1.环形列表
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:40.2 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了21.14%的用户
*/
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return false;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast==slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
2.环形链表 II
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:40 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了36.04%的用户
*/
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast==slow) break;
}
if (slow!=fast) return null;
slow = head;
while (slow!=fast){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
3.相交链表
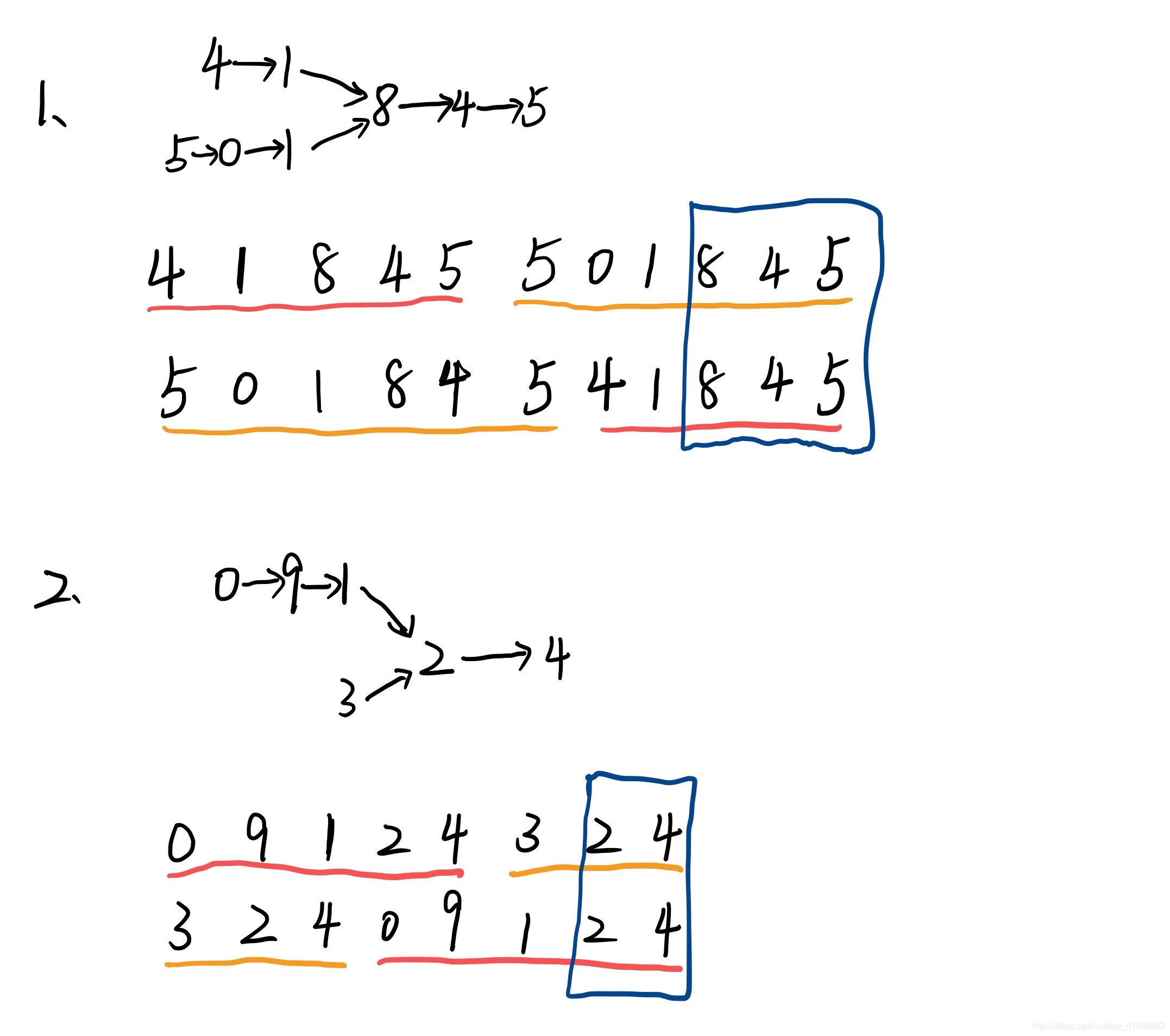
/*
执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:42.3 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了97.90%的用户
*/
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA==null||headB==null) return null;
ListNode A = headA;
ListNode B = headB;
while (A!=B){
A = A!=null?A.next:headB;
B = B!=null?B.next:headA;
}
return A;
}
4.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:38.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了27.98%的用户
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head==null||(head.next==null&&n == 1)) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = head;
// 让快指针先走n步
while (n>0){
fast = fast.next;
n--;
}
// 当fast=null时,说明移除的是第一个元素
if (fast == null){
head = head.next;
}
// 当fast=null时,slow指向被删除的值
while (fast!=null){
fast = fast.next;
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
pre.next = slow.next;
return head;
}
5.反转链表
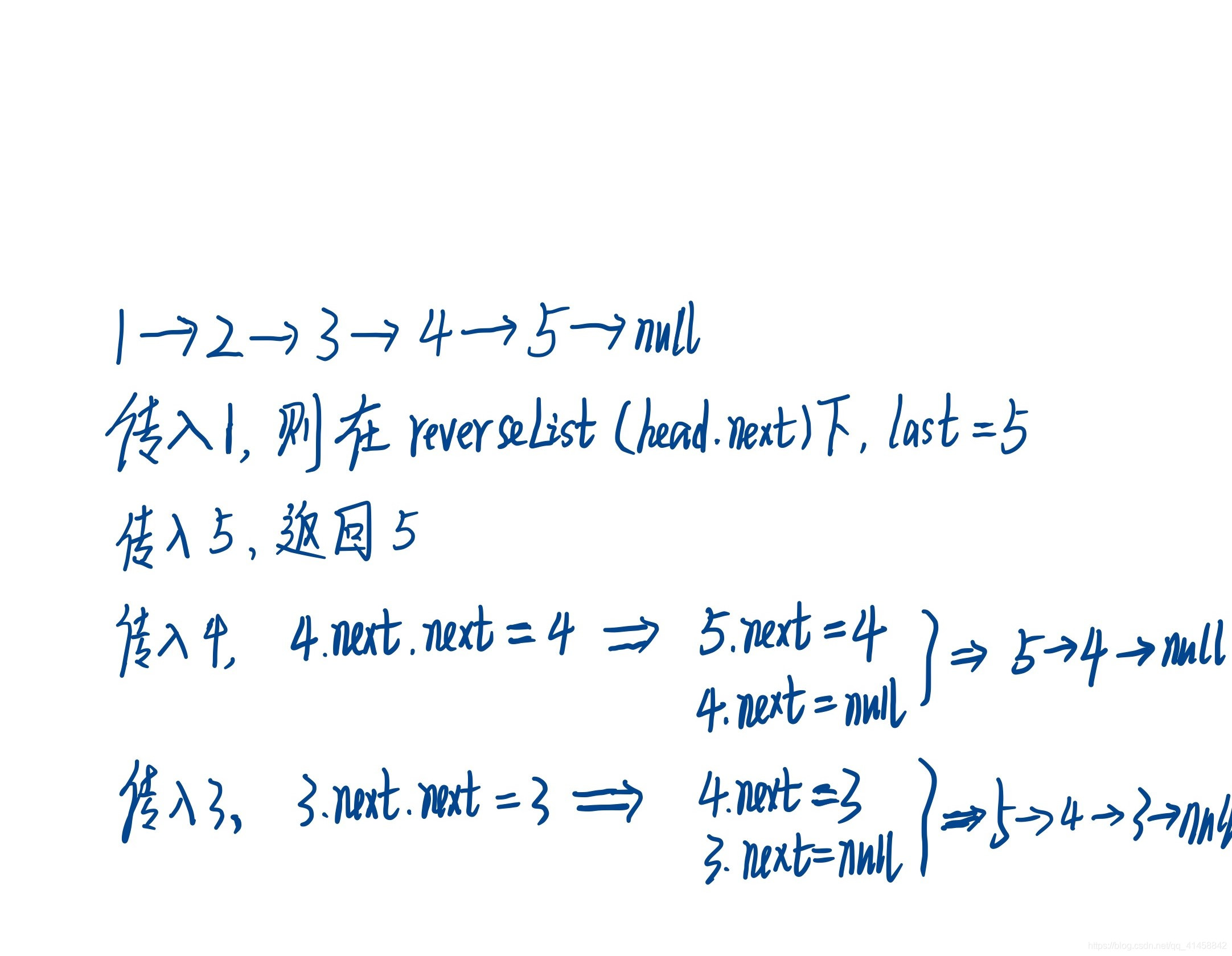
/*
递归做法,图解如上图
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:39.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了68.79%的用户
