文章目录
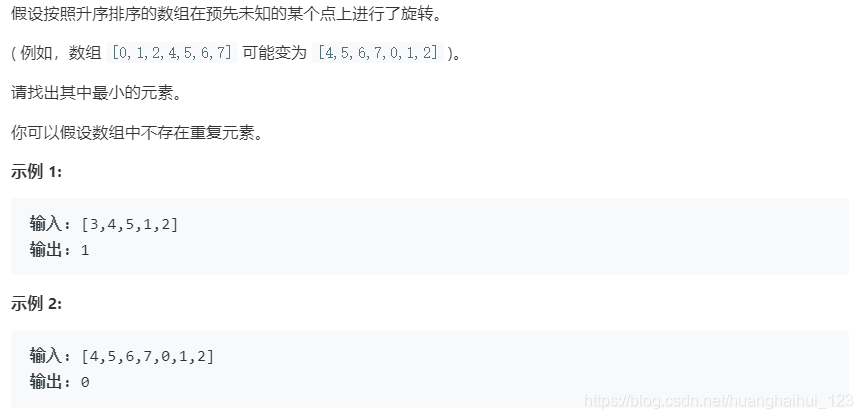
153. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
思路一:
比较暴力的求解,找到翻转的点(由升序变为降序),有找到这个点,则就是下一个点就是。没有找到这个点,就是第一个点。
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& nums) {
int size = nums.size();
int i,tmp;
if(size==1){
return nums[0];
}
for(i=1,tmp=nums[0];i<size;i++){
if(nums[i]<tmp){
break;
}
tmp=nums[i];
}
if(i!=size){
return nums[i];
}else{
return nums[0];
}
}
};
思路二:
我们需要知道,对于一个区间A,如果A[start] < A[stop],那么该区间一定是有 序的了。
另外,由于不含重复元素,需要分两种情况。
对于一个轮转了的排序了的数组,
如果nums[mid]>nums[left],最小值一定在右半区间
如果nums[mid]<nums[left],最小值一定在左半区间
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& nums) {
for (int low = 0, high = nums.size() - 1; low <= high;){
if (nums[low] <= nums[high]){
return nums[low];
}
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[high]){
low = mid + 1;
} else {//[3,1,2]
high = mid;
}
}
return INT_MIN;
}
};
static const auto __lamda = []() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
return nullptr;
}();
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积

正序成一次,逆序乘一次,每次的时间复杂度都是O(n)
即:
0 1 1x2 1x2x3
4x3x2, 4x3, 4, 0
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> productExceptSelf(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> shun;
int size=nums.size();
int tmp=1;
shun.push_back(1);
for(int i=1;i<size;i++){
shun.push_back(shun[i-1]*nums[i-1]);
}
for(int j=1;j<size;j++){
tmp=tmp*nums[size-j];
shun[size-j-1]*=tmp;
}
return shun;
}
};
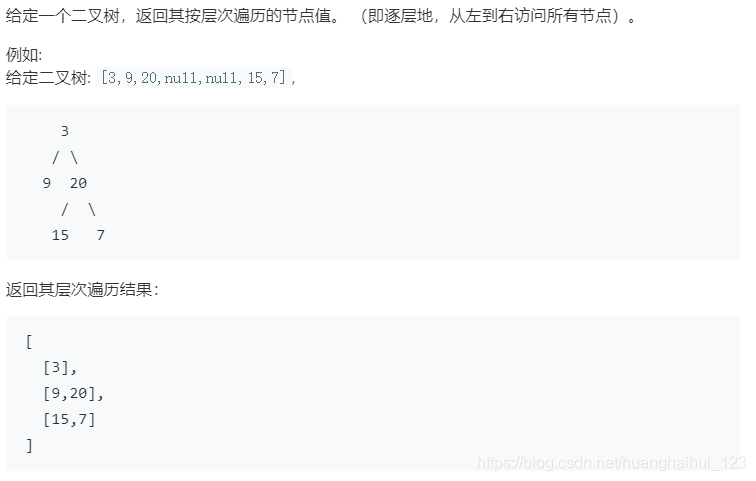
102. 二叉树的层次遍历
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
1.首先找到需要删除的节点;
2.如果找到了,删除它。
说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
删除的节点有三种情况
1.删除的节点无子节点。无子节点直接删除该节点
2.删除的节点有且仅有一个子节点。子节点替换删除节点
3.删除的节点同时有两个节点。一种是从删除节点的右分支查找最小值,赋值给删除节点,再去删除找到的这个最小值;另一种是从删除节点的左分支查找最大值,赋值给删除节点,再去删除这个最大值。
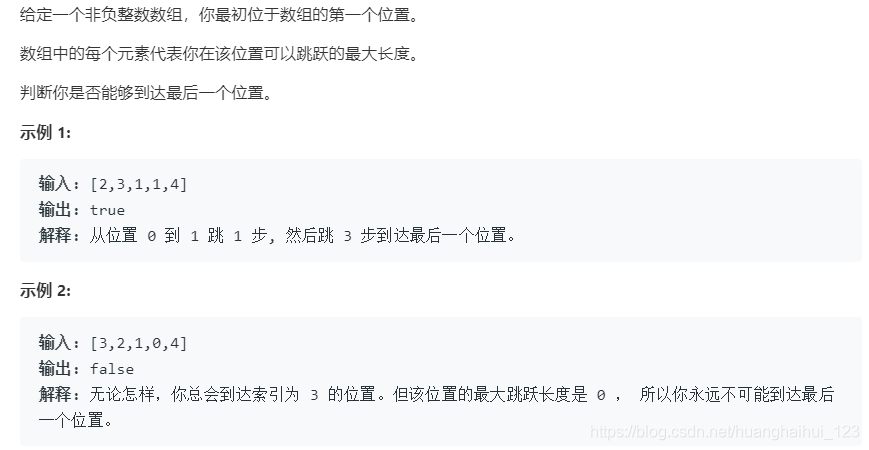
55.跳跃游戏
1.方法一:动态规划
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> dp(nums.size(), 0);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], nums[i - 1]) - 1;
if (dp[i] < 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}; //dp[i]记录了到第i个数,还能再往前多少。(不包括第i个数)
2.贪心法,同样的思路,记录当前位置下,最大的路径是多少,这里用的是全局的坐标。

