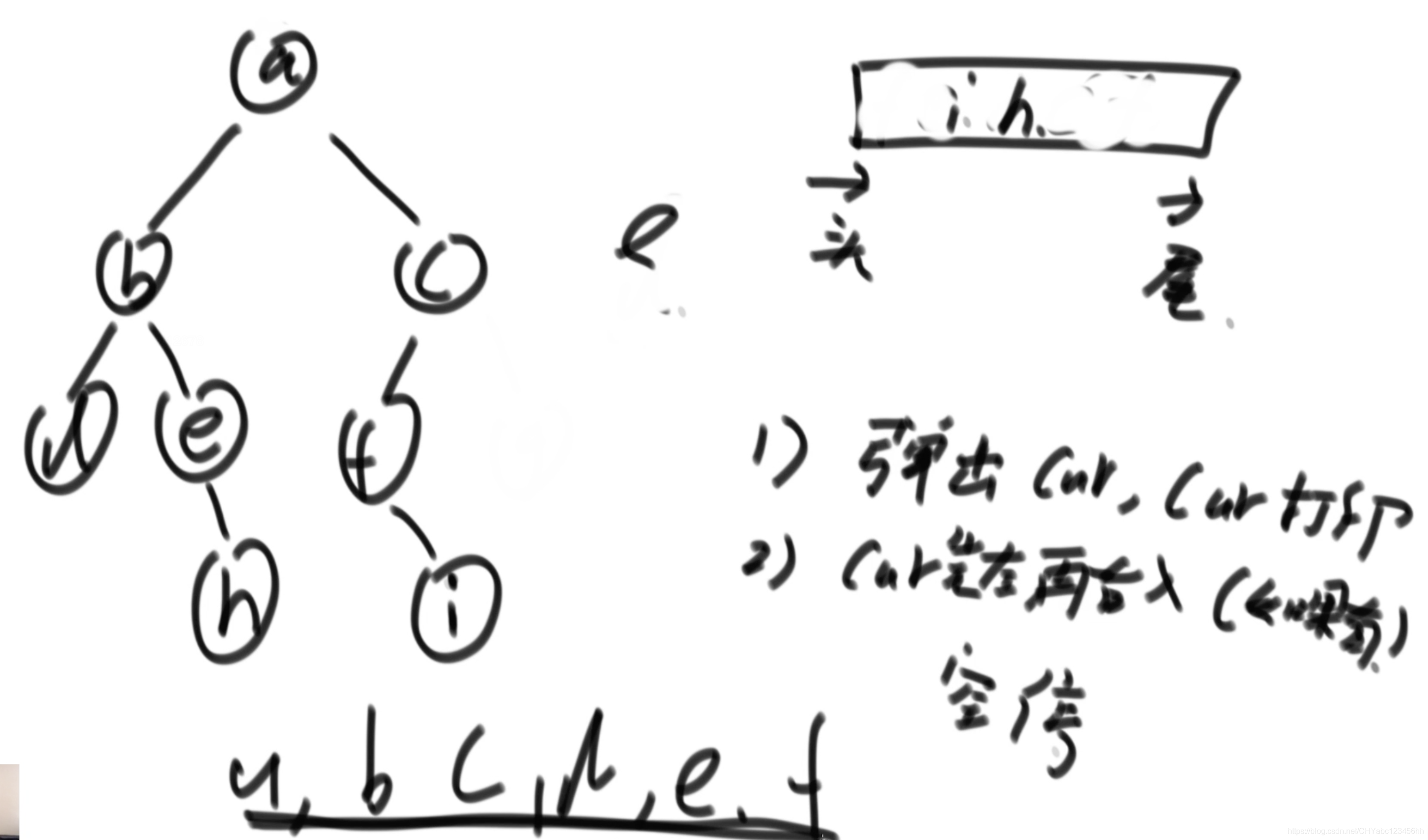
牛客网 算法入门篇 左程云老师 个人复习,如果侵全,设为私密
二叉树遍历(递归)
-
先序遍历(中,左,右)
-
中序遍历(左,中,右)
-
后序遍历(左,右,中)
- 如上图所示结构,二叉树的遍历本质上都是递归序,1、2和3节点每个都会出现三次,比如从节点1出发,来到节点2,节点2的左边为空,返回,打印2,右边为空,返回打印2,再返回到节点1,节点3类似。所以最后输出的序列为1,2,2,2,1,3,3,3,1。
- 如果打印递归序出现的第1次的元素,就是先序遍历
- 如果打印递归序出现的第2次的元素,就是中序遍历
- 如果打印递归序出现的第3次的元素,就是后序遍历
二叉树遍历(非递归)
先序遍历

- 二叉树的结构如图所示,准备一个栈用于接收数据
- 原则只有两点:1,栈中弹出节点叫做cur(当前节点),弹出就打印;2,先打印cur的右节点,仔打印左节点,没有就无需操作。栈空就停止。
- 1进栈,弹出1,打印1;将3和2压入栈中,弹出2,打印2,将2的孩子节点4和5押入栈中;因为先押入右,再压左,因此先将5押入,再押入4;弹出4,打印4;如上所述,先序遍历为1,2,4,5,3,6,7
代码
package class05;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Code01_PreInPosTraversal {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void f(Node head) {
// 1
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// 1
f(head.left);
//2
//2
f(head.right);
// 3
// 3
}
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head) {
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.add(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.right != null) {
stack.push(head.right);
}
if (head.left != null) {
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) {
System.out.print("in-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>();
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop();
s2.push(head);
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void posOrderUnRecur2(Node h) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (h != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(h);
Node c = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
c = stack.peek();
if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.left);
} else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.right);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " ");
h = c;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
head.right.right.right = new Node(11);
// recursive
System.out.println("==============recursive==============");
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
preOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("in-order: ");
inOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
posOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
// unrecursive
System.out.println("============unrecursive=============");
preOrderUnRecur(head);
inOrderUnRecur(head);
posOrderUnRecur1(head);
posOrderUnRecur2(head);
}
}
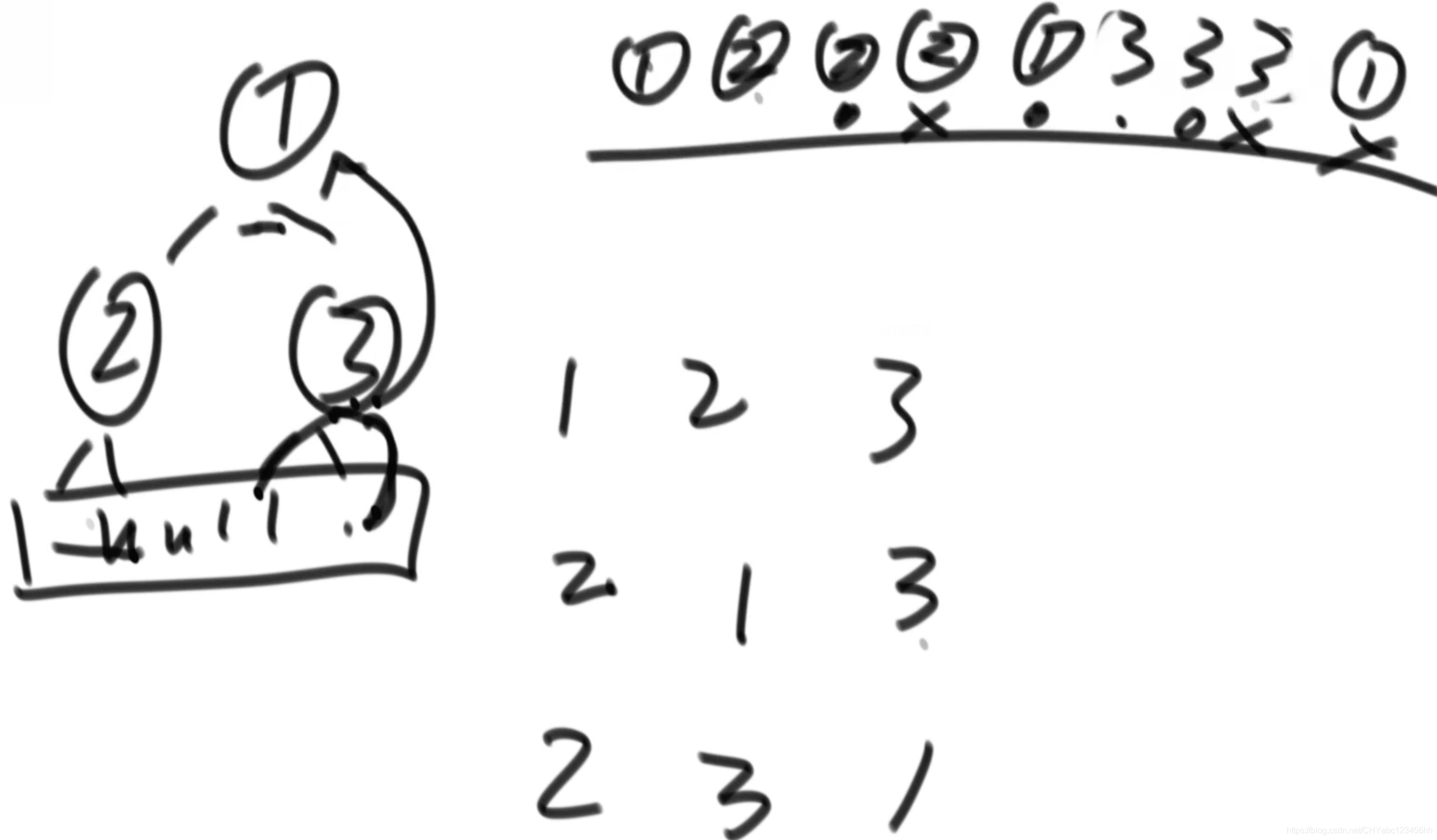
中序遍历(非递归)
- 原则只有两点:1,栈中弹出节点叫做cur(当前节点),弹出就打印;2,先打印cur的左节点,仔打印右节点,没有就无需操作。栈空就停止。
- 不断将右节点分成左和中节点
后序遍历(非递归)
- 原则只有两点:1,栈中弹出节点叫做cur(当前节点),弹出不打印,放到一个新的栈中;2,最后将第二个栈中的元素打印,相当于是(左,右,中),即后序遍历
