InternalError("Enclosing constructor not found");
}
}
//如果本类是在另外一个类中定义的,返回外层类的Class对象
@CallerSensitive
public Class<?> getDeclaringClass() throws SecurityException {
final Class<?> candidate = getDeclaringClass0();
if (candidate != null)
candidate.checkPackageAccess(
ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true);
return candidate;
}
private native Class<?> getDeclaringClass0();
//如果本类是在另外一个类中定义的,返回外层类的Class对象
@CallerSensitive
public Class<?> getEnclosingClass() throws SecurityException {
EnclosingMethodInfo enclosingInfo = getEnclosingMethodInfo();
Class<?> enclosingCandidate;
if (enclosingInfo == null) {
enclosingCandidate = getDeclaringClass();
} else {
Class<?> enclosingClass = enclosingInfo.getEnclosingClass();
if (enclosingClass == this || enclosingClass == null)
throw new InternalError("Malformed enclosing method information");
else
enclosingCandidate = enclosingClass;
}
if (enclosingCandidate != null)
enclosingCandidate.checkPackageAccess(
ClassLoader.getClassLoader(Reflection.getCallerClass()), true);
return enclosingCandidate;
}
大部分都封装的native方法,具体查看jdk。
13.ClassLoader
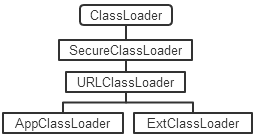
类加载器用于将.java编译后的.class文件加载到jvm。当请求查找类或资源时, ClassLoader实例将在尝试查找类或资源本身之前将类或资源的搜索任务委托给其父类加载器。 虚拟机的内置类加载器Bootstrap (称为“引导类加载器”)本身不具有父级,但可以作为ClassLoader实例的顶层父级。 继承关系图如下:
Bootstrap ClassLoader:
加载核心类库,路径为“%JRE_HOME%\lib”。包括rt.jar、resources.jar、charsets.jar和class等。这个类是C/C++写的,本身属于jvm的一部分。
Extention ClassLoader:
加载扩展类,路径为“%JRE_HOME%\lib\ext”。
Appclass Loader:
当前应用的classpath的类。
类加载过程:
加载、验证、准备、解析、初始化、使用、卸载。其中解析可以在初始化之后再进行用于支持java的运行时绑定的特性。
双亲委托防止重复加载:
当前ClassLoader首先从自己已经加载的类中查询是否此类已经加载,如果已经加载则直接返回原来已经加载的类。
当前classLoader的缓存中没有找到被加载的类的时候,委托父类加载器去加载,父类加载器采用同样的策略,首先查看自己的缓存,然后委托父类的父类去加载,一直到bootstrp ClassLoader。
当所有的父类加载器都没有加载的时候,再由当前的类加载器加载,并将其放入它自己的缓存中,以便下次有加载请求的时候直接返回。
类加载器工作实质是把编译后的类文件从硬盘加载到内存中,ClassLoader是一个顶层抽象类,构造函数源码如下:
//构造器
private ClassLoader(Void unused, ClassLoader parent) {
//这个是父加载器,以实现双亲委托
this.parent = parent;
if (ParallelLoaders.isRegistered(this.getClass())) {
parallelLockMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
package2certs = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
domains =Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<ProtectionDomain>());
assertionLock = new Object();
} else {
// no finer-grained lock; lock on the classloader instance
parallelLockMap = null;
package2certs = new Hashtable<>();
domains = new HashSet<>();
assertionLock = this;
}
}
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
this(checkCreateClassLoader(), parent);
}
protected ClassLoader() {
this(checkCreateClassLoader(), getSystemClassLoader());
}
接下来loadClass方法实现类加载,同时依托相关方法实现双亲委托,源码还是比较清晰的。值得注意的是loadClass用于类加载,在所有父加载器的缓存中均找不到这个类,且顶层的Bootstrap加载失败(加载成功返回该类Class对象,失败返回null)之后,会调用findClass方法(默认抛出异常),所以这就是我们在自己实现类加载器时不建议重写loadClass而是重写findClass的原因。代码如下:
//加载类
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
//自己的缓存中找不到
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
//委托给父加载器
if (parent != null) {
//父加载器同样的策略:先找自身缓存,找不到再向上委托
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
//缓存中没有,且当前加载器是Bootstrap加载器,直接使用它来加载
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);//这个方法加载类,成功返回该类Class对象,不成功返回null
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
//如果Bootstrap加载器加载后返回null,说明加载失败
if (c == null) {
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
//抛出异常
c = findClass(name);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
//查找类,查找自己的缓存
private native final Class<?> findLoadedClass0(String name);
protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) {
if (!checkName(name))
return null;
return findLoadedClass0(name);
}
//调用Bootstrap器去加载类,并返回该类的一个Class对象
private native Class<?> findBootstrapClass(String name);
private Class<?> findBootstrapClassOrNull(String name)
{
if (!checkName(name)) return null;
return findBootstrapClass(name);
}
private native Class<?> findBootstrapClass(String name);
接下来是defineClass方法,加载byte[ ]数组表示的类。通常我们实现自定义网络类加载器时可以重写findClass,然后在findClass方法中调用此方法以接收网络上传输的用字节数组表示的类。源码如下:
//定义类
//加载byte[]数组表示的类,并返回该类的Class对象,当需要加载的源文件不是.class时可以用这个方法
//封装native方法得到一系列重载
private native Class<?> defineClass0(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain pd);