*/
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return head;
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
/*
迭代做法
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:40 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了9.74%的用户
*/
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp!=null){
ListNode n = temp.next;
temp.next = pre;
pre = temp;
temp = n;
}
return pre;
}
6.反转链表 II
/*
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:37.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了95.79%的用户
*/
class Solution {
//保存第n+1个结点
ListNode note = null;
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if(m==1) return reverseN(head, n);
//找到需要反转的第一个结点
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next,m-1,n-1);
return head;
}
private ListNode reverseN(ListNode head, int n){
if (n==1) {
note = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverseN(head.next, n-1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = note;
return last;
}
}
7.移除链表元素
/*
执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了99.71%的用户
内存消耗:40.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了71.74%的用户
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp!=null){
ListNode n = temp.next;
//当temp为选定的目标值时
if(temp.val == val){
//当链表的第一个元素为所选定的目标值时
if(pre==null){
head = n;
temp = n;
}else{
pre.next = n;
temp = n;
}
}
//当temp不是该目标值,继续往下走
else{
pre = temp;
temp = n;
}
}
return head;
}
8.奇偶链表
9.回文链表
/*
1.找到中间位 2.从中间位开始逆转 3.比较
执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了99.72%的用户
内存消耗:43.3 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了38.26%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return true;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = head;