class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
int N = nums.size();
int maxreach = 0; //注意是下标值,而不是元素值
for(int i = 0; i !=N;++i)
{
if(i > maxreach) //注意false的条件,就是maxreach停止了,而i仍然在增加,一直到超过maxreach也没有停止,对应题目中的反例很好理解
return false;
maxreach = max(maxreach, i + nums[i]); //注意更新方法
if (maxreach >= N-1) //一个小细节,要写成>=而不是写成==
return true;
}
return false;
}
};

146. LRU缓存机制

用哈希表unordered_map 来进行快速查找缓存中是否有存在key键,value代表了key在list中的位置,是一个迭代器
用list来存储最近常用的的元素。有序,能够快速删除和排序。
LRU缓存机制:
class LRUCache {
public:
int max_val;
list<pair<int,int>> record_list;
unordered_map<int,list<pair<int,int>>::iterator> test;
LRUCache(int capacity) {
max_val=capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
auto i = test.find(key);
if(i!=test.end()){
put(key, test[key]->second);
return test[key]->second;
}else
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto i = test.find(key);
if(i!=test.end()){ //map本身就存在key
record_list.erase(i->second);
}else if(record_list.size()==max_val){ //map本身不存在key
test.erase(record_list.back().first);
record_list.pop_back();
}
record_list.push_front(make_pair(key,value));
test[key]= record_list.begin();
}
};
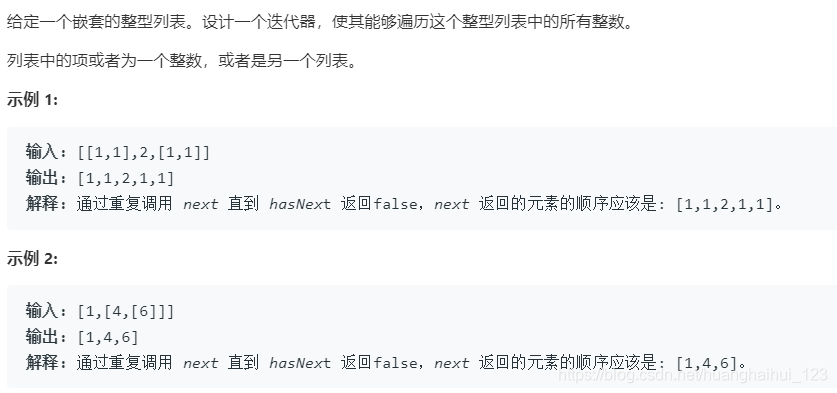
341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
方法一:栈来求解。把vector元素逆序压入栈中, hasNext()目的把栈顶不是整数的元素转化为整数
class NestedIterator {
public:
stack<NestedInteger *> st;
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
int i;
for(i = nestedList.size()-1 ; i>=0; i--)
st.push(&nestedList[i]);
}
int next() {
int ret = st.top()->getInteger();
st.pop();
return ret;
}
bool hasNext() {
if(st.empty())
return false;
NestedInteger *tmp = st.top();
while(!tmp->isInteger()) {
st.pop();
vector<NestedInteger> &list = tmp->getList();
int i;
for(i = list.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
st.push(&list[i]);
if(st.empty())
return false;
tmp = st.top();
}
return true;
}
};
方法二:在初始化的时候就直接用一个队列存所有的整数。
class NestedIterator {
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
_NestedIterator(nestedList, a);
}
void _NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList,queue<int> & a){
int n_size = nestedList.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n_size ; i ++ ){
if(nestedList[i].isInteger())
a.push(nestedList[i].getInteger());
else
_NestedIterator(nestedList[i].getList(), a); //const_cast<vector<NestedInteger>>
}
}
int next() {
int i = a.front();
a.pop();
return i;
}
bool hasNext() {
if(a.empty())
return false;
return true;
}
queue<int> a;
};