六. 智能合约
6.1 Golang版本的ChainCode的代码结构
-
链代码的包名的指定
// xxx.go package main // main不能改 -
必须要引入的包
// go get github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim import { // 客户端需要和Fabric框架通信 "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim" //通信的接口就需要shim pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer" //pb 起别名 peer=>客户端请求响应结果需要的包 } -
链码的书写要求
//自定义一个结构体 -类, 实现一些接口函数 type Test struct { //名字自定义 // 空着即可 } func (t *Test) Init(stub ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response { } func (t *Test) Invoke(stub ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response { } -
链码API查询
https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim // 其中必须实现的接口 type Chaincode interface { // Init is called during Instantiate transaction after the chaincode container // has been established for the first time, allowing the chaincode to // initialize its internal data Init(stub ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response // Invoke is called to update or query the ledger in a proposal transaction. // Updated state variables are not committed to the ledger until the // transaction is committed. Invoke(stub ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response }
6.2 shim包的核心方法
6.2.1 Response结构
type Response struct {
// A status code that should follow the HTTP status codes. 状态
Status int32 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=status,proto3" json:"status,omitempty"`
// A message associated with the response code.
Message string `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=message,proto3" json:"message,omitempty"`
// A payload that can be used to include metadata with this response.
// 状态描述
Payload []byte `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=payload,proto3" json:"payload,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{
} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
交易最后要结束时调用的函数:
6.2.2 Success
func Success(payload []byte) pb.Response // 返回值是pb.Response函数 payload是成功提示信息
//示例代码
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
return shim.Success([]byte("Success invoke!"))
}
6.2.3 Error
func Error(msg string) pb.Response //同理
//示例代码
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
return shim.Error("Error invoke!")
}
对链码做调试的时候调整链码中运行日志的级别(一般下调)方便调试, 调试结束后要发布了一般就调高:
6.2.4 LogLevel 设置日志级别

func LogLevel(levelString string) (LoggingLevel, error) //string => LoggingLevel
func SetLoggingLevel(level LoggingLevel) //LoggingLevel作为参数
//示例
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
lv,_ := shim.LogLevel("DEBUG")
shim.SetLoggingLevel(lv)
return shim.Success([]byte("Success invoke!"))
}
6.2.5 ChaincodeStubInterface接口中的核心方法
不管是Init还是Invoke参数都是这个接口实例
在shim包中有一个接口ChaincodeStubinterface,该接口提供了一组方法,可以非常方便的操作Fabric中的账本数据,其核心的方法大概分为四大类:系统管理、存储管理、交易管理、调动外部chaincode
1. 系统管理常用方法
GetFunctionAndParameters
// 赋值接收调用chaincode的客户端传递过来的参数
func GetFunctionAndParameters() (function string, params []string);
//示例
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
_, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters()
var a_param = args[0]
var a_param = args[1]
var a_param = args[2]
return shim.Success([]byte("Success invoke!"))
}
2. 存储管理相关的方法
PutState
//把客户端传递过来的数据保存到Fabric中,数据格式为键值对
func PutState(key string, value []byte) error;
//实例代码
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
//数据写入
stub.PutState("user1", []byte("putvalue"))
return shim.Success([]byte("Success invoke user1!"))
