应用见
SpringBoot:详解@EnableAsync + @Async 实现共享线程池
学习注解,从注释和源码入手
注释
部分关键注释,我自己标注了一些中文注释便于理解:
- 作用:启用Spring的异步方法执行功能
/**
* Enables Spring's asynchronous method execution capability, similar to functionality
* found in Spring's {@code <task:*>} XML namespace.
* <p>
* -- 与@Configuration注解配合使用,在Spring应用程序上下文中实现注解驱动的异步处理功能
* <p>To be used together with @{@link Configuration Configuration} classes as follows,
* enabling annotation-driven async processing for an entire Spring application context:
* <p>
- 配置类中使用方式如下
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @EnableAsync
* public class AppConfig {
*
* }</pre>
* <p>
- 开发人员可以在方法上标注@Async注解,使得该方法加入线程池运行
* {
@code MyAsyncBean} is a user-defined type with one or more methods annotated with
* either Spring's {
@code @Async} annotation, the EJB 3.1 {
@code @javax.ejb.Asynchronous}
* annotation, or any custom annotation specified via the {
@link #annotation} attribute.
* The aspect is added transparently for any registered bean, for instance via this
* configuration:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class AnotherAppConfig {
*
* @;Bean
* public MyAsyncBean asyncBean() {
* return new MyAsyncBean();
* }
* }</pre>
* <p>
- 默认情况下,Spring搜索一个线程池定义
* <p>By default, Spring will be searching for an associated thread pool definition:
* either a unique {
@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor} bean in the context,
* or an {
@link java.util.concurrent.Executor} bean named "taskExecutor" otherwise. If
* neither of the two is resolvable, a {
@link org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor}
* will be used to process async method invocations. Besides, annotated methods having a
* {
@code void} return type cannot transmit any exception back to the caller. By default,
* such uncaught exceptions are only logged.
* <p>
- 开发者要实现AsyncConfigurer接口,自己提供线程池和异常处理器
实际开发中也可以不实现此接口,在配置类中的方法(如命名方法为asyncServiceExecutor)加上@Bean注解,在调用的方法上使用@Async(“asyncServiceExecutor”),来指定运行此方法的线程池
* <p>To customize all this, implement {
@link AsyncConfigurer} and provide:
* <ul>
* <li>your own {
@link java.util.concurrent.Executor Executor} through the
* {
@link AsyncConfigurer#getAsyncExecutor getAsyncExecutor()} method, and</li>
* <li>your own {
@link org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler
* AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} through the {
@link AsyncConfigurer#getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler
* getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler()}
* method.</li>
* </ul>
- 讲了依赖与延迟加载
* <p><b>NOTE: {
@link AsyncConfigurer} configuration classes get initialized early
* in the application context bootstrap. If you need any dependencies on other beans
* there, make sure to declare them 'lazy' as far as possible in order to let them
* go through other post-processors as well.</b>
* <p>
- 代码示例
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @EnableAsync
* public class AppConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
*
* @Override
* public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
* ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
* executor.setCorePoolSize(7);
* executor.setMaxPoolSize(42);
* executor.setQueueCapacity(11);
* executor.setThreadNamePrefix("MyExecutor-");
* executor.initialize();
* return executor;
* }
*
* @Override
* public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
* return new MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler();
* }
* }</pre>
*/
源码
注解源码
- 注解自身还有四个注解,包括三个基本注解和一个导入注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) 表示可修饰的范围:接口、类、枚举
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)表示保留的时间范围:运行时
@Documented表示可以配合javadoc
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)导入了AsyncConfigurationSelector类,与mode()方法有关
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAsync {
- 监测 @async 注解的方法
/**
* Indicate the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class
* or method level.
* <p>By default, both Spring's @{@link Async} annotation and the EJB 3.1
* {@code @javax.ejb.Asynchronous} annotation will be detected.
* <p>This attribute exists so that developers can provide their own
* custom annotation type to indicate that a method (or all methods of
* a given class) should be invoked asynchronously.
*/
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
- 代理方式设置,默认false 只针对@Async注解的方法,如果true将在所有Spring管理的bean上生效
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies.
* <p><strong>Applicable only if the {@link #mode} is set to {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}</strong>.
* <p>The default is {@code false}.
* <p>Note that setting this attribute to {@code true} will affect <em>all</em>
* Spring-managed beans requiring proxying, not just those marked with {@code @Async}.
* For example, other beans marked with Spring's {@code @Transactional} annotation
* will be upgraded to subclass proxying at the same time. This approach has no
* negative impact in practice unless one is explicitly expecting one type of proxy
* vs. another — for example, in tests.
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
- 指定异步能生效的模式,默认为Porxy(JDK proxy-based advice.),另一种是ASPECTJ(AspectJ weaving-based advice)
/**
* Indicate how async advice should be applied.
