参考书籍:《java并发编程艺术》
线程池的执行顺序
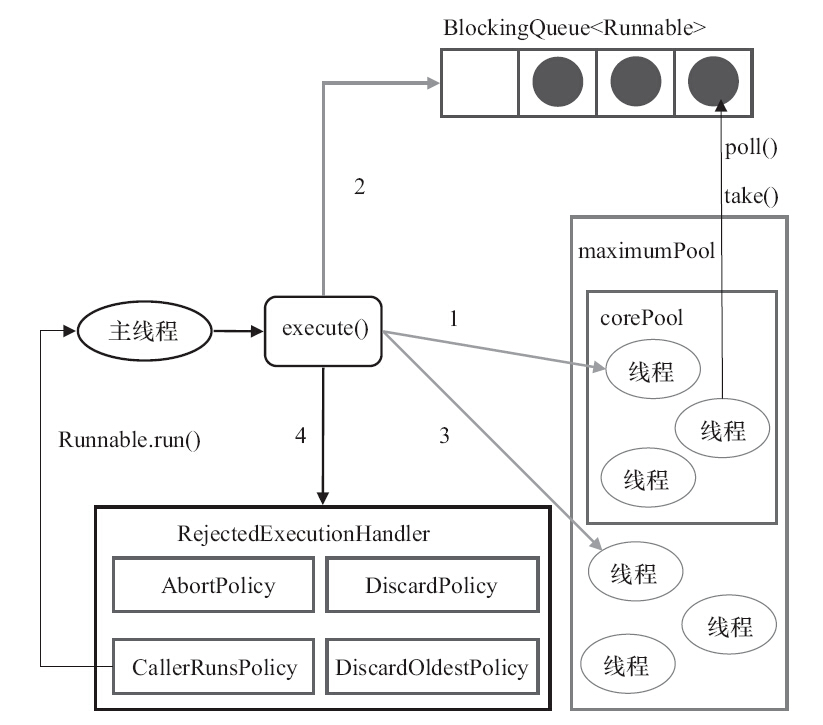
线程池的执行逻辑如下:
-
少于corePoolSize,新建线程任务
-
等于或多于corePoolSize,则放进BlockQueue存储
-
BlockQueue 存储满的时候,创建新的线程
-
超过maxmiumPoolSize,拒绝创建,并调用RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectExecutor();
线程池的创建
核心参数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
-
当线程数小于corePoolSize,默认是新增一个线程任务创建一个线程,也可以用实例调用prestartAllCoreThread开启所有线程。
-
ThreadFactory 用于设置创建线程的工厂。
-
RejectedExecutionHandler当队列线程池满了之后,处理策略。默认是AbortPolicy。抛出异常。
- AbortPolicy 抛出异常
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
- CallerRunsPolicy 当前线程运行任务
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
- DiscardOldestPolicy 抛弃现有队列中的最后一个任务
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
- DiscardPolicy 不处理
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
- keepAliveTime:线程池的工作空闲之后,存活的时间。
线程池任务的提交
- execute方法
theadPool.execute(new Runnable(){
run(){
}
})
- submit 方法,有返回值,可以查看返回的结果
Future<Object> future = executor.submit(harReturnValuetask);
try {
Object s = future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//
}