Outline
- Focal stack.
- Confocal stereo.
- Lightfield.
- Plenoptic camera.
Focal Stack
capture images focused at multiple planes, and merge them into a single all in-focus image
analogous to what we did in HDR, focal stack instead of exposure stack
- How to merge a focal stack ?
- assign the weight: measure local sharpness(Laplacian operator + Gaussian blurring), just for example
- → \rightarrow → Depth from focus
- Problem: blurry.
- Can we use any extra information to get per-pixel depth? Confocal stereo!
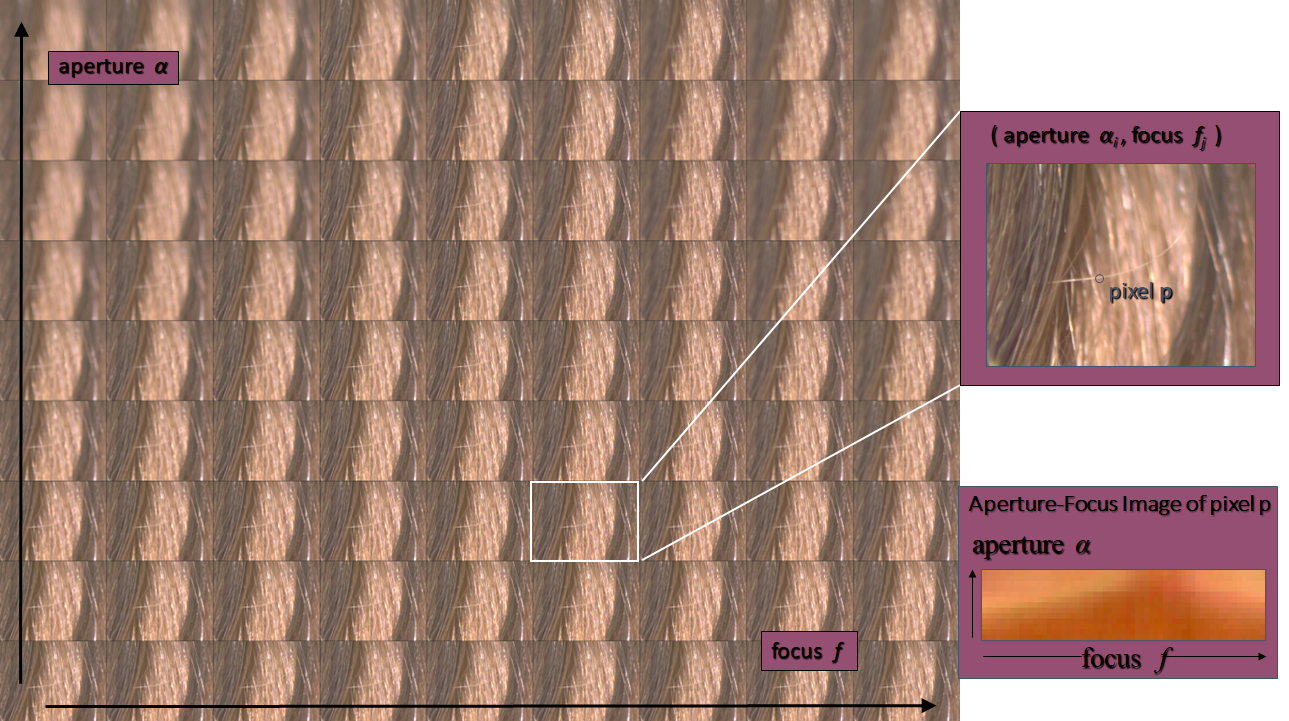
Confocal stereo
capture a 2D stack by varying both focus and aperture
Key idea: When a point is in focus, its color and intensity remain the same for all apertures. This property is called confocal constancy

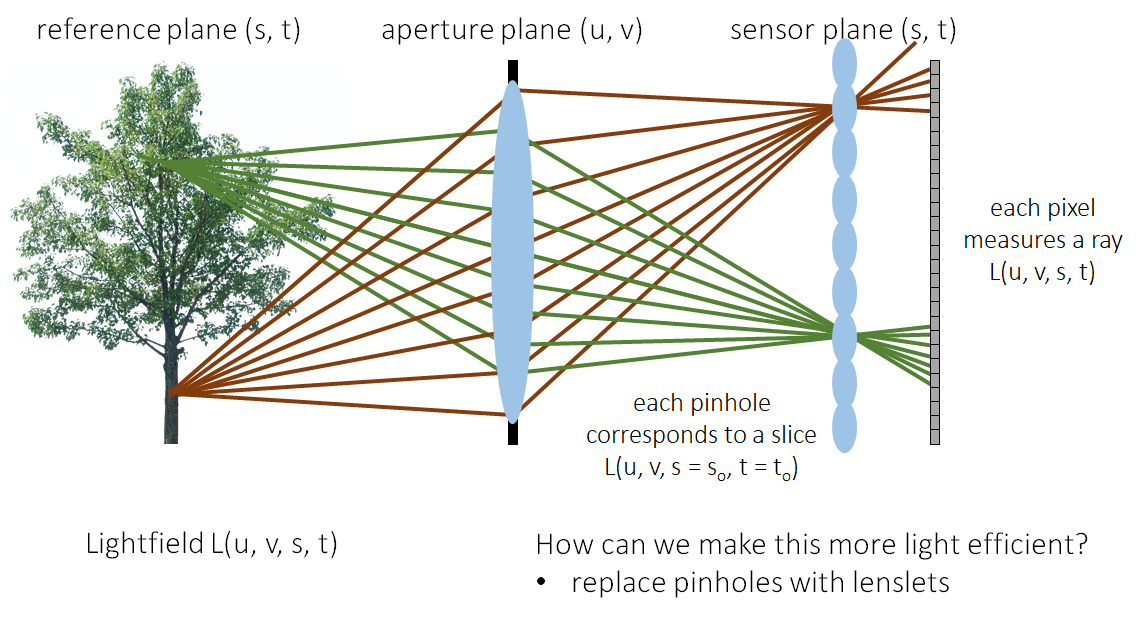
Lightfield: all rays in a scene
- What does L ( u = u 0 , v = v 0 , s , t ) L(u = u_0, v = v_0, s, t) L(u=u0,v=v0,s,t) look like?
- a pinhole image from a certain viewpoint
- What does L ( u , v , s = s 0 , t = t 0 ) L(u, v, s = s_0, t = t_0) L(u,v,s=s0,t=t0) look like?
- radiance emitted by a certain (in-focus) point at various directions


How to measure lightfield
Option 1: use a camera array
Option 2: take multiple images with one camera
Option 3: use a plenoptic camera
Plenoptic camera 全光相机

reference:
- CMU 15-463: lecture 12