直观打印二叉树
package class05;
public class Code02_PrintBinaryTree {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(-222222222);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
head.right.left = new Node(55555555);
head.right.right = new Node(66);
head.left.left.right = new Node(777);
printTree(head);
head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(4);
head.right.left = new Node(5);
head.right.right = new Node(6);
head.left.left.right = new Node(7);
printTree(head);
head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(1);
head.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(1);
head.right.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left.right = new Node(1);
printTree(head);
}
}求二叉树的最大宽度
使用队列
- 使用一个队列,从头部进入,从尾巴出来;
- 原则:弹出当前节点cur,弹出并打印;当前节点的话存在左右节点的话,先放入左节点,再放入右节点。如果不存在孩子节点,等队列为null的话,就停止输出。但是,存在一个问题,我们不知道哪些节点是类属于一层的,因此需要进行指定。需要引入哈希表来统计相关的层数、以及最大的跨度
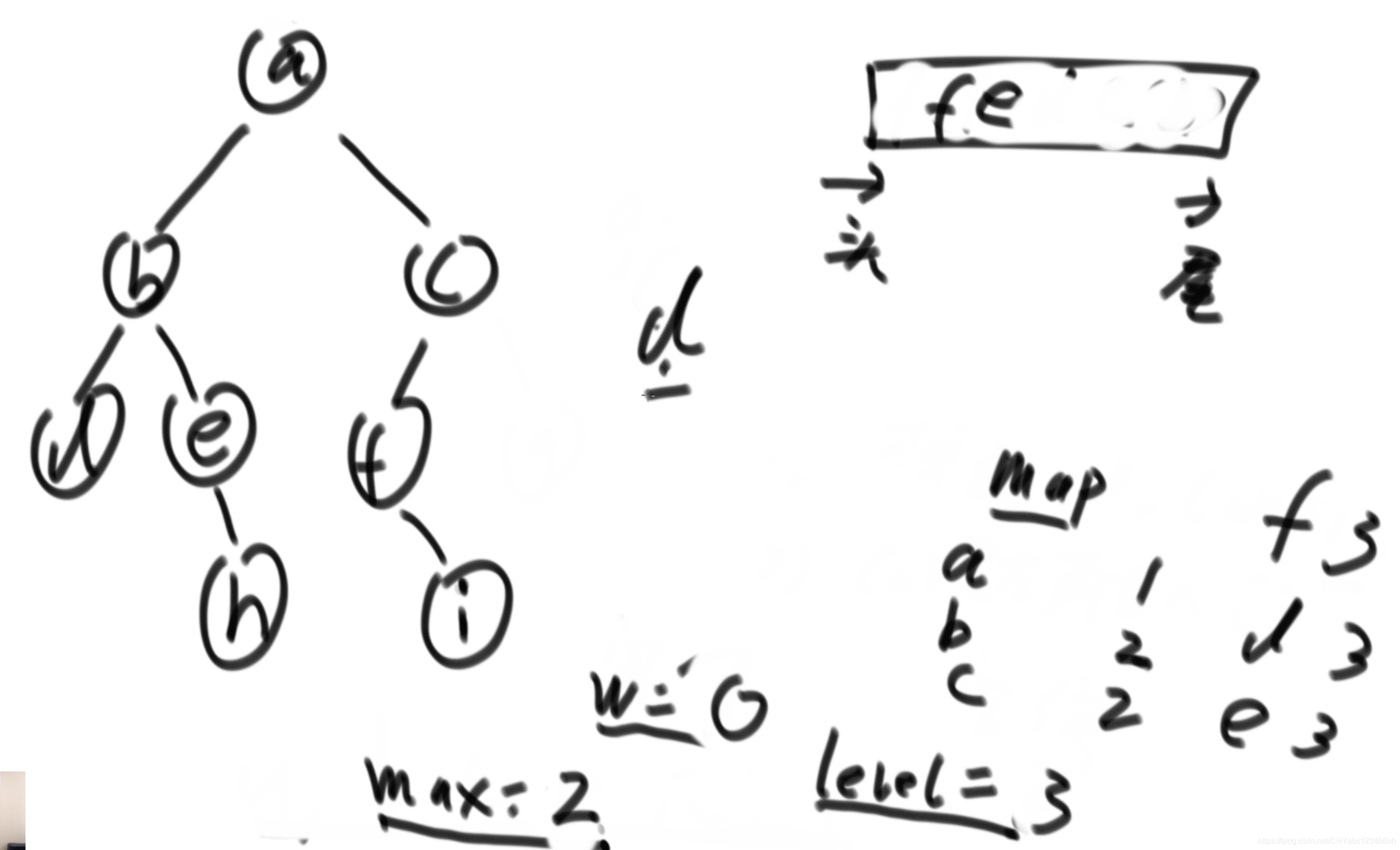
使用哈希表
- 引入哈希表,设置三个变量,max为全局最大宽度,w为统计当前层级的宽度值,level记录统计层级
- 初始设置max=-1,w=0,level=1;当a输入队列,w变为1,level显示当前层级为1,当a出队列,将其孩子节点b和c放入队列,当b出队列,level查询发现b是2层的,因此将w和max比较大小,将大的数值赋值给max,然后将w清除数据,重新统计第二层级的数的个数。以此类推。
代码
package class05;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Code03_TreeMaxWidth {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static int w(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>();
levelMap.put(head, 1);
int curLevel = 1;
int curLevelNodes = 0;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
int curNodeLevel = levelMap.get(cur);
if(curNodeLevel == curLevel) {
curLevelNodes++;
} else {
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes);
curLevel++;
curLevelNodes = 1;
}
if(cur.left !=null) {
levelMap.put(cur.left, curNodeLevel+1);
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right !=null) {
levelMap.put(cur.right, curNodeLevel+1);
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int getMaxWidth(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
int maxWidth = 0;
int curWidth = 0;
// 目前的层数
int curLevel = 0;
// node 所在的层数
HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>();
levelMap.put(head, 1);
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
Node node = null;
Node left = null;
Node right = null;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node = queue.poll();
left = node.left;
right = node.right;
if (left != null) {
levelMap.put(left, levelMap.get(node) + 1);
queue.add(left);
}
if (right != null) {
levelMap.put(right, levelMap.get(node) + 1);
queue.add(right);
