链表
含义:链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针指向来表示的。
相关功能代码:
结点类
每个结点都由一个数据域和一个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据,指针域用来指向其后续结点。头结点不存储数据,指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
private class Node {
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next=next;
}
}
添加元素:
public void insert(T t){
//找到当前最后一个结点
Node n=head;
while (n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
}
//创建新结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
//让最后一个结点指向新结点
n.next=newNode;
//元素个数加1
N++;
}
向指定位置添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t){
//找到i位置前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur = pre.next;
//创建一个新节点,新结点指向原来i位置的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t,cur);
//i位置前一个结点指向新结点
pre.next=newNode;
//元素个数加1
N++;
}
删除i位置的元素,并返回其值
public T remove(int i){
//找到i位置的前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur = pre.next;
//找到i位置的下一个结点
Node next = cur.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点
pre.next=next;
//元素个数减1
N--;
return cur.item;
}
查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n=head; //head并不存储数据
for (int index=0;index<N;index++){
n=n.next;
if (n.item==t){
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
遍历链表
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new LIterator();
}
public class LIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public LIterator() {
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object
next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
反转链表(面试高频题目)
public void reverse(){
if (isEmpty()){
return;
}
reverse(head.next);
}
//反转指定的结点cur,并把反转后的结点返回
public Node reverse(Node cur){
if (cur.next==null){
head.next=cur;
return cur;
}
//递归反转cur的下一个结点,返回值为链表反转后,当前结点的上一个结点
Node pre = reverse(cur.next);
//让返回的结点下一个结点变为cur
pre.next=cur;
//把当前结点的下一个结点变为null
cur.next=null;
return cur;
}
完整代码
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
private Node head; //Node结点:即带指向的一个元素
private int N; //head并不存储数据
public LinkList() {
//初始化头结点
this.head=new Node(null,null);
//初始化数组长度
this.N=0;
}
//创建内部类
private class Node {
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next=next;
}
}
//清空列表
public void clear(){
head.next=null;
this.N=0;
}
//获取链表的长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
//获取指定位置i的元素
public T get(int i){
//通过循环从头结点开始往后找
Node n=head.next;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//插入一个元素
public void insert(T t){
//找到当前最后一个结点
Node n=head;
while (n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
}
//创建新结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
//让最后一个结点指向新结点
n.next=newNode;
//元素个数加1
N++;
}
//向指定位置添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t){
//找到i位置前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur = pre.next;
//创建一个新节点,新结点指向原来i位置的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t,cur);
//i位置前一个结点指向新结点
pre.next=newNode;
//元素个数加1
N++;
}
//删除i位置的元素,并返回其值
public T remove(int i){
//找到i位置的前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur = pre.next;
//找到i位置的下一个结点
Node next = cur.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点
pre.next=next;
//元素个数减1
N--;
return cur.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n=head; //head并不存储数据
for (int index=0;index<N;index++){
n=n.next;
if (n.item==t){
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new LIterator();
}
public class LIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public LIterator() {
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object
next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
//反转链表
public void reverse(){
if (isEmpty()){
return;
}
reverse(head.next);
}
//反转指定的结点cur,并把反转后的结点返回
public Node reverse(Node cur){
if (cur.next==null){
head.next=cur;
return cur;
}
//递归反转cur的下一个结点,返回值为链表反转后,当前结点的上一个结点
Node pre = reverse(cur.next);
//让返回的结点下一个结点变为cur
pre.next=cur;
//把当前结点的下一个结点变为null
cur.next=null;
return cur;
}
}
双向链表
顾名思义,双向链表结点不止可以从前往后指,也可以从后往前指。每个结点是由一个数据域和两个指针域组成的。
它的基本方法和单项链表相差不多,在此不一一列举。
完整代码
public class TwoWayLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int N;
public TwoWayLinkList() {
this.head=new Node(null,null,null);
this.last=null;
this.N=0;
}
private class Node {
public T item;
public Node pre;
public Node next;
public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next){
this.item=item;
this.pre=pre;
this.next=next;
}
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
