Java 8 实战学习笔记
@(JAVASE)[java8, 实战, lambda]
参考内容
Lambda表达式
Lambda环绕执行模式(抽离步骤)
原始代码
public static String processFile() throws IOException {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("data.txt"))) {
// 行为
return br.readLine();
}
}第1步 行为参数化
// 打印一行
String result = processFile((BufferedReader br) ->br.readLine());
// 打印两行
String result = processFile((BufferedReader br) ->br.readLine() + br.readLine());第2步 使用函数式接口来传递行为
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BufferedReaderProcessor {
String process(BufferedReader b) throws IOException;
}
public static String processFile(BufferedReaderProcessor p) throws IOException {
…
}第3步 执行一个行为
public static String processFile(BufferedReaderProcessor p) throws IOException {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("data.txt"))) {
return p.process(br);
}
}第4步 传递Lambda
// 打印一行
String oneLine = processFile((BufferedReader br) ->br.readLine());
// 打印两行
String twoLines = processFile((BufferedReader br) ->br.readLine() + br.readLine());函数接口及其原始类型特化
| 函数式接口 | 函数描述符 | 原始类型特化 |
|---|---|---|
Predicate<T> |
T->boolean |
IntPredicate,LongPredicate, DoublePredicate |
Consumer<T> |
T->void |
IntConsumer,LongConsumer, DoubleConsumer |
Function<T,R> |
T->R |
IntFunction<R>,IntToDoubleFunction,IntToLongFunction,LongFunction<R>,LongToDoubleFunction,LongToIntFunction,DoubleFunction<R>,ToIntFunction<T>,ToDoubleFunction<T>,ToLongFunction<T> |
Supplier<T> |
()->T |
BooleanSupplier,IntSupplier, LongSupplier, DoubleSupplier |
UnaryOperator<T> |
T->T |
IntUnaryOperator,LongUnaryOperator, DoubleUnaryOperator |
BinaryOperator<T> |
(T,T)->T |
IntBinaryOperator,LongBinaryOperator, DoubleBinaryOperator |
BiPredicate<L,R> |
(L,R)->boolean |
|
BiConsumer<T,U> |
(T,U)->void |
ObjIntConsumer<T>,ObjLongConsumer<T>, ObjDoubleConsumer<T> |
BiFunction<T,U,R> |
(T,U)->R |
ToIntBiFunction<T,U>,ToLongBiFunction<T,U>, ToDoubleBiFunction<T,U> |
方法引用
Lambda及其等效方法引用的例子
| Lambda | 等效的方法引用 |
|---|---|
(Apple a) -> a.getWeight() |
Apple::getWeight |
() -> Thread.currentThread().dumpStack() |
Thread.currentThread()::dumpStack |
(str, i) -> str.substring(i) |
String::substring |
(String s) -> System.out.println(s) |
System.out::println |
方法引用主要有三类
指向静态方法的方法引用
指向任意类型实例方法的方法引用
指向现有对象的实例方法的方法引用
构造函数引用
Supplier<Apple> c1 = Apple::new;
Apple a1 = c1.get();
// 这就等价于
Supplier<Apple> c1 = () -> new Apple();
Apple a1 = c1.get();
Function<Integer, Apple> c2 = Apple::new;
Apple a2 = c2.apply(110);
// 这就等价于
Function<Integer, Apple> c2 = (weight) -> new Apple(weight);
Apple a2 = c2.apply(110);
BiFunction<String, Integer, Apple> c3 = Apple::new;
Apple c3 = c3.apply("green", 110);
// 这就等价于