private native Class<?> defineClass1(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain pd, String source);
private native Class<?> defineClass2(String name, java.nio.ByteBuffer b,
int off, int len, ProtectionDomain pd,
String source);
protected final Class<?> defineClass(byte[] b, int off, int len)throws ClassFormatError
{
return defineClass(null, b, off, len, null);
}
protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len)throws ClassFormatError
{
return defineClass(name, b, off, len, null);
}
protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)throws ClassFormatError
{
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class<?> c = defineClass1(name, b, off, len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, java.nio.ByteBuffer b,ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)throws ClassFormatError
{
int len = b.remaining();
if (!b.isDirect()) {
if (b.hasArray()) {
return defineClass(name, b.array(),
b.position() + b.arrayOffset(), len,
protectionDomain);
} else {
byte[] tb = new byte[len];
b.get(tb);
return defineClass(name, tb, 0, len, protectionDomain);
}
}
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class<?> c = defineClass2(name, b, b.position(), len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
还有一部分值得注意的是并行类加载器相关,详细见《深入理解OSGI》。AppClassLoader->ExtClassLoader->BootstrapClassLoader这种固定的加载顺序无法实现分模块热替换,OSGI的规范要求每个模块都有自己的类加载器,而模块之间的依赖关系,就形成了各个类加载器之间的委派关系。这种委派关系是动态的,所有的bundle之间的类加载形成了错综复杂的网状结构,不再是一沉不变的单一的树状结构。
jdk1.6之前直接同步整个loadClass方法使得网状加载关系会造成死锁:比如模块A 和模块B 互相引用了对方的包。这样在A加载B的包时,A在自己的类加载器的loadClass方法中,会最终调用到B的类加载器的loadClass方法。也就是说,A首先锁住自己的类加载器,然后再去申请B的类加载器的锁;当B加载A的包时,正好相反。这样,在多线程下,就会产生死锁。所以jdk1.8使用代码段的行级锁,使用一个ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>,将ClassName和一个Object关联,每次类加载时返回ClassName映射Object的引用作为监视器对象,源码如下:
//并行加载器,需要调用此方法在初始化是加载自身
@CallerSensitive
protected static boolean registerAsParallelCapable() {
Class<? extends ClassLoader> callerClass =
Reflection.getCallerClass().asSubclass(ClassLoader.class);
//注册自身
return ParallelLoaders.register(callerClass);
}
private static class ParallelLoaders {
private ParallelLoaders() {}
//使用set保存注册过的类加载器
private static final Set<Class<? extends ClassLoader>> loaderTypes =
Collections.newSetFromMap(
new WeakHashMap<Class<? extends ClassLoader>, Boolean>());
static {
synchronized (loaderTypes) { loaderTypes.add(ClassLoader.class); }
}
//注册
static boolean register(Class<? extends ClassLoader> c) {
synchronized (loaderTypes) {
if (loaderTypes.contains(c.getSuperclass())) {
//将加载器本身注册为并行
loaderTypes.add(c);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
//检查是否注册
static boolean isRegistered(Class<? extends ClassLoader> c) {
synchronized (loaderTypes) {
return loaderTypes.contains(c);
}
}
}
//并行监视器对象:jdk1.6之后出现的防止网状结构的加载链造成的死锁问题
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> parallelLockMap;
//获取监视器对象
protected Object getClassLoadingLock(String className) {
Object lock = this;
if (parallelLockMap != null) {
Object newLock = new Object();
//putIfAbsent检查kv是否已经映射,是返回k,否则建立映射并返回v
//这样将每个className都关联一个对象,加载这个类时返回这个对象作为锁对象
lock = parallelLockMap.putIfAbsent(className, newLock);
if (lock == null) {
lock = newLock;
}
}
//parallelLockMap为空:返回this(这与同步整个loadClass相等了,据说这是为了向前兼容)
//parallelLockMap不为空:直接返回
return lock;
}
14.Compiler
JIT编译器:
即时编译器,java程序一开始由解释器(Interpreter)来解释执行的,但当jvm发现某些代码运行频繁会将他们认定为热点代码(HotSpot Code),jvm将这些代码编译成本地机器码并进行各种层次的优化,JTI用于完成上述任务。
Interpreter解释器:
解释执行class文件
HotSpot虚拟机:
有两种JTI编译器c1和c2(client和server),早期是是一个编译器和一个解释器配合工作,jdk1.7后还采用了分层编译(c1和c2可同时工作)。
而Compiler类仅是jvm中JTI编译器的占位符,仅在存在编译器可用时本类才有效,源码如下:
public final class Compiler {
//禁止实例化
private Compiler() {}
private static native void initialize();
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
boolean loaded = false;
//访问系统属性,查看是否有JIT编译器
String jit = System.getProperty("java.compiler");
if ((jit != null)&&(!jit.equals("NONE"))&&(!jit.equals("")))
{
try {
//加载JTI编译器的本地库
System.loadLibrary(jit);
initialize();
loaded = true;//加载成功
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
//加载JTI编译器的本地库失败
System.err.println("Warning: JIT compiler \"" +jit + "\" not found. Will use interpreter.");
}
}
String info = System.getProperty("java.vm.info");
//加载成功或失败,分别修改系统属性
if (loaded) {
