NMS是目标检测的基础,原理比较简单,不在这里赘述,直接上代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
x1 = dets[:,0]
y1 = dets[:,1]
x2 = dets[:,2]
y2 = dets[:,3]
areas = (y2-y1+1) * (x2-x1+1)
scores = dets[:,4]
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size >0:
i = index[0] # every time the first is the biggst, and add it directly
keep.append(i)
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) # calculate the points of overlap
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22-x11+1) # the weights of overlap
h = np.maximum(0, y22-y11+1) # the height of overlap
overlaps = w*h
ious = overlaps / (areas[i]+areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]
index = index[idx+1] # because index start from 1
return keep
def plot_bbox(dets, c='k'):
x1 = dets[:,0]
y1 = dets[:,1]
x2 = dets[:,2]
y2 = dets[:,3]
plt.plot([x1,x2], [y1,y1], c)
plt.plot([x1,x1], [y1,y2], c)
plt.plot([x1,x2], [y2,y2], c)
plt.plot([x2,x2], [y1,y2], c)
plt.title(" nms")
if __name__ == "__main__" :
boxes=np.array([[100,100,210,210,0.72],
[250,250,420,420,0.8],
[220,220,320,330,0.92],
[100,100,210,210,0.72],
[230,240,325,330,0.81],
[220,230,315,340,0.9]])
plt.figure(1)
ax1 = plt.subplot(1,2,1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.sca(ax1)
plot_bbox(boxes,'k') # before nms
keep = py_cpu_nms(boxes, thresh=0.7)
plt.sca(ax2)
plot_bbox(boxes[keep], 'r')# after nms
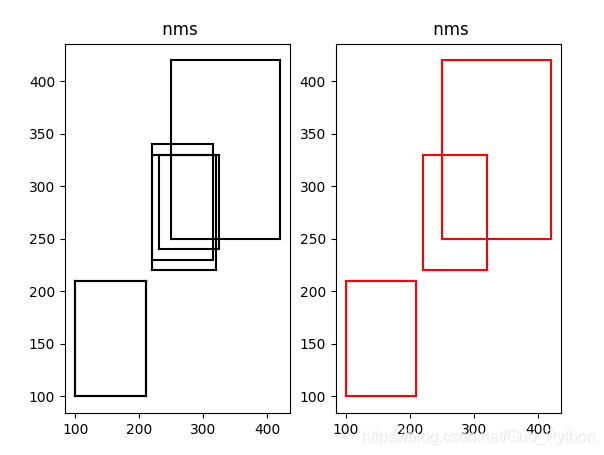
plt.show()效果图如下,黑色的bbox为原始的框,红色的bbox为经过nms的框:
注:上面的代码只针对一类做的nms, 如果是多类别,在外层套一个循环即可。
每天进步一点点!!!