BiFunction<String, Integer, Apple> c3 = (color, weight) -> new Apple(color, weight);
Apple c3 = c3.apply("green", 110);使用流
归约
中间操作和终端操作
| 操作 | 类型 | 返回类型 | 使用的类型/函数式接口 | 函数描述符 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
filter |
中间 | Stream<T> |
Predicate<T> |
T -> boolean |
distinct |
中间(有状态-无界) | Stream<T> |
||
skip |
中间(有状态-有界) | Stream<T> |
long |
|
limit 中间(有状态-有界) |
Stream<T> |
long |
||
map |
中间 | Stream<R> |
Function<T,R> |
T -> R |
flatMap |
中间 | Stream<R> |
Function<T,Stream<R>> |
T -> Stream<R> |
sorted |
中间(有状态-无界) | Stream<T> |
Comparator<T> |
(T, T) -> int |
anyMatch |
终端 | boolean |
Predicate<T> |
T -> boolean |
noneMatch |
终端 | boolean |
Predicate<T> |
T -> boolean |
allMatch |
终端 | boolean |
Predicate<T> |
T -> boolean |
findAny |
终端 | Optional<T> |
||
findFirst |
终端 | Optional<T> |
||
forEach |
终端 | void |
Consumer<T> |
T -> void |
collect |
终端 | R |
Collector<T, A, R> |
|
reduce |
终端(有状态-有界) | Optional<T> |
BinaryOperator<T> |
(T, T) -> T |
count |
终端 | long |
数值流
原始类型流特化
IntStream、DoubleStream和LongStream。
映射到数值流
int calories = menu.stream()
.mapToInt(Dish::getCalories)
.sum();转换回对象流
IntStream intStream = menu.stream().mapToInt(Dish::getCalories);
Stream<Integer> stream = intStream.boxed();默认值OptionalInt
OptionalInt maxCalories = menu.stream()
.mapToInt(Dish::getCalories)
.max();
int max = maxCalories.orElse(1);数值范围
IntStream和LongStream的静态方法range和rangeClosed
IntStream evenNumbers = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 100).filter(n -> n % 2 == 0);
System.out.println(evenNumbers.count());构建流
由值创建流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Java 8 ", "Lambdas ", "In ", "Action");
stream.map(String::toUpperCase).forEach(System.out::println);
// 空流
Stream<String> emptyStream = Stream.empty();由数组创建流
int[] numbers = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13};
int sum = Arrays.stream(numbers).sum();由文件生成流
long uniqueWords = 0;
try(Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("data.txt"), Charset.defaultCharset())){
uniqueWords = lines.flatMap(line -> Arrays.stream(line.split(" ")))
.distinct()
.count();
} catch(IOException e) {
}由函数生成流:创建无限流
Stream API提供了两个静态方法来从函数生成流:
Stream.iterate和Stream.generate。一般来说,应该使用limit(n)来对这种流加以限制,以避免打印无穷多个值。
迭代
流的第一个元素是初始值0。然后加上2来生成新的值2,再加上2来得到新的值4,以此类推。这种iterate操作基本上是顺序的,因为结果取决于前一次应用。
// (T,UnaryOperator<T>)
Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 2)
.limit(10)
.forEach(System.out::println);生成
// Supplier<T>
Stream.generate(Math::random)
.limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);用流收集数据
Collectors类的静态工厂方法
| 工厂方法 | 返回类型 | 用于 | 使用示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