System.setProperty("java.vm.info", info + ", " + jit);//加载成功
} else {
System.setProperty("java.vm.info", info + ", nojit");//加载失败
}
return null;
}
});
}
//编译指定的类
public static native boolean compileClass(Class<?> clazz);
//编译名称与指定字符串匹配的所有类
public static native boolean compileClasses(String string);
//检查参数类型及其字段并执行一些文档化操作
public static native Object command(Object any);
//导致编译器恢复运行
public static native void enable();
//导致编译器停止运行
public static native void disable();
}
15.System
System类会在类加载时调用其静态的初始化方法,会初始化系统属性、流等,并给出一系列系统级别的方法包括currentTimeMillis()、arraycopy()、exit()、gc()、getenv()、runFinalization()等等。
类申明源码如下:
public final class System {
}
构造方法私有不允许外部实例化,源码如下:
//禁止实例化,方法均静态
private System() {
}
类加载时注册,会由jvm调用System的初始化方法,源码如下:
//方法注册
//注释说会jvm调用initializeSystemClass
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
//初始化System类
private static void initializeSystemClass() {
//初始化系统属性
props = new Properties();
initProperties(props);//native方法,由jvm调用
sun.misc.VM.saveAndRemoveProperties(props);
//得到行分隔符
lineSeparator = props.getProperty("line.separator");
sun.misc.Version.init();
//初始化流
FileInputStream fdIn = new FileInputStream(FileDescriptor.in);
FileOutputStream fdOut = new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out);
FileOutputStream fdErr = new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.err);
setIn0(new BufferedInputStream(fdIn));
setOut0(newPrintStream(fdOut, props.getProperty("sun.stdout.encoding")));
setErr0(newPrintStream(fdErr, props.getProperty("sun.stderr.encoding")));
loadLibrary("zip");
Terminator.setup();
sun.misc.VM.initializeOSEnvironment();
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
current.getThreadGroup().add(current);
setJavaLangAccess();
sun.misc.VM.booted();
}
private static void setJavaLangAccess() {
// Allow privileged classes outside of java.lang
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.setJavaLangAccess(new sun.misc.JavaLangAccess(){
public sun.reflect.ConstantPool getConstantPool(Class<?> klass) {
return klass.getConstantPool();
}
public boolean casAnnotationType(Class<?> klass, AnnotationType oldType, AnnotationType newType) {
return klass.casAnnotationType(oldType, newType);
}
public AnnotationType getAnnotationType(Class<?> klass) {
return klass.getAnnotationType();
}
public Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> getDeclaredAnnotationMap(Class<?> klass) {
return klass.getDeclaredAnnotationMap();
}
public byte[] getRawClassAnnotations(Class<?> klass) {
return klass.getRawAnnotations();
}
public byte[] getRawClassTypeAnnotations(Class<?> klass) {
return klass.getRawTypeAnnotations();
}
public byte[] getRawExecutableTypeAnnotations(Executable executable) {
return Class.getExecutableTypeAnnotationBytes(executable);
}
public <E extends Enum<E>>
E[] getEnumConstantsShared(Class<E> klass) {
return klass.getEnumConstantsShared();
}
public void blockedOn(Thread t, Interruptible b) {
t.blockedOn(b);
}
public void registerShutdownHook(int slot, boolean registerShutdownInProgress, Runnable hook) {
Shutdown.add(slot, registerShutdownInProgress, hook);
}
public int getStackTraceDepth(Throwable t) {
return t.getStackTraceDepth();
}
public StackTraceElement getStackTraceElement(Throwable t, int i) {
return t.getStackTraceElement(i);
}
public String newStringUnsafe(char[] chars) {
return new String(chars, true);
}
public Thread newThreadWithAcc(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) {
return new Thread(target, acc);
}
public void invokeFinalize(Object o) throws Throwable {
o.finalize();
}
});
}
给出流,源码如下:
//流
public final static InputStream in = null;
public final static PrintStream out = null;
public final static PrintStream err = null;
//设置流
public static void setIn(InputStream in) {
checkIO();
setIn0(in);
}
public static void setOut(PrintStream out) {
checkIO();
setOut0(out);
}
public static void setErr(PrintStream err) {
checkIO();
setErr0(err);
}
private static native void setIn0(InputStream in);
private static native void setOut0(PrintStream out);
private static native void setErr0(PrintStream err);
private static void checkIO() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setIO"));
}
}
private static PrintStream newPrintStream(FileOutputStream fos, String enc) {
if (enc != null) {
try {