};
GetState
//从Fabric中取出数据
func GetState(key string) ([]byte, error);
//实例代码
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
//数据读取
keyvalue, err := stub.GetState("user1")
return shim.Success(keyvalue)
};
GetStateByRange
//根据key的访问查询相关的数据 根据key的范围取查询数据
func GetStateByRange(startKey, endKey string)(StateQueryIteratorInterface, error);
//示例代码
func (t *TestStudy) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response{
startKey := "startKey"
endKey := "endKey"
//范围查询,得到一个StateQueryIteratorInterface迭代器接口
keysIter, err := stub.GetStateByRange(startKey, endKey)
//关闭迭代器接口
defer keysIter.Close()
var keys []string
for keysIter.HasNext(){
//得到下一个键值对
response, iterErr := keysIter.Next()
if iterErr != nil{
return shim.Error("iterErr")
}
keys = append(keys, response.Key) //储存到数组中
}
//编码keys数组成json格式
jsonKeys, err := json.Marshal(keys)
if err != nil{
return shim.Error("toJsonErr")
}
//完成后向客户端传递
return shim.Success(jsonkeys)
};
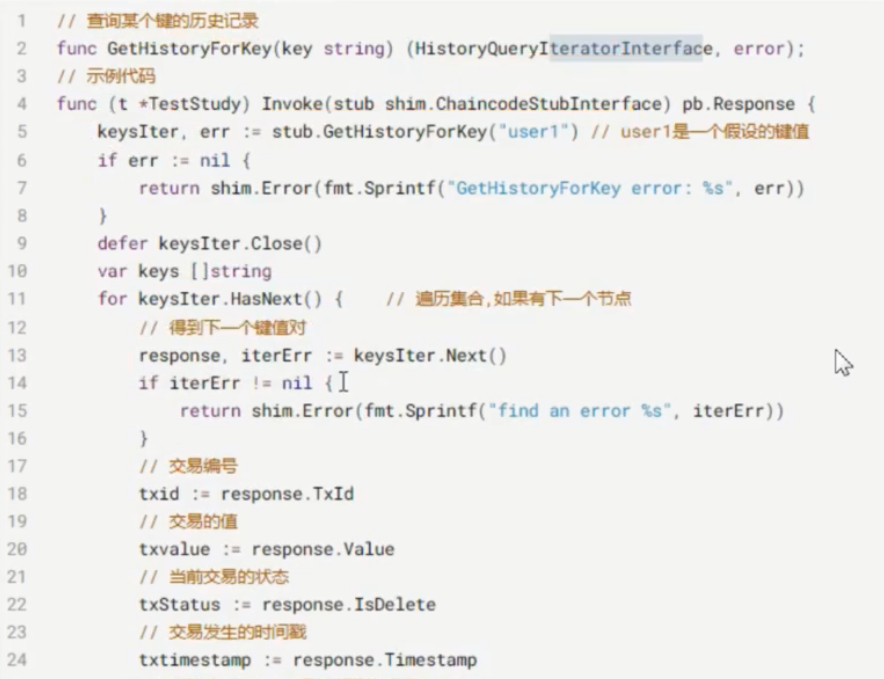
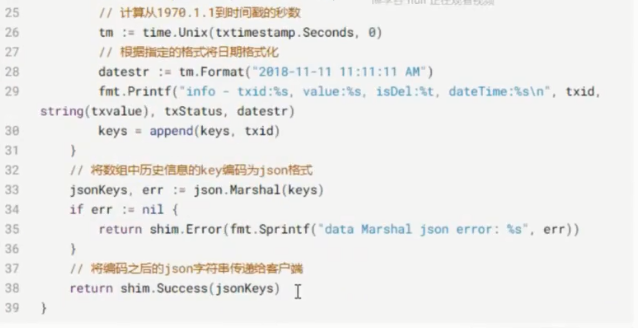
GetHistoryForKey
//根据key查询其历史记录
func (stub *ChaincodeStub) GetHistoryForKey(key string) (HistoryQueryIteratorInterface, error)
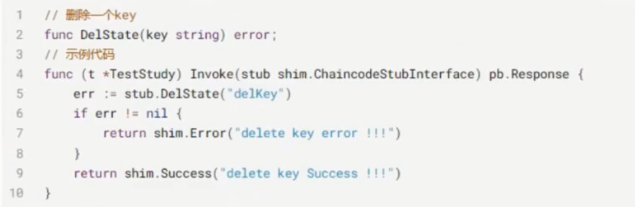
DelState
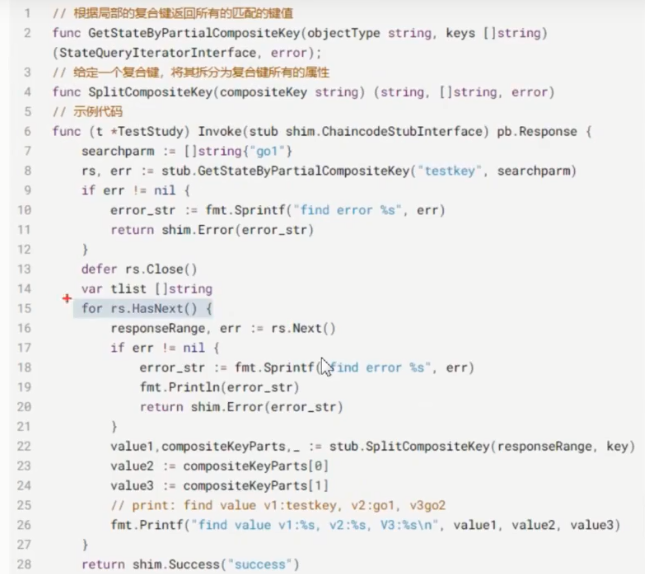
CreateCompositeKey

GetStateByPartialCompositeKey/SplitCompositeKey
3. 交易管理相关的方法
GetTxTimestamp

4. 调用其他chaincode的方法
InvokeChaincode

6.3 chaincode交易的背书策略(endorse)

6.3.1背书策略的指定/设置
背书策略在链码初始化的时候就需要指定:
peer chaincode instantiate -o orderer.xwj.com:7050 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/xwj.com/orderers/orderer.xwj.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.xwj.com-cert.pem -C xwjchannel -n testcc -l golang -v 1.0 -c '{"Args":["init","a","100","b","200"]}' -P "AND ('OrgGoMSP.member', 'OrgCppMSP.member')"
# -P "AND ('OrgGoMASP.member', 'OrgCppMSP.member')"
# AND表示这两个组织中的成员都需要参与,member表示组织中任一节点均可。如果是“OR”则表示任何一个组织成员都可以


背书规则只对chaincode中写入数据的操作进行校验,对于查询类操作不进行背书
Fabric的背书是发生在客户端的,需要进行相关的代码的编写才能完成整个背书的操作
6.3.2 背书策略的调用
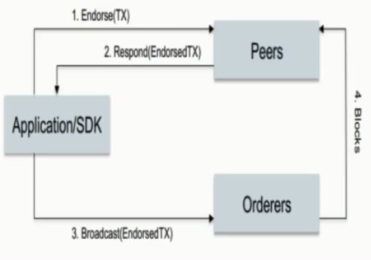
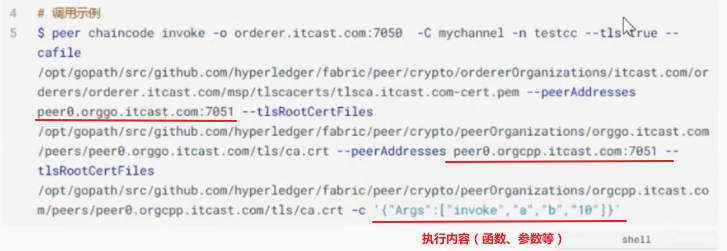
上面显示的invoke函数调用指定了两个peer背书节点(可以指定任意数量的节点),那么执行时就会先给这个两个节点执行,返回结果后再由orderer节点写进区块中。
七、链码
//chaincode/go/test1/test.go -》 对应链码名testcc
package main
import {
}
type Test struct{
}
func (t *Test)Init();
func (t *Test)Invoke(); //业务逻辑1
func main(){
}
//chaincode/go/test2/test1.go -》 对应链码名testcc1
package main
import {
}
type Test struct{
}
func (t *Test)Init();
func (t *Test)Invoke(); //业务逻辑2
func main(){
}
不同的链码名称对应这不同的Go文件
示例链码解析
调用的json:
- 初始化json:’{“Args”:[“init”,“a”,“100”,“b”,“200”]}’
- 调用的json:’{“Args”:[“invoke”,“a”,“b”,“10”]}’
官方示例fabric-samples/chaincode/chaincode_example02/go/chaincode_example02.go文件:
package main
//WARNING - this chaincode's ID is hard-coded in chaincode_example04 to illustrate one way of
//calling chaincode from a chaincode. If this example is modified, chaincode_example04.go has
//to be modified as well with the new ID of chaincode_example02.