this.head.next=null;
this.last=null;
this.N=0;
}
//获取链表长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
//获取第一个元素
public T getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素
public T getLast(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
//插入元素
public void insert(T t){
//如果链表为空
if (isEmpty()){
//创建新的结点
Node newnode = new Node(t, head, null);
//让新结点成为尾结点
last=newnode;
//让头结点指向尾结点
head.next=last;
}
//如果链表不为空
else{
//创建新结点
Node oldLast=last;
Node newnode = new Node(t, oldLast, null);
//让当前的尾结点指向新结点
oldLast.next=newnode;
//让新结点成为尾结点
last=newnode;
}
//元素个数加一
N++;
}
//向指定位置添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t){
//找到i位置前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur=pre.next;
//创建一个新节点,新结点指向原来i位置的结点
Node newnode = new Node(t, pre, cur);
//i位置前一个结点的下一个结点为新结点
pre.next=newnode;
//让i位置前一个结点成为新结点
cur.pre=newnode;
//元素个数加1
N++;
}
//获取指定位置的元素
public T get(int i){
Node n=head.next;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n=head; //head并不存储数据
for (int index=0;index<N;index++){
n=n.next;
if (n.item==t){
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
//删除指定位置的元素,并返回其值
public T remove(int i){
//找到前一个结点
Node pre=head;
for (int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node cur=pre.next;
//找到下一个结点
Node nextnode=cur.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点
pre.next=nextnode;
//下一个结点的的上一个节点变为上一个结点
nextnode.pre=pre;
//元素个数-1
N--;
return cur.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new aIterator();
}
public class aIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public aIterator() {
this.n = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
介绍完两种链表类型,再说一下单项链表解决的几个实际问题。这几个问题都是用快慢指针来完成的。
结点类
private static class Node<T>{
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next; //按shift选择多个属性
}
}
①中间值问题:找到一组数据中的中间值
private static String getMid(Node<String> first) {
//定义两个指针
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow.item;
}
②单项链表是否有环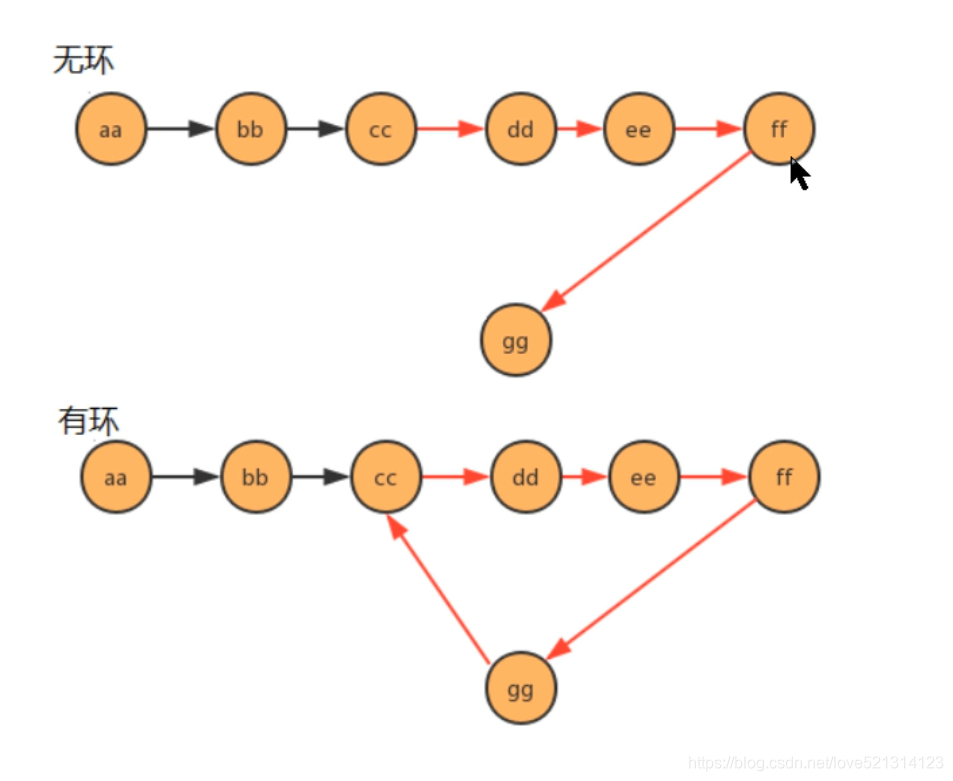
private static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
//定义快慢指针
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
//遍历链表
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast.equals(slow)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
③找到环的入口结点
private static Node<String> getEntrance(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
Node<String> temp=null;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast.equals(slow)){
temp=first;
continue;
}
//临时结点变换
if (temp!=null){
temp=temp.next;
//判断临时指针是否和慢指针相遇
if(temp.equals(slow)){
break;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
完整代码:
public class FastSlowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建结点
Node<String> first=new Node<String>("aa",null);
Node<String> second=new Node<String>("bb",null);
Node<String> third=new Node<String>("cc",null);
Node<String> fourth=new Node<String>("dd",null);
Node<String> fifth=new Node<String>("ee",null);
Node<String> sixth=new Node<String>("ff",null);
Node<String> seventh=new Node<String>("gg",null);
//完成结点之间的指向
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
third.next=fourth;
fourth.next=fifth;
fifth.next=sixth;
sixth.next=seventh;
//产生环
seventh.next=third;
//查找中间值
/*String mid=getMid(first);
System.out.println("中间值为:"+mid);
//判断单项链表是否有环
boolean circle=isCircle(first);
System.out.println("first链表中是否有环:"+circle);*/
//查找环的入口结点
Node<String> entrance=getEntrance(first);
System.out.println("环的入口结点为:"+entrance.item);
}
private static Node<String> getEntrance(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
Node<String> temp=null;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast.equals(slow)){
temp=first;
continue;
}
//临时结点变换
if (temp!=null){
temp=temp.next;
//判断临时指针是否和慢指针相遇
if(temp.equals(slow)){
break;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
private static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
//定义快慢指针
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
//遍历链表
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast.equals(slow)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static String getMid(Node<String> first) {
//定义两个指针
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow.item;
}
private static class Node<T>{
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next; //按shift选择多个属性
}
}
}
关于链表的介绍就到这里。
b站详细讲解网址:http://yun.itheima.com/course/639.html