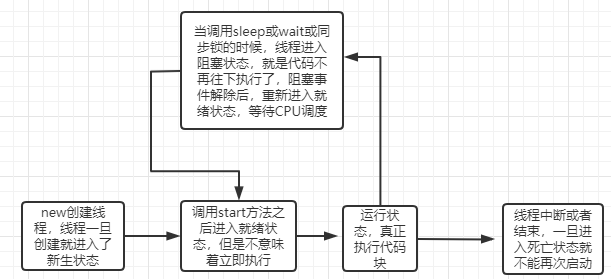
1、线程状态
2、线程的终止
不推荐使用JDK提供的stop方法、destory方法,他们已经被废弃,这里使用标志位来终止线程
public class TestStop implements Runnable { private boolean flag=true; @Override public void run() { int i=0; while(flag){ System.out.println("Thread"+i++); } } public void stop(){ this.flag=false; System.out.println("线程停止了!!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { TestStop testStop=new TestStop(); new Thread(testStop).start(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("main"+i);//主线程循环到800的时候,让创建的线程停止 if(i==900){ testStop.stop(); } } } }
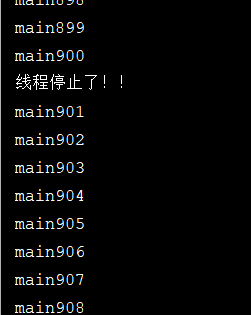
线程被终止之后,只有主线程在运行
3、线程的休眠
需要指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数,时间到达之后就进入就绪状态,可以模拟网络延时、倒计时等。每一个对象都有一把锁,sleep不会释放锁
(1)模拟网络延时:
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{ private int ticketsNums=10; @Override public void run() { while(true){ if(ticketsNums<=0){ break; } try { Thread.sleep(200);//延时200ms } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"拿到了"+ticketsNums--+"张票"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { TestSleep testThread=new TestSleep(); new Thread(testThread,"zhai").start(); new Thread(testThread,"zhang").start(); new Thread(testThread,"liu").start(); } }
如果不添加延时的代码,就会被第1个线程全部取走,当然,这个程序也体现了,在多个线程操作同一个数据的时候,存在线程安全的问题。
(2)模拟倒计时
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { int num=10; while(true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(num--); if(num<=0){ break; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { TestSleep testSleep=new TestSleep(); testSleep.run(); } }
主线程每隔一秒钟调用一次run方法,参数为一千毫秒,也就是一秒钟

(3)读取系统时间
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { Date startTime=null; while (true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } startTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime)); } } public static void main(String[] args) { TestSleep testSleep=new TestSleep(); testSleep.run(); } }
主线程每隔一秒钟读取一次系统时间,是通过调用run方法实现的
4、线程礼让
让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞,将线程从运行状态,变为就绪状态,让CPU重新调度,礼让不一定成功
public class TestYield implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行"); Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行"); } public static void main(String[] args) { TestYield testYield=new TestYield(); new Thread(testYield,"a").start(); new Thread(testYield,"b").start(); } }
a线程开始执行
b线程开始执行
a线程停止执行
b线程停止执行
5、合并线程
待其它线程执行完成后,再执行调用JOIN方法的线程,此线程阻塞
public class JoinTest implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("线程VIP来了"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { JoinTest joinTest=new JoinTest(); Thread thread=new Thread(joinTest); thread.start(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ if(i==200){ try { thread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("main-----"+i); } } }
测试:
main-----194 main-----195 main-----196 main-----197 main-----198 main-----199 线程VIP来了 线程VIP来了 线程VIP来了 线程VIP来了 线程VIP来了 线程VIP来了
当组线程执行到200的时候,主线程被阻塞,开始执行定义的VIP线程,直到VIP线程执行完毕,再开始执行主线程
6、线程的状态
public class StateTest implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("---------------"); }); Thread.State state = thread.getState(); System.out.println(state); thread.start(); state = thread.getState(); System.out.println(state); while (state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED){//只要线程不终止,就一直输出线程的状态 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } state=thread.getState(); System.out.println(state); } } }
测试:
NEW RUNNABLE TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING TIMED_WAITING --------------- TERMINATED