}
if (levelMap.get(node) > curLevel) {
curWidth = 1;
curLevel = levelMap.get(node);
} else {
curWidth++;
}
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, curWidth);//更新最后一层,因为最后一层没有触发逻辑
}
return maxWidth;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
二叉树的递归套路
如何判断一棵树是满二叉树
- 性质 节点数 = 2^树的高度 - 1
- 思路 假设以x为头节点,只有满足性质才是一个满二叉树。在容许向左右两个孩子要信息的前提下,应该要什么信息,才可以解决问题。
public class IsFull{
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
public static boolean isFull(Node head){
Info info = processInfo(head);
int size = info.size;
int height = info.height;
return size == (1<<height) - 1;
}
public static class Info{
public int size;
public int height;
public Info(int s,int h){
size = s;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info processInfo(Node x){
if(x == 0){
return new Info(0,0);
}
Info leftInfo = processInfo(x.left);
Info rightInfo = processInfo(x.right);
int size = leftInfo.size + rightInfo.size + 1;
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height,rightInfo.height) + 1;
return new Info(size, height);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}方法归纳
- 假设要求以x为头的答案
- 向左右两个孩子要信息,去分析构成答案的主要元素
- 确定向左右孩子要的信息,有可能左右要的信息不一样
- 组织收集到的信息
判断以x为头的二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
- 判断左右孩子的高度差是否相差小于等于1
- 如果左右孩子不满足平衡二叉树,那么此平衡二叉树不成立
代码
import jdk.vm.ci.code.site.Infopoint;
public class IsFull{
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
public static class Info{
public boolean isBalanced;
public int height;
public Info(boolean is,int h){
isBalanced = is;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x){
if(x == nll){
return new Info(true,0);
//return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int subTreeMaxHeight = 0;
if(leftInfo != null){
subTreeMaxHeight = leftInfo.height;
}
if(rightInfo!=null){
subTreeMaxHeight = Math.max(subTreeMaxHeight,rightInfo.height);
}
int height = 1 + subTreeMaxHeight;
boolean isBalanced = true;
if(leftInfo!=null && !leftInfo.isBalanced){
isBalanced=false;
}
if(rightInfo!= null && !rightInfo.isBalanced){
isBalanced = false;
}
int leftH = leftInfo != null ? leftInfo.height : 0;
int rightH = leftInfo != null ? rightInfo.height : 0;
if(Math.abs(leftH - rightH)>1){
isBalanced = false;
}
return new Infopoint(isBalanced, height);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}求树中两个节点的最大距离
情况分类
和头节点x无关
- 左树上的最大距离
- 右树上的最大距离
和头节点x相关
-
左边距离x最远和x到右边最远距离(树的高度)
代码
import org.graalvm.compiler.nodes.calc.LeftShiftNode;
import org.graalvm.compiler.nodes.calc.RightShiftNode;