//chaincode_example05 show's how chaincode ID can be passed in as a parameter instead of
//hard-coding.
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
)
// SimpleChaincode example simple Chaincode implementation
type SimpleChaincode struct {
}
func (t *SimpleChaincode) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
fmt.Println("ex02 Init")
_, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters() // 获取调用的函数参数, 返回值_就是Init,args是后接的参数
var A, B string // Entities
var Aval, Bval int // Asset holdings
var err error
if len(args) != 4 {
//判断参数个数
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 4")
}
// Initialize the chaincode
A = args[0]
Aval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[1])
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Expecting integer value for asset holding")
}
B = args[2]
Bval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[3])
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Expecting integer value for asset holding")
}
fmt.Printf("Aval = %d, Bval = %d\n", Aval, Bval)
// Write the state to the ledger 把数据写入账本中
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
err = stub.PutState(B, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Bval)))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
func (t *SimpleChaincode) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
//交易函数
fmt.Println("ex02 Invoke")
function, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters() //获取参数,function是第一个参数代表保存的函数名,这里是invoke
//“路由设置”
if function == "invoke" {
// Make payment of X units from A to B
return t.invoke(stub, args)
} else if function == "delete" {
// Deletes an entity from its state
return t.delete(stub, args)
} else if function == "query" {
// the old "Query" is now implemtned in invoke
return t.query(stub, args)
}
return shim.Error("Invalid invoke function name. Expecting \"invoke\" \"delete\" \"query\"")
}
// Transaction makes payment of X units from A to B
func (t *SimpleChaincode) invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
var A, B string // Entities
var Aval, Bval int // Asset holdings
var X int // Transaction value
var err error
if len(args) != 3 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 3")
}
A = args[0]
B = args[1]
// Get the state from the ledger
// TODO: will be nice to have a GetAllState call to ledger
Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A) //获取A的资产
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to get state")
}
if Avalbytes == nil {
return shim.Error("Entity not found")
}
Aval, _ = strconv.Atoi(string(Avalbytes))
Bvalbytes, err := stub.GetState(B) //获取B的资产
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to get state")
}
if Bvalbytes == nil {
return shim.Error("Entity not found")
}
Bval, _ = strconv.Atoi(string(Bvalbytes))
// Perform the execution
X, err = strconv.Atoi(args[2]) //获取转账金额
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Invalid transaction amount, expecting a integer value")
}
Aval = Aval - X // 转账
Bval = Bval + X
fmt.Printf("Aval = %d, Bval = %d\n", Aval, Bval)
// Write the state back to the ledger
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval))) //重新写入
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
err = stub.PutState(B, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Bval))) //重新写入
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// Deletes an entity from state
func (t *SimpleChaincode) delete(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) != 1 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 1")
}
A := args[0]
// Delete the key from the state in ledger
err := stub.DelState(A) //删除账本中的key,假删除,这个操作是被记录的
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to delete state")
}
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// query callback representing the query of a chaincode
func (t *SimpleChaincode) query(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
//查询函数
var A string // Entities
var err error
if len(args) != 1 {
return shim.Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting name of the person to query")
}
A = args[0]
// Get the state from the ledger
Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A) //取出值
if err != nil {
jsonResp := "{\"Error\":\"Failed to get state for " + A + "\"}"
return shim.Error(jsonResp)
}
if Avalbytes == nil {
jsonResp := "{\"Error\":\"Nil amount for " + A + "\"}"
return shim.Error(jsonResp)
}
jsonResp := "{\"Name\":\"" + A + "\",\"Amount\":\"" + string(Avalbytes) + "\"}" //拼接成字符串给客户端
fmt.Printf("Query Response:%s\n", jsonResp)
return shim.Success(Avalbytes)
}
func main() {
err := shim.Start(new(SimpleChaincode)) //写法固定 SimpleChaincode就是定义的空结构体
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error starting Simple chaincode: %s", err)
}
}
如果要自定义函数,函数的格式:(自定义函数一般都是在Invoke函数中被调用的)
func (t *自定义结构体)functionName (stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
xxxxx
}