第一题
-
什么叫做类与类的继承,作用是什么?
就是子类继承父类的属性和行为,使得子类对象具有与父类相同的属性、相同的行为。 作用是子类复用父类内容。 -
继承后,父类与子类之间,各成员有什么样的影响?
成员变量: 不重名,没有影响。 重名,就近使用,使用super区分父类变量。 构造方法: 无影响,但是子类构造方法默认调用父类构造方法 成员方法: 不重名,没有影响。 重名,子类重写父类方法。 -
子类中,如何调用父类的成员?如何使用本类的成员?
父类成员方法:super.方法名 父类非私有成员变量:super.变量名 子类成员方法:this.方法名 子类成员变量:this.变量名 -
抽象方法与普通成员方法有什么区别?
抽象方法使用abstract关键字修饰,没有方法体。 成员方法有方法体。 -
抽象类与普通类有什么区别?
方法: 抽象类可以包含抽象方法和成员方法。 普通类不可以包含抽象方法,只有成员方法。 对象: 抽象类不可以创建对象。 普通类可以创建对象。
第二题
-
语法点:继承,抽象类
-
按步骤编写代码,效果如图所示:
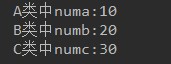
-
编写步骤:
定义抽象类A,抽象类B继承A,普通类C继承B A类中,定义成员变量numa,赋值为10,抽象showA方法。 B类中,定义成员变量numb,赋值为20,抽象showB方法。 C类中,定义成员变量numc,赋值为30,重写showA方法,打印numa,重写showB方法,打印numb,定义showC方法,打印numc。 测试类中,创建C对象,调用showA方法,showB方法,showC方法。 -
参考答案:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建C对象
C c = new C();
// 调用c 中方法
c.showA();
c.showB();
c.showC();
}
}
abstract class A{
int numa = 10;
public abstract void showA();
}
abstract class B extends A{
int numb = 20;
public abstract void showB();
}
class C extends B{
int numc = 30;
@Override
public void showA() {
System.out.println("A类中numa:"+numa);
}
@Override
public void showB() {
System.out.println("B类中numb:"+numb);
}
public void showC(){
System.out.println("C类中numc:"+numc);
}
}
第三题
-
语法点:继承,抽象类
-
按步骤编写代码,效果如图所示:
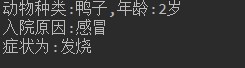 扫描二维码关注公众号,回复: 11304561 查看本文章
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复: 11304561 查看本文章
-
编写步骤:
模拟农学院动物医疗系统信息。 定义抽象家禽类(Poultry) 私有成员变量:动物种类(name),症状(symptom),年龄(age), 病因(illness) 提供空参和带参构造方法 成员方法: 抽象方法症状(showSymptom) 普通方法基本信息(showMsg) 提供setXxx和getXxx方法 定义普通鸭子类(Duck) 提供空参和带参构造方法 重写showSymptom方法,打印症状信息。 -
参考答案:
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Duck duck = new Duck("鸭子", "感冒", "发烧", 2);
duck.showMsg();
duck.showSymptom();
}
}
/*
1.定义抽象家禽类(Poultry)
*/
abstract class Poultry {
// i.成员变量(私有):
private String name;
private String illness;
// 症状(symptom)
private String symptom;
// 年龄(age)
private int age;
// ii.成员方法: showSymptom
public abstract void showSymptom();
// 成员方法: showMsg
public void showMsg() {
System.out.print("动物种类:" + name);
System.out.println(",年龄:" + age + "岁");
System.out.println("入院原因:" + illness);
}
// iii.提供空参和带参构造方法
public Poultry() {
super();
}
public Poultry(String name, String illness, String symptom, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.illness = illness;
this.symptom = symptom;
this.age = age;
}
// iv.提供setXxx和getXxx方法
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getIllness() {
return illness;
}
public void setIllness(String illness) {
this.illness = illness;
}
public String getSymptom() {
return symptom;
}
public void setSymptom(String symptom) {
this.symptom = symptom;
}
}
// Duck 类
class Duck extends Poultry {
public Duck() {
}
public Duck(String name, String illness, String symptom, int age) {
super(name, illness, symptom, age);
}
@Override
public void showSymptom() {
System.out.println("症状为:" + getSymptom());
}
}
第四题
-
语法点:继承
-
按步骤编写代码,效果如图所示:
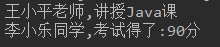
-
编写步骤:
模拟教学管理系统师生信息。 定义Person类。 属性:姓名、年龄 构造方法:无参构造方法,有参构造方法 成员方法:getXxx方法,setXxx方法,显示基本信息showMsg方法 定义Teacher类,继承Person 属性:学科 构造方法:无参构造方法,有参构造方法 成员方法:getXxx方法,setXxx方法,讲课方法 定义Student类,继承Person 属性:分数 构造方法:无参构造方法,有参构造方法 成员方法:getXxx方法,setXxx方法,考试方法 -
参考答案:
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// i.创建老师对象t,并把名称赋值为”王小平”,年龄赋值为30,工资赋值为8000
Teacher t = new Teacher("王小平", 30, "Java");
// iii.调用老师对象t的讲解方法
t.teach();
// iv.创建学生对象 s,并把名称赋值为”李小乐”,年龄赋值为14,成绩赋值为90分.
