我们在使用Spring框架中,特别是框架级的功能,经常看到有@Import导入功能,
我就介绍下它能导入什么,首先声明下@Import是注解,导入类型可分为三类:
1. 导入配置 @Configuration,类似于spring早期版本2.5的import xml文件一样,
只是现在注解抢了风头,但目的一样,用于使用所有标有@configuration注解的配置。
下面我就写个小例子,怎么建java项目就略了
先建java主包com.spring, 然后分别建子包
1.1 建立服务接口
1.2 建立服务实现类,分三种情况,控制台、文件和数据库mysql
1.3 写配置类,三个服务实现类对应三个@Configuration
然后@Import注解登场了
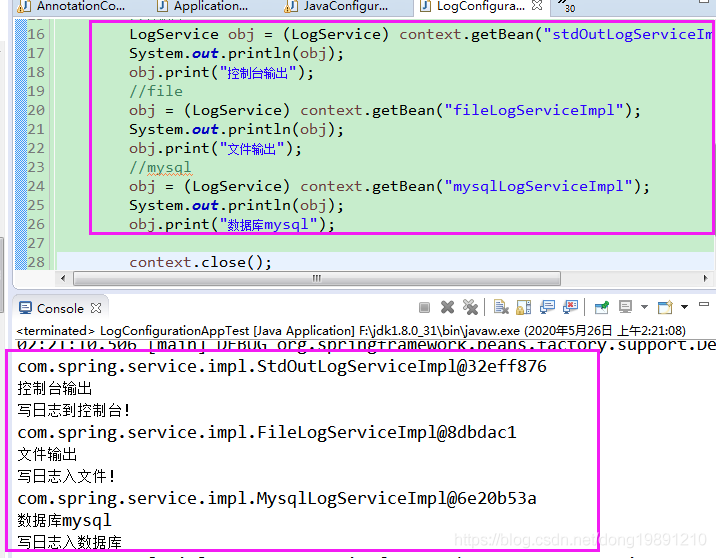
1.4 建立测试类看效果
输出效果
2. 导入实现ImportSelector接口或子接口DeferredImportSelector的类
@Import annotation can also be configured with an ImportSelector implementation to select @Configuration classes programmatically, based on some selection criteria.
下面我也演示下,这个很重要,框架里和spring扩展开发用的多,先建立备用子包com.spring.bean和com.spring.importSelector,然后建立配置文件目录conf
2.1 实现了ImportSelector
2.1.1 建立辅助类ApplicationProperties.java和外置配置文件myapp.properties
然后在conf目录下建立配置文件myapp.properties,内容如下:
2.1.2 建立@Configuration配置类
2.1.3 建立实现了ImportSelector接口的导入类,返回列表里的值是有标志@Configuration
2.1.4 建立有@import功能的配置类,导入2.1.3的实现类
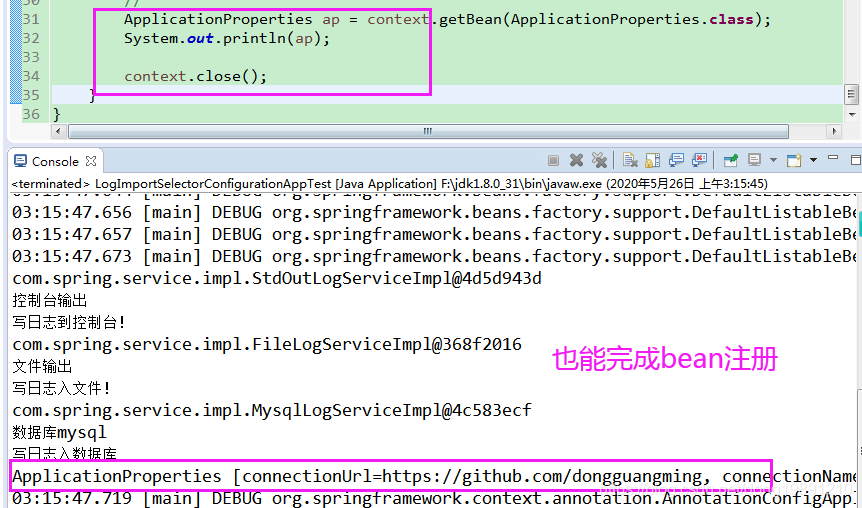
2.1.5 编写测试类
输出效果:
效果不错,也能完成bean的注册
还有一种基于注解的变体,我也示例下,先建个子包com.spring.annotation
建立自定义注解:
然后修改导入选择器实现类,根据启用日志功能时传的参数绝对加载哪个bean
修改配置类,追加自定义注解@EnableLogService,并设置参数为file(可选stdout,file,mysql)
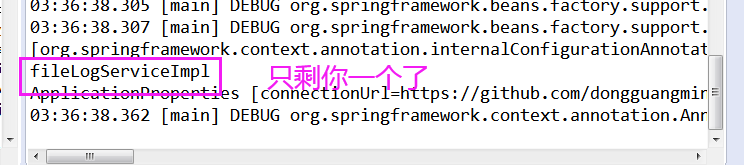
修改测试类,此时不再是三种日志实现的bean都加载,按配置参数加载
就因为配置了@EnableLogService(logType="file"),只加载了一个日志实现bean
2.2 实现了 DeferredImportSelector
可是看出它是2.1的子接口