import jdk.vm.ci.code.site.Infopoint;
public class IsFull{
public static int maxDistance(Node head){
Info info = process(head);
return info.maxDistance;
}
public static class Info{
public int maxDistance;
public int height;
public Info(boolean is,int h){
maxDistance = d;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x){
if(x == null){
return new Info(0,0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height,rightInfo.height) + 1;
int maxDistance = Math.max(leftInfo.height + rightInfo.height + 1,Math.max(leftInfo.height,rightInfo.height));
return new Info(maxDistance,height);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}判断一个树是否是搜索二叉树
套路
判定条件
- 左树是否是搜索二叉树
- 右树是否是搜索二叉树
- 左边最大的是否小于 x节点
- 右边最小的是否大于 x节点
代码
package class05;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
import class05.Code01_PreInPosTraversal.Node;
public class Code04_IsBST {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static class ReturnData {
public boolean isBST;
public int min;
public int max;
public ReturnData(boolean is, int mi, int ma) {
isBST = is;
min = mi;
max = ma;
}
}
public static ReturnData process(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return null;
}
ReturnData leftData = process(x.left);
ReturnData rightData = process(x.right);
int min = x.value;
int max = x.value;
if(leftData!=null) {
min = Math.min(min, leftData.min);
max = Math.max(max, leftData.max);
}
if(rightData!=null) {
min = Math.min(min, rightData.min);
max = Math.max(max, rightData.max);
}
// boolean isBST = true;
// if(leftData!=null && (!leftData.isBST || leftData.max >= x.value )) {
// isBST= false;
// }
// if(rightData!=null && ( !rightData.isBST || x.value >= rightData.min )) {
// isBST= false;
// }
boolean isBST = false;
if(
(leftData != null ? (leftData.isBST && leftData.max < x.value) : true)
&&
(rightData !=null ? (rightData.isBST && rightData.min > x.value) : true)
) {
isBST = true;
}
return new ReturnData(isBST, min, max);
}
public static boolean isF(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return true;
}
Info data = f(head);
return data.nodes == (1 << data.height - 1);
}
public static class Info{
public int height;
public int nodes;
public Info(int h, int n) {
height = h;
nodes = n;
}
}
public static Info f(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return new Info(0,0);
}
Info leftData = f(x.left);
Info rightData = f(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftData.height,rightData.height)+1;
int nodes = leftData.nodes + rightData.nodes + 1;
return new Info(height, nodes);
