介绍
unordered_set 是一个封装哈希表的无序容器,其中每个元素仅可出现一次。
unordered_multiset 是一个封装哈希表的无序容器,其中每个元素可出现任意次。
unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 均定义于头文件 <unordered_set> 中,各自声明如下:
template<
class Key,
class Hash = std::hash<Key>,
class KeyEqual = std::equal_to<Key>,
class Allocator = std::allocator<Key>
> class unordered_set;
template<
class Key,
class Hash = std::hash<Key>,
class KeyEqual = std::equal_to<Key>,
class Allocator = std::allocator<Key>
> class unordered_multiset;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
到这里可能有一个问题:
set和unordered_set/multiset和unordered_set应该使用哪一种 (关联式容器和无序容器应该使用哪一种)?
考虑一个容器好坏,有一个标准是查看插入元素和查询元素的复杂度。
对于顺序容器,往往是插入复杂度高,查询复杂度低;又或者插入复杂度低,查询复杂度高,两者不能兼顾。
对于关联式容器,通过基于树结构,可以实现插入和查询都具有不太高的复杂度,而且其中元素是有序的。
对于无序容器,通过线性+链表,可以使得插入和查询复杂度更低,但是元素顺序会被打乱。从上面的比较可以看出,在选择关联式容器和无序容器时,如果题目不涉及有序问题,应优先使用无序容器。
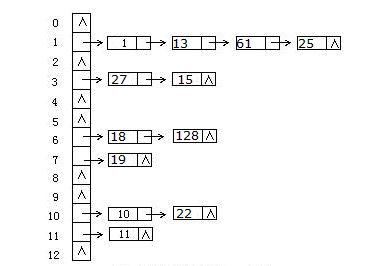
unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 都是基于哈希表实现的,而且冲突策略采用的是链地址法。示意图如下:
如图所示,容器每一行都是一条链,在unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 中称其为一个桶,所有冲突的元素放在同一个桶中。
我们知道哈希表实现中需要避免冲突,因为冲突过大会导致其退化为 线性表;同时如果最初分配空间过大,会造成极大的浪费。因此unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 容器中桶的个数会根据元素个数动态变化。
初始化
unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 基于哈希表实现,因此当创建一个容器时,需要指定 hash 函数 和 冲突查询时的 equal 函数。
对于基本数据类型,标准库提供了一个简单的 hash 和 equal 函数。但是对于复杂的数据类型,则需要我们自己指定。
指定 hash 和 equal 函数的方法如下:
- 以 类型参数 定义,需要定义一个 函数对象。
struct MyHash { // 这里假定 T = pair<int,int> // 函数参数需要 const,函数本身也必须是 const size_t operator()(const T& a) const { // hash<int>()(num) 是标准库定义的用于获取基本数据类型的 hash 函数 return hash<int>()(a.first) ^ hash<int>()(a.second); } };
struct MyEqual {
// 这里假定 T = pair<int,int>
// 函数参数需要 const,函数本身也必须是 const
bool operator()(const T& a,const T& b) const
{
// equal_to<int>()(num) 是标准库定义的用于判断基本数据类型是否相等的函数
return (equal_to<int>()(a.first,b.first) && (equal_to<int>()(a.second,b.second)));
}
};
unordered_set<pair<int,int>,MyHash,MyEqual> us;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
以下构造函数都不涉及定义 hash 和 equal 函数,均采用默认的 hash 和 equal 函数。
unordered_set<T> us; / unordered_multiset<T> ums;
创建一个空的unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器。unordered_set<int> us;- 1
unordered_set<T> us(bucket_count); / unordered_multiset<T> ums(bucket_count);
创建一个空的unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器,且该容器至少含有 bucket_count个桶。unordered_set<int> us(8); cout << us.bucket_count() << endl; // 输出结果为 11- 1
- 2
unordered_set<T> us({num1,num2,……}) / unordered_multiset<T> ums({num1,num2,……})
创建一个以初值列元素为初值的unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器。unordered_set<int> us({0,1,3,5});- 1
unordered_set<T> us = {num1,num2,……} / unordered_multiset<T> ums = {num1,num2,……}
创建一个以初值列元素为初值的unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器。unordered_set<int> us = {0,1,3,5};- 1
修改
unordered_set / unordered_multiset 容器禁止修改元素内容。
查询
empty()
判断unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器是否为空。size()
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中的元素个数。max_size()
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器大小的理论极限值,即当前内存情况下,允许创建unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中元素个数的最大可能值。count(key)
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中元素值为 key 的元素个数。find(key)
判断unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中是否存在元素值为 key 的元素,如果存在,则返回第一个符合条件的迭代器,否则返回end()。
比较
仅提供两个重载运算符 == 和 != 用于 unordered_set / unordered_multiset 容器的比较。
增加
insert(value)
向unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中插入一个元素 value。
对于unordered_set容器,返回值类型为pair<unordered_set<T>::iterator,bool>。unordered_set<T>::iterator指向插入元素位置的迭代器,bool表示插入是否成功。
对于unordered_multiset容器,返回指向插入位置的迭代器。unordered_set<int> us = {0,4,2}; us.insert(3);- 1
- 2
insert(begin_iterator,end_iterator);
向unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中插入迭代器区间 [begin_iterator,end_iterator) 内的所有元素。
对于unordered_set容器而言,可能存在元素插入失败。unordered_set<int> us1 = {2,4,5}; unordered_set<int> us = {1,2,4}; us.insert(us1.begin(),++us1.begin()); // us 容器迭代元素依次为:5,4,2,1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
删除
clear()
清空unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器。erase(pos_iterator)
移除unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器指定位置 pos_iterator 处元素。unordered_set<int> us = {0,2,3,4}; us.erase(us.begin()); // us 容器迭代元素依次为:3,2,0 // 仅仅通过代码,是无法得知到底移除的是哪一个元素,因为容器内部元素是无序的。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
erase(begin_iterator,end_iterator)
移除unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器指定迭代器区间 [begin_iterator,end_iterator) 内的所有元素。unordered_set<int> us = {1,3,10,5,2,99,8}; us.erase(us.begin(),++(++us.begin())); // us 容器迭代元素依次为:2,5,10,3,1- 1
- 2
- 3
erase(key)
移除unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器内元素值等于 key 的所有元素,返回移除元素数目。
其他操作
equal_range(key)
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中元素值等于 key 的迭代器区间。
其返回值为pair<iterator,iterator>,iterator指向第一个元素值等于 key 的迭代器位置,第二个iterator指向最后一个元素值等于 key 迭代器位置的下一个位置。bucket_count()
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器中桶的个数。bucket_size(index)
返回unordered_set / unordered_multiset容器特定桶中元素数目。
</div><div><div></div></div>
<link href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/mdeditor/markdown_views-ff98e99283.css" rel="stylesheet">
</div>
介绍
unordered_set 是一个封装哈希表的无序容器,其中每个元素仅可出现一次。
unordered_multiset 是一个封装哈希表的无序容器,其中每个元素可出现任意次。
unordered_set 和 unordered_multiset 均定义于头文件 <unordered_set> 中,各自声明如下:
template<
class Key,
class Hash = std::hash<Key>,
class KeyEqual = std::equal_to<Key>,
class Allocator = std::allocator<Key>
> class unordered_set;