* <p><b>The default is {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}.</b>
* Please note that proxy mode allows for interception of calls through the proxy
* only. Local calls within the same class cannot get intercepted that way; an
* {@link Async} annotation on such a method within a local call will be ignored
* since Spring's interceptor does not even kick in for such a runtime scenario.
* For a more advanced mode of interception, consider switching this to
* {@link AdviceMode#ASPECTJ}.
*/
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
- 处理的优先级顺序
/**
* Indicate the order in which the {@link AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* should be applied.
* <p>The default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE} in order to run
* after all other post-processors, so that it can add an advisor to
* existing proxies rather than double-proxy.
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
实现源码
点进@EnableAsync的@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
AsyncConfigurationSelector中,selectImports方法在spring容器扫描bean的时候,根据通知模型判断要导入哪一个类
/**
* Returns {@link ProxyAsyncConfiguration} or {@code AspectJAsyncConfiguration}
* for {@code PROXY} and {@code ASPECTJ} values of {@link EnableAsync#mode()},
* respectively.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {
ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {
ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
默认是proxy
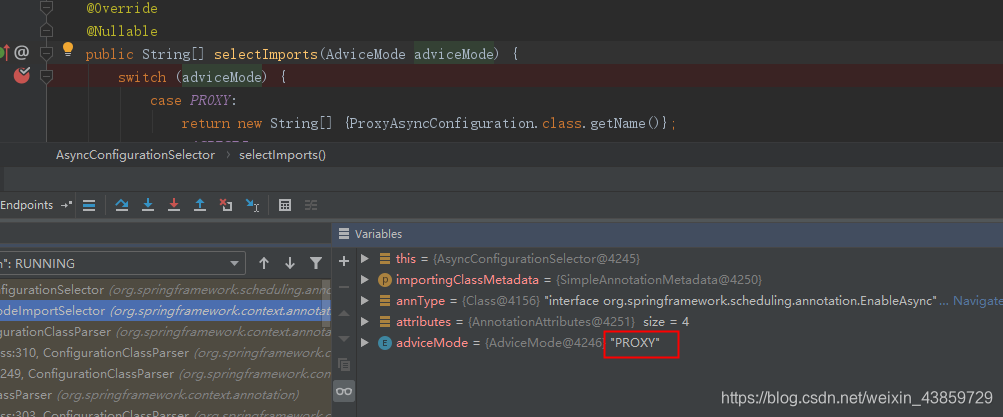
返回的类为ProxyAsyncConfiguration
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor() {
Assert.notNull(this.enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected");
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
bpp.configure(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
Class<? extends Annotation> customAsyncAnnotation = this.enableAsync.getClass("annotation");
if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation")) {
bpp.setAsyncAnnotationType(customAsyncAnnotation);
}
bpp.setProxyTargetClass(this.enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass"));
bpp.setOrder(this.enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return bpp;
}
}
这个类是一个配置类,实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,它向spring容器中添加了一个AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的bean后置处理器,其父类AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor中定义了处理器
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.advisor == null || bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
// 类中加@Async的bean会走到这个if里,添加advisor
if (bean instanceof Advised) {
Advised advised = (Advised) bean;
if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) {
// Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain...
if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor);
}
else {
advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
}
return bean;
}
}
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory);
}
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// No proxy needed.
return bean;
}
可以看出前置处理器未做处理,后置处理器对添加了@Async的bean进行了addAdvisor,后续使用bean时,debug看一下,该bean中会有响应的advisor
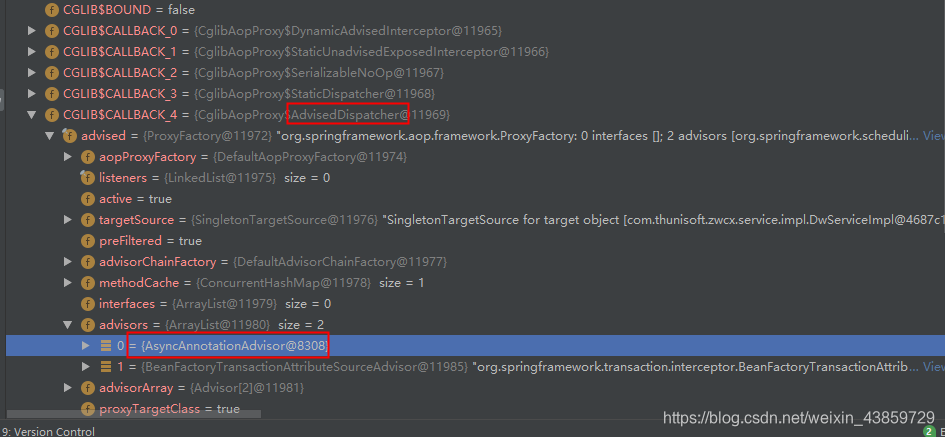
总结
@EnableAsync通过向Spring引入后置处理器AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,在bean的创建过程中对bean进行advisor增强,对@Async标识的bean增强异步功能