}
public static boolean inOrderUnRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
if (head.value <= pre) {
return false;
}
pre = head.value;
head = head.right;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isBST(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Node> inOrderList = new LinkedList<>();
process(head, inOrderList);
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (Node cur : inOrderList) {
if (pre >= cur.value) {
return false;
}
pre = cur.value;
}
return true;
}
public static void process(Node node, LinkedList<Node> inOrderList) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
process(node.left, inOrderList);
inOrderList.add(node);
process(node.right, inOrderList);
}
}
也可以中序遍历
-
只要递增,就是搜索二叉树
-
基于非递归中序遍历改进,由先前的打印,变为和前一个节点比较
代码
public static boolean inOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return true;
}
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || head != null){
if(head != null){
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
}else{
head = stack.pop();
if(head.value <= pre){
return false;
}
pre = head.value;
head = head.right;
}
}
return true;
}不可以使用套路来做
判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
-
如果使用条件,左子树是否是完全二叉树,右子树是否是完全二叉树来判定根节点是否是完全二叉树
- 即使左子树和右子树都是完全二叉树,但是左子树比右子树少整整一层的情形下,判定失败
思路
- 宽度优先遍历,任何一个节点不能有右节点,没有左节点。
- 当第一次发现某节点左右不双全,后续节点都是右节点
package class05;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Code05_IsCBT {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static boolean isCBT(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 是否遇到过左右两个孩子不双全的节点
boolean leaf = false;
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
if (
// 如果遇到了不双全的节点之后,又发现当前节点不是叶节点
(leaf && !(l == null && r == null))
||
(l == null && r != null)
) {
return false;
}
if (l != null) {
queue.add(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.add(r);
}
if (l == null || r == null) {
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
}
求n1和n2的最低公共主先
划分情况(x为头节点)
- x无n1和n2
- x只有n1
- x只有n2
- x有n1和n2:左n1n2;右n1n2;左n1右n2;左n2右n1
代码
package class05;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Code07_LowestCommonAncestor {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node lowestAncestor(Node head, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (head == null || head == o1 || head == o2) { // base case
return head;
}
Node left = lowestAncestor(head.left, o1, o2);
Node right = lowestAncestor(head.right, o1, o2);
if (left != null && right != null) {
return head;
}
// 左右两棵树,并不都有返回值