The configuration class directly registered with the application context given preference over imported one. That means a bean of type T, configured in the main configuration will be used instead of a bean of the same type T from imported configuration. That applies to ImportSelector as well. On the other hand, DeferredImportSelector applies after all other configuration beans have been processed.
我们可以比较下实现两种接口的区别
在主选择器的配置类LogImportSelectorConfig.java中增加
在文件配置类FileLogConfig.java中修改为
选择器实现类还是
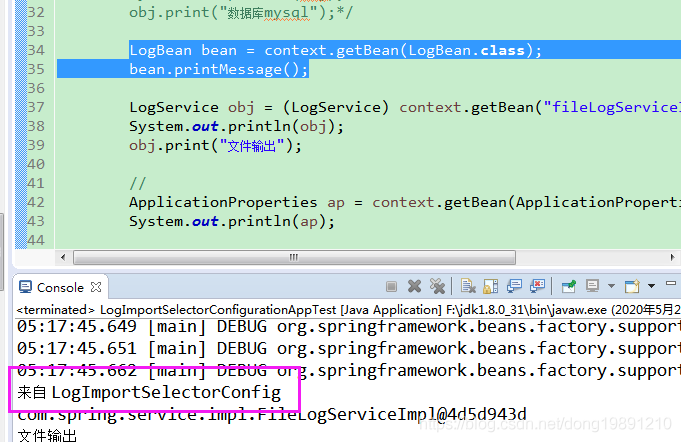
执行测试代码
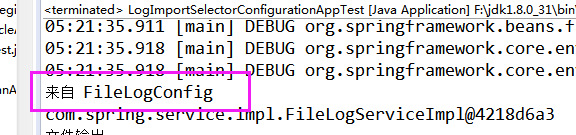
此时修改选择器实现的接口改为DeferredImportSelector,其它不改
再次=执行测试
2.3 导入实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的类
可以先瞄下接口的如何定义和定义了什么
This Interface is to be implemented by types that register additional bean definitions when processing @Configuration classes.
具体可参考还记得我以前写的博文Spring Bean注册的几种方式https://blog.csdn.net/dong19891210/article/details/105798650吗,详细看第5.2小节,这里就不再重复啰嗦写了。
其实你搞懂了Bean,spring本身、及衍生的第三方扩展, 99.99%的问题都不再是问题了!!!
小结:一图
务必掌握好2和3,写扩展很有用,甚至spring本身都在大量使用。
spring围绕着bean运转的,注册的几种方式,每种注册方式的条件性选择
最后请慢慢学会忘记xml格式的配置文件,现在或往后都是注解式了,虽然xml配置并不影响功能!
附部分注解图一张:
参考:
0. @Import Annotation in Spring Framework
https://javabeat.net/use-import-importing-javaconfig-files-spring-projects/
1. Spring向容器注册Bean的高级应用 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1497795
2. how spring import annotation parse(要翻墙) https://laptrinhx.com/spring-import-annotation-source-parsing-3074679655/
注意我说的墙不是下面这样的墙