return new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(fos, 128), true, enc);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {}
}
return new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(fos, 128), true);
}
会初始化一些系统属性,可以指定键名获取,源码如下:
//系统属性
private static Properties props;
//初始化所有系统属性
private static native Properties initProperties(Properties props);
//返回所有系统属性
public static Properties getProperties() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertiesAccess();
}
return props;
}
//返回指定系统属性
public static String getProperty(String key) {
checkKey(key);//检查属性名称
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertyAccess(key);
}
return props.getProperty(key);
}
public static String getProperty(String key, String def) {
checkKey(key);
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertyAccess(key);
}
return props.getProperty(key, def);
}
//设置所有系统属性
public static void setProperties(Properties props) {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertiesAccess();
}
if (props == null) {
props = new Properties();
initProperties(props);
}
System.props = props;
}
//设置指定系统属性
public static String setProperty(String key, String value) {
checkKey(key);
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new PropertyPermission(key,
SecurityConstants.PROPERTY_WRITE_ACTION));
}
return (String) props.setProperty(key, value);
}
//清除指定系统属性
public static String clearProperty(String key) {
checkKey(key);
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new PropertyPermission(key, "write"));
}
return (String) props.remove(key);
}
//检查属性名称
private static void checkKey(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key can't be null");
}
if (key.equals("")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key can't be empty");
}
}
还包括一些常用的系统方法,源码如下:
//返回操作系统时间的毫秒数
public static native long currentTimeMillis();
//拷贝数组
//Arrays.copyOf也是基于本方法实现
//数组克隆也可以实现拷贝,但是没有此方法效率高
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length);
//行分隔符
private static String lineSeparator;
public static String lineSeparator() {
return lineSeparator;
}
//退出虚拟机
//唯一终止程序却不走finally
public static void exit(int status) {
Runtime.getRuntime().exit(status);
}
//运行垃圾回收
public static void gc() {
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();
}
//与当前jvm唯一关联的控制台对象
private static volatile Console cons = null;
public static Console console() {
if (cons == null) {
synchronized (System.class) {
cons = sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaIOAccess().console();
}
}
return cons;
}
//获取指定的环境变量
public static String getenv(String name) {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("getenv."+name));
}
return ProcessEnvironment.getenv(name);
}
//获取所有的环境变量
public static java.util.Map<String,String> getenv() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("getenv.*"));
}
return ProcessEnvironment.getenv();
}
//返回对象hash码
public static native int identityHashCode(Object x);
//返回jvm的时间,纳秒
public static native long nanoTime();
//加载指定本机库
@CallerSensitive
public static void load(String filename) {
Runtime.getRuntime().load0(Reflection.getCallerClass(), filename);
}
//加载指定本机库
@CallerSensitive
public static void loadLibrary(String libname) {
Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary0(Reflection.getCallerClass(), libname);
}
//将库表名称映射到特定字符串
public static native String mapLibraryName(String libname);
//强制调用已经失去引用的对象的finalize方法
public static void runFinalization() {
Runtime.getRuntime().runFinalization();
}
public static Channel inheritedChannel() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().inheritedChannel();
}
16.Package
介绍
17.Void
void可以看做是一种基本数据类型,Void可以看做是其包装类。源码如下:
//Void是一个占位符类
public final class Void {
//可用于反射判断void类型的方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static final Class<Void> TYPE = (Class<Void>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("void");
//不可实例化
private Void() {}
}
给出一个测试类,代码如下:
public class testJDK {
//void方法
public void method1(){
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException{
//打印方法返回类型
System.out.println(testJDK.class.getMethod("method1").getReturnType());//void
//判断方法返回类型
System.out.println(testJDK.class.getMethod("method1").getReturnType()==Void.TYPE);//true
}
}