为什么要语义化?
-
代码结构: 使页面没有css的情况下,也能够呈现出很好的内容结构
-
有利于SEO: 爬虫依赖标签来确定关键字的权重,因此可以和搜索引擎建立良好的沟通,帮助爬虫抓取更多的有效信息
-
提升用户体验: 例如title、alt可以用于解释名称或者解释图片信息,以及label标签的灵活运用。
-
便于团队开发和维护: 语义化使得代码更具有可读性,让其他开发人员更加理解你的html结构,减少差异化
-
方便其他设备解析: 如屏幕阅读器、盲人阅读器、移动设备等,以有意义的方式来渲染网页
HTML5常用的语义元素
HTML5提供了新的语义元素来定义网页的不同部分,它们被称为“切片元素”,如图所示
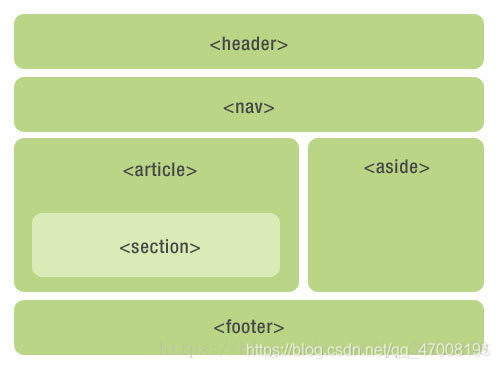
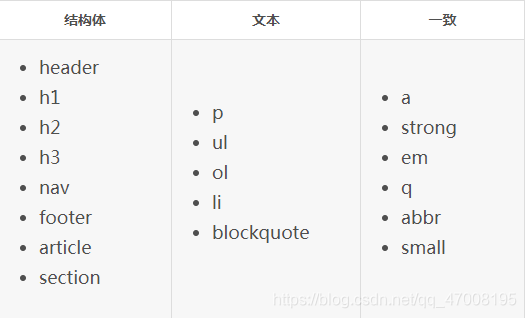
大约有100多个HTML语义元素可供选择,以下是常用的语义元素
h1-h6元素
定义页面的标题,h1元素具有最高等级,h6元素具有最低的等级
<h1>top level heading</h1>
<section>
<h2>2nd level heading</h2>
<h3>3nd level heading</h3>
<h4>4th level heading</h4>
<h5>5th level heading</h5>
<h6>6th level heading</h6>
</section>
header元素
用于定义页面的介绍展示区域,通常包括网站logo、主导航、全站链接以及搜索框。也适合对页面内部一组介绍性或导航性内容进行标记。
<header>
<h1>HTML Reference</h1>
<nav>
<a>Home</a>
<a>About</a>
<a>Contact</a>
</nav>
</header>
nav元素
定义页面的导航链接部分区域,不是所有的链接都需要包含在
<nav>
<a>Home</a>
<a>About</a>
<a>Contact</a>
</nav>
main元素
定义页面的主要内容,一个页面只能使用一次。如果是web应用,则包围其主要功能。
<main>
<h1>My blog test</h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec viverra nec nulla vitae mollis.</p>
<p>etc.</p>
</main>
article元素
定义页面独立的内容,它可以有自己的header、footer、sections等,专注于单个主题的博客文章,报纸文章或网页文章。article可以嵌套article,只要里面的article与外面的是部分与整体的关系。
<article>
<header>
<h3>
<a href="">My blog post</a>
</h3>
</header>
<section>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec viverra nec nulla vitae mollis.
</p>
</section>
<footer>
<small>
Posted on <time datetime="2017-04-29T19:00">Apr 29</time> in <a href="">Code</a>
</small>
</footer>
</article>
section元素
元素用于标记文档的各个部分,例如长表单文章的章节或主要部分。
<section>
<h2>Section title</h2>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec viverra nec nulla vitae mollis.</p>
</section>
aside元素
定义与主要内容相关的内容块。通常显示为侧边栏。
<aside>
<h3>About the author</h3>
<p>Frontend Designer from Bordeaux, currently working for Improbable in sunny London.</p>
</aside>
footer元素
定义文档的底部区域,通常包含文档的作者,著作权信息,链接的使用条款,联系信息等
<footer>
COPYRIGHT@dingFY_Demi
</footer>
small元素
为较不重要的内容定义小字体。如果被包围的字体已经是字体模型所支持的最小字号,那么 标签将不起任何作用。
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec viverra nec nulla vitae mollis.</p>
<small>Posted on <time datetime="2017-04-29T19:00">Apr 29</time> in <a href="/category/code">Code</a></small>
strong元素
把文本定义为语气更强的强调的内容,以表示内容的重要性。
HTML should only be used to write <strong>content</strong>, and keep CSS for <strong>styling</strong> the web page.
em元素
标记内容着重点(大量用于提升段落文本语义),通常呈现为斜体文字。
HTML should only be used to write <em>content</em>, and keep CSS for <em>styling</em> the web page.
blockquote元素
定义块引用,浏览器会在 blockquote 元素前后添加换行,并增加外边距。cite属性可用来规定引用的来源
<blockquote cite="https://en.wikiquote.org/wiki/Marie_Curie">
Here is a long quotation here is a long quotation here is a long quotation
here is a long quotation here is a long quotation here is a long quotation
here is a long quotation here is a long quotation here is a long quotation.
</blockquote>
abbr元素
解释缩写词。使用title属性可提供全称,只在第一次出现时使用就ok。
The <abbr title="People's Republic of China">PRC</abbr> was founded in 1949.