MySQL,用了好多年了吧,在你印象里是不是一直都是四平八稳,做为一个基础组件,也不期待啥了。
如果说想线下调度,集成测试,想用一个内存数据库,你可能会说那H2, Derby吧,不都可以嘛。
但差别是你在自己线下时跑了多少不说,但不同的数据库,不同的特性,可能有些地方无法真正还原线上。为什么不安装一个?费事,哈哈。
今天咱们介绍的这位,可以理解为嵌入MySQL,免安装。不同的测试时还可以切换不同的版本,Cool。
使用起来也不费劲,加个 Maven 依赖就行,分分钟的事儿。
就是它:
<dependency> <groupId>com.wix</groupId> <artifactId>wix-embedded-mysql</artifactId> <version>x.y.z</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
代码也简单,直接定义你需要的版本,数据库信息,把要初始化的SQL 给它,走起。
MysqldConfig config = aMysqldConfig(v5_6_23) //这里是版本
.withCharset(UTF8)
.withPort(2215)
.withUser("user1", "pwd2")
.withTimeZone("Europe/Vilnius")
.withTimeout(2, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.withServerVariable("max_connect_errors", 666)
.build();
EmbeddedMysql mysqld = anEmbeddedMysql(config)
.addSchema("aschema", ScriptResolver.classPathScript("db/001_init.sql"))
.start();
//do work
mysqld.stop(); //optional, as there is a shutdown hook
这有啥优势:
测试可以跑在和生产环境基本一致的环境,同样的版本,同样的编码和配置,database/schema/user settings 等等
比安装一个更容易,想切换版本,改配置也更轻松;
本地每个项目可以使用不同的版本,不同的配置,啥都不用担心;
对于MySQL的多个版本支持 - 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 8.0;
多种平台和环境都支持。
原理
这背后是怎么实现的呢?
咱们是「刨根究底」公众号,一起来看看。
上面代码配置之后的 start ,到底 start 了啥?
咱们看下面这几小段代码:
protected EmbeddedMysql(
final MysqldConfig mysqldConfig,
final DownloadConfig downloadConfig) {
this.config = mysqldConfig;
IRuntimeConfig runtimeConfig = new RuntimeConfigBuilder().defaults(mysqldConfig, downloadConfig).build();
MysqldStarter mysqldStarter = new MysqldStarter(runtimeConfig);
localRepository.lock();
try {
this.executable = mysqldStarter.prepare(mysqldConfig);
} finally {
localRepository.unlock();
}
try {
executable.start();
getClient(SCHEMA, mysqldConfig.getCharset()).executeCommands(
format("CREATE USER '%s'@'%%' IDENTIFIED BY '%s';", mysqldConfig.getUsername(), mysqldConfig.getPassword()));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
protected MysqldProcess start(
final Distribution distribution,
final MysqldConfig config,
final IRuntimeConfig runtime) throws IOException {
logger.info("Preparing mysqld for startup");
Setup.apply(config, executable, runtime);
logger.info("Starting MysqldProcess");
return new MysqldProcess(distribution, config, runtime, this);
}
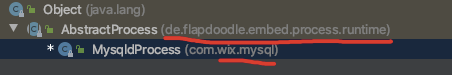
其实这背后依赖了一个叫embed.process的开源项目,
public AbstractProcess(Distribution distribution, T config, IRuntimeConfig runtimeConfig, E executable)
throws IOException {
this.config = config;
this.runtimeConfig = runtimeConfig;
this.executable = executable;
this.distribution = distribution;
// pid file needs to be set before ProcessBuilder is called
this.pidFile = pidFile(this.executable.getFile().executable());
ProcessOutput outputConfig = runtimeConfig.getProcessOutput();
// Refactor me - to much things done in this try/catch
String nextCall="";
try {
nextCall="onBeforeProcess()";
onBeforeProcess(runtimeConfig);
nextCall="newProcessBuilder()";
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = ProcessControl.newProcessBuilder(
runtimeConfig.getCommandLinePostProcessor().process(distribution,
getCommandLine(distribution, config, this.executable.getFile())),
getEnvironment(distribution, config, this.executable.getFile()), true);
nextCall="onBeforeProcessStart()";
onBeforeProcessStart(processBuilder, config, runtimeConfig);
nextCall="start()";
process = ProcessControl.start(config.supportConfig(), processBuilder);
nextCall="writePidFile()";
if (process.getPid() != null) {
writePidFile(pidFile, process.getPid());
}
nextCall="addShutdownHook()";
if (runtimeConfig.isDaemonProcess() && !executable.isRegisteredJobKiller()) {
ProcessControl.addShutdownHook(new JobKiller());
registeredJobKiller = true;
}
nextCall="onAfterProcessStart()";
onAfterProcessStart(process, runtimeConfig);
} catch (IOException iox) {
stop();
throw iox;
}
}
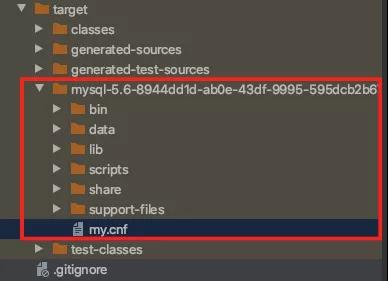
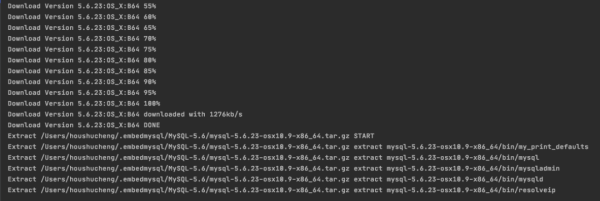
它又操作了什么呢?从名字你也猜到了,它是直接操作进程的,实际在运行时,会下载一个MySQL,然后通过脚本启停。
初次启动的时候,会直接下载
有了这些,在测试的时候就可以和生产环境一样,启动时加载初始化SQL脚本,开始你的工作了。
github地址:https://github.com/wix/wix-embedded-mysql
本文转载自微信公众号「Tomcat那些事儿」,可以通过以下二维码关注。转载本文请联系Tomcat那些事儿公众号。
【编辑推荐】
【责任编辑:武晓燕 TEL:(010)68476606】