题目描述:
夜空深处,闪亮的星星以星群的形式出现在人们眼中,形态万千。
一个星群是指一组非空的在水平,垂直或对角线方向相邻的星星的集合。
一个星群不能是一个更大星群的一部分。
星群可能是相似的。
如果两个星群的形状、包含星星的数目相同,那么无论它们的朝向如何,都认为它们是相似的。
通常星群可能有 88 种朝向,如下图所示:
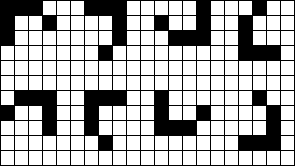
现在,我们用一个二维 0101 矩阵来表示夜空,如果一个位置上的数字是 11,那么说明这个位置上有一个星星,否则这个位置上的数字应该是 00。
给定一个夜空二维矩阵,请你将其中的所有星群用小写字母进行标记,标记时相似星群用同一字母,不相似星群用不同字母。
标注星群就是指将星群中所有的 11 替换为小写字母。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数 WW,表示矩阵宽度。
第二行包含一个整数 HH,表示矩阵高度。
接下来 HH 行,每行包含一个长度为 WW 的 0101 序列,用来描述整个夜空矩阵。
输出格式
输出标记完所有星群后的二维矩阵。
用小写字母标记星群的方法很多,我们将整个输出读取为一个字符串,能够使得这个字符串字典序最小的标记方式,就是我们想要的标记方式。
输出这个标记方式标出的最终二维矩阵。
数据范围
0≤W,H≤1000≤W,H≤100,
0≤0≤ 星群数量 ≤500≤500,
0≤0≤ 不相似星群数量 ≤26≤26,
1≤1≤ 星群中星星的数量 ≤160≤160
输入样例:
23
15
10001000000000010000000
01111100011111000101101
01000000010001000111111
00000000010101000101111
00000111010001000000000
00001001011111000000000
10000001000000000000000
00101000000111110010000
00001000000100010011111
00000001110101010100010
00000100110100010000000
00010001110111110000000
00100001110000000100000
00001000100001000100101
00000001110001000111000
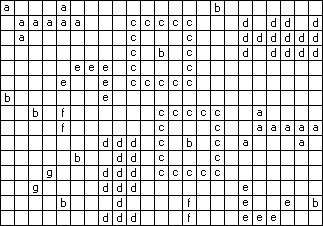
输出样例:
a000a0000000000b0000000
0aaaaa000ccccc000d0dd0d
0a0000000c000c000dddddd
000000000c0b0c000d0dddd
00000eee0c000c000000000
0000e00e0ccccc000000000
b000000e000000000000000
00b0f000000ccccc00a0000
0000f000000c000c00aaaaa
0000000ddd0c0b0c0a000a0
00000b00dd0c000c0000000
000g000ddd0ccccc0000000
00g0000ddd0000000e00000
0000b000d0000f000e00e0b
0000000ddd000f000eee000
样例解释
样例对应的星空图如下:
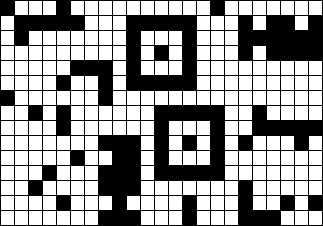
答案对应的标记后星空图如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int MAX = 109;
const double eps = 1e-6;
char g[MAX][MAX];
int n, m;
PII q[MAX * MAX]; // 记录连通块
int top;
double getdis(PII a, PII b)
{
double dx = a.x - b.x;
double dy = a.y - b.y;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
double get_hash()
{
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < top; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < top; j++)
{
sum += getdis(q[i], q[j]);
}
}
return sum;
}
char get_id(double h_num)
{
static double Hash[30];
static int id = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < id; i++)
{
if(fabs(Hash[i] - h_num) < eps)
return i + 'a';
}
Hash[id++] = h_num;
return id - 1 + 'a';
}
void dfs(int a, int b)
{
q[top++] = {a, b};
g[a][b] = '0';
for(int x = a - 1; x <= a + 1; x ++)
{
for(int y = b - 1; y <= b + 1; y++)
{
if(x == a && y == b)
continue;
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == '1')
dfs(x, y);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> g[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if(g[i][j] == '1')
{
top = 0;
dfs(i, j);
char c = get_id(get_hash());
for(int k = 0; k < top; k++)
g[q[k].x][q[k].y] = c;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << g[i] << endl;
return 0;
}