Student s = new Student("李小乐", 14, 90);
// vi.调用学生对象 s 的考试方法
s.exam();
}
}
class Person {
// 名称(name)
private String name;
// 年龄(age)
private int age;
// 空参构造
public Person() {
}
// 带参构造
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// setXxx和getXxx方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
/*
2.定义老师类(Teacher),继承Person类
*/
class Teacher extends Person {
// course(科目)
private String course;
// 空参构造
public Teacher() {
}
// 带参构造方法
public Teacher(String name,int age, String course) {
super(name,age);
this.course = course;
}
// 提供setXxx和getXxx方法
public String getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(String course) {
this.course = course;
}
public void teach() {
System.out.println(getName() +"老师,讲授"+course +"课");
}
}
/*
3.定义学生类(Student),继承Person类
*/
class Student extends Person {
// score(成绩)
private int score;
// 无参构造
public Student() {
super();
}
// 带参构造
public Student(String name, int age,int score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
// 提供setXxx和getXxx方法
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void exam(){
System.out.println(getName()+"同学,考试得了:"+ score +"分");
}
}
第五题
-
语法点:继承
-
按步骤编写代码,效果如图所示:
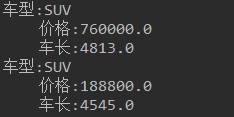
-
编写步骤
模拟汽车网站信息。 定义汽车Auto类 属性:品牌,车长,价格 定义SUV继承Auto类 属性:小型车车长标准值:4295,中型车车长标准值:5070。 定义判断车型方法 判断小型车:小于小型车车长标准值 判断大型车:大于中型车车长标准值 判断中型车:大于小型车车长标准值并且小于等于中型车车长标准值 测试类中,创建若干SUV对象,保存到集合,遍历集合,输出中型SUV。 -
参考答案:
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建SUV对象
SUV suv1 = new SUV(5079, 750000);
SUV suv2 = new SUV(4813, 760000);
SUV suv3 = new SUV(4270, 127800);
SUV suv4 = new SUV(4545, 188800);
//添加到集合中
ArrayList<SUV> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(suv1);
list.add(suv2);
list.add(suv3);
list.add(suv4);
// 遍历集合,查询中型SUV
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
SUV suv = list.get(i);
if (suv.midSUV()){
suv.showMsg();
}
}
}
}
// 定义汽车类
class Auto {
private String type;
private double length;
private double price;
public Auto() {
}
public Auto(String type, double length, double price) {
this.type = type;
this.length = length;
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void showMsg() {
System.out.println("车型:" + type);
System.out.println("\t价格:" + price);
System.out.println("\t车长:" + length);
}
}
// 定义SUV类
class SUV extends Auto {
// 车长标准
private int miniLength = 4295;
private int midLength = 5070;
public SUV(double length, double price) {
super("SUV", length, price);
}
// 判断 小型车
public boolean miniSUV() {
return getLength() <= miniLength;
}
// 判断 大型车
public boolean largeSUV() {
return getLength() > midLength;
}
// 判断 中型车
public boolean midSUV() {
return getLength() > miniLength && getLength() <= midLength;
}
}
第六题
- 找一组图形的最大面积及其对应的下标志
- 参考答案:
public class ShapeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[4];
shapes[0] = new Square(1);
shapes[1] = new Circle(1);
shapes[2] = new Square(2);
shapes[3] = new Circle(2);
maxArea(shapes);
}
public static void maxArea(Shape[] shapes){
double maxArea = shapes[0].area();
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <shapes.length ; i++) {
double area = shapes[i].area();
if (area>maxArea){
maxArea = area;
maxIndex = i;
}
}
System.out.println("最大面积:" + maxArea+"下标为"+maxIndex);
}
}
abstract class Shape{
double c;
abstract double area();
}
class Square extends Shape{
public Square(double c){
this.c = c;
}
@Override
double area() {
return 0.0625*c*c;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
public Circle(double c){
this.c = c;
}
@Override
double area() {
return 0.0796*c*c;
}
}