//当链表的个数为奇数时,slow最终停在中点处
//为偶数时,slow最终停在左边中点处
while (fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = reverse(slow.next);
while (slow.next!=null){
if (head.val!=slow.next.val){
return false;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head.next==null) return head;
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
10.合并两个有序链表
/*
执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了63.12%的用户
内存消耗:39.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了24.87%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode ll = new ListNode(0);
ListNode l3 = ll;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val<=l2.val){
l3.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
else{
l3.next = l2;
l2= l2.next;
}
l3 = l3.next;
}
l3.next = l1==null?l2:l1;
return ll.next;
}
}
11.两数相加
/*
看似简单,实则需要考虑进位问题,在将多次尝试将字符串转化成数字结果溢出之后,借鉴网上代码。
执行用时:2 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了99.89%的用户
内存消耗:40 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了24.93%的用户
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head1 = l1;
ListNode head2 = l2;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode head3 = newHead;
// 进位标志
boolean carry = false;
while (head1 != null || head2 != null) {
// 获取对应位置的值然后相加
int x = (head1 != null) ? head1.val : 0;
int y = (head2 != null) ? head2.val : 0;
int sum = carry ? (x + y + 1) : (x + y);
// 处理进位
if (sum >= 10){
sum -= 10;
carry = true;
} else {
carry = false;
}
// 新增节点
head3.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
head3 = head3.next;
if (head1 != null) head1 = head1.next;
if (head2 != null) head2 = head2.next;
}
if (carry) {
head3.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return newHead.next;
}
}