return left != null ? left : right;
}
public static class Record1 {
private HashMap<Node, Node> map;
public Record1(Node head) {
map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
if (head != null) {
map.put(head, null);
}
setMap(head);
}
private void setMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.left != null) {
map.put(head.left, head);
}
if (head.right != null) {
map.put(head.right, head);
}
setMap(head.left);
setMap(head.right);
}
public Node query(Node o1, Node o2) {
HashSet<Node> path = new HashSet<Node>();
while (map.containsKey(o1)) {
path.add(o1);
o1 = map.get(o1);
}
while (!path.contains(o2)) {
o2 = map.get(o2);
}
return o2;
}
}
public static class Record2 {
private HashMap<Node, HashMap<Node, Node>> map;
public Record2(Node head) {
map = new HashMap<Node, HashMap<Node, Node>>();
initMap(head);
setMap(head);
}
private void initMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
map.put(head, new HashMap<Node, Node>());
initMap(head.left);
initMap(head.right);
}
private void setMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
headRecord(head.left, head);
headRecord(head.right, head);
subRecord(head);
setMap(head.left);
setMap(head.right);
}
private void headRecord(Node n, Node h) {
if (n == null) {
return;
}
map.get(n).put(h, h);
headRecord(n.left, h);
headRecord(n.right, h);
}
private void subRecord(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
preLeft(head.left, head.right, head);
subRecord(head.left);
subRecord(head.right);
}
private void preLeft(Node l, Node r, Node h) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
preRight(l, r, h);
preLeft(l.left, r, h);
preLeft(l.right, r, h);
}
private void preRight(Node l, Node r, Node h) {
if (r == null) {
return;
}
map.get(l).put(r, h);
preRight(l, r.left, h);
preRight(l, r.right, h);
}
public Node query(Node o1, Node o2) {
if (o1 == o2) {
return o1;
}
if (map.containsKey(o1)) {
return map.get(o1).get(o2);
}
if (map.containsKey(o2)) {
return map.get(o2).get(o1);
}
return null;
}
}
// for test -- print tree
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(4);
head.left.right = new Node(5);
head.right.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(7);
head.right.right.left = new Node(8);
printTree(head);
System.out.println("===============");
Node o1 = head.left.right;
Node o2 = head.right.left;
System.out.println("o1 : " + o1.value);
System.out.println("o2 : " + o2.value);
System.out.println("ancestor : " + lowestAncestor(head, o1, o2).value);
System.out.println("===============");
}
}