toList |
List<T> |
把流中所有项目收集到一个List |
List<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect(toList()); |
toSet |
Set<T> |
把流中所有项目收集到一个Set,删除重复项 |
Set<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect(toSet()); |
toCollection |
Collection<T> |
把流中所有项目收集到给定的供应源创建的集合 | Collection<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect( toCollection(),ArrayList::new); |
counting |
Long |
计算流中元素的个数 | long howManyDishes = menuStream.collect(counting()); |
summingInt |
Integer |
对流中项目的一个整数属性求和 | int totalCalories = menuStream.collect( summingInt(Dish::getCalories)); |
averagingInt |
Double |
计算流中项目Integer属性的平均值 |
double avgCalories = menuStream.collect( averagingInt(Dish::getCalories)); |
summarizingInt |
IntSummaryStatistics |
收集关于流中项目Integer属性的统计值,例如最大、最小、总和与平均值 |
IntSummaryStatistics menuStatistics = menuStream.collect( summarizingInt(Dish::getCalories)); |
joining |
String |
连接对流中每个项目调用toString方法所生成的字符串 |
String shortMenu = menuStream.map(Dish::getName).collect( joining(", ")); |
maxBy |
Optional<T> |
一个包裹了流中按照给定比较器选出的最大元素的Optional,或如果流为空则为Optional.empty() |
Optional<Dish> fattest = menuStream.collect( maxBy(comparingInt(Dish::getCalories))); |
minBy |
Optional<T> |
一个包裹了流中按照给定比较器选出的最小元素的Optional,或如果流为空则为Optional.empty() |
Optional<Dish> lightest = menuStream.collect( minBy(comparingInt(Dish::getCalories))); |
reducing |
归约操作产生的类型 | 从一个作为累加器的初始值开始,利用BinaryOperator与流中的元素逐个结合,从而将流归约为单个值 |
int totalCalories = menuStream.collect(reducing(0, Dish::getCalories, Integer::sum)); |
collectingAndThen |
转换函数返回的类型 | 包裹另一个收集器,对其结果应用转换函数 | int howManyDishes = menuStream.collect( collectingAndThen(toList(),List::size)); |
groupingBy |
Map<K, List<T>> |
根据项目的一个属性的值对流中的项目作问组,并将属性值作为结果Map的键 |
Map<Dish.Type,List<Dish>> dishesByType = menuStream.collect( groupingBy(Dish::getType)); |
partitioningBy |
Map<Boolean,List<T>> |
根据对流中每个项目应用谓词的结果来对项目进行分区 | Map<Boolean,List<Dish>> vegetarianDishes = menuStream.collect( partitioningBy(Dish::isVegetarian)); |
收集器接口
- T是流中要收集的项目的泛型。
- A是累加器的类型,累加器是在收集过程中用于累积部分结果的对象。
- R是收集操作得到的对象(通常但并不一定是集合)的类型。
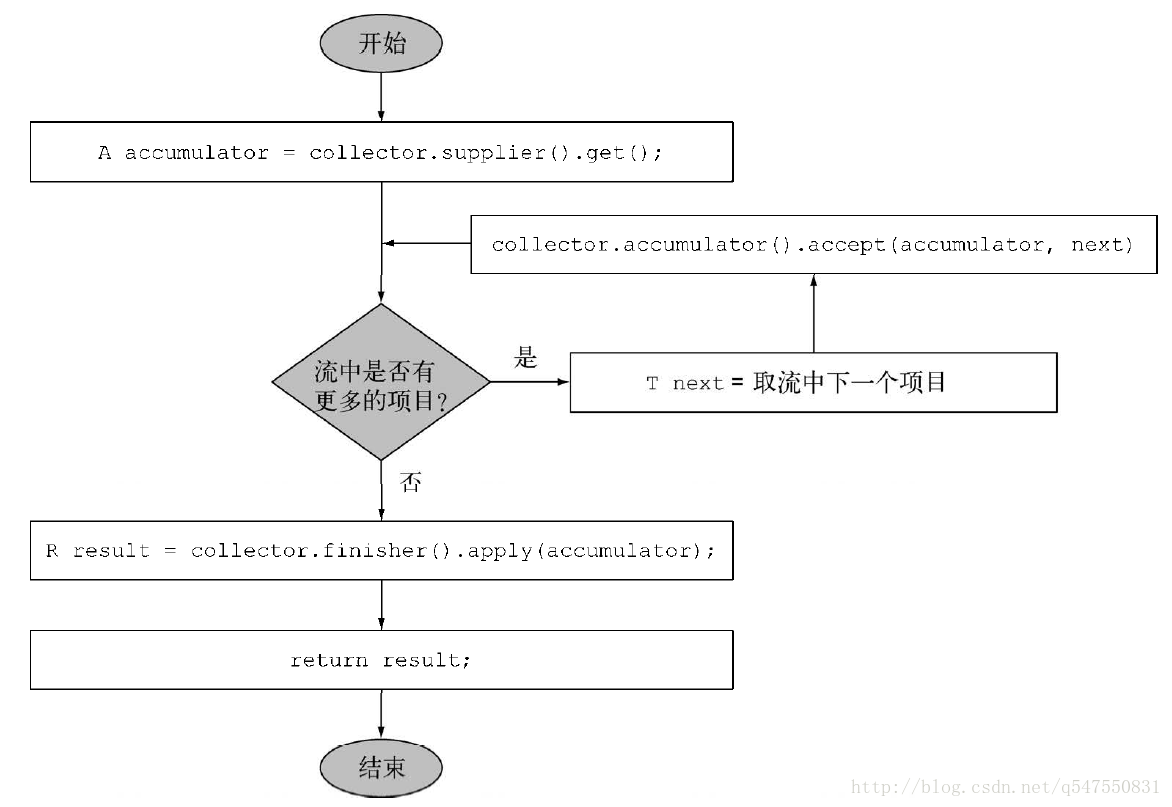
public interface Collector<T, A, R> {
// 建立新的结果容器
Supplier<A> supplier();
// 将元素添加到结果容器
BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator();
// 对结果容器应用最终转换
Function<A, R> finisher();
// 合并两个结果容器
BinaryOperator<A> combiner();
// UNORDERED——归约结果不受流中项目的遍历和累积顺序的影响。
// CONCURRENT——accumulator函数可以从多个线程同时调用,且该收集器可以并行归约流。如果收集器没有标为UNORDERED,那它仅在用于无序数据源时才可以并行归约。
// IDENTITY_FINISH——这表明完成器方法返回的函数是一个恒等函数,可以跳过。这种情况下,累加器对象将会直接用作归约过程的最终结果。这也意味着,将累加器A不加检查地转换为结果R是安全的。
Set<Characteristics> characteristics();
}顺序归约过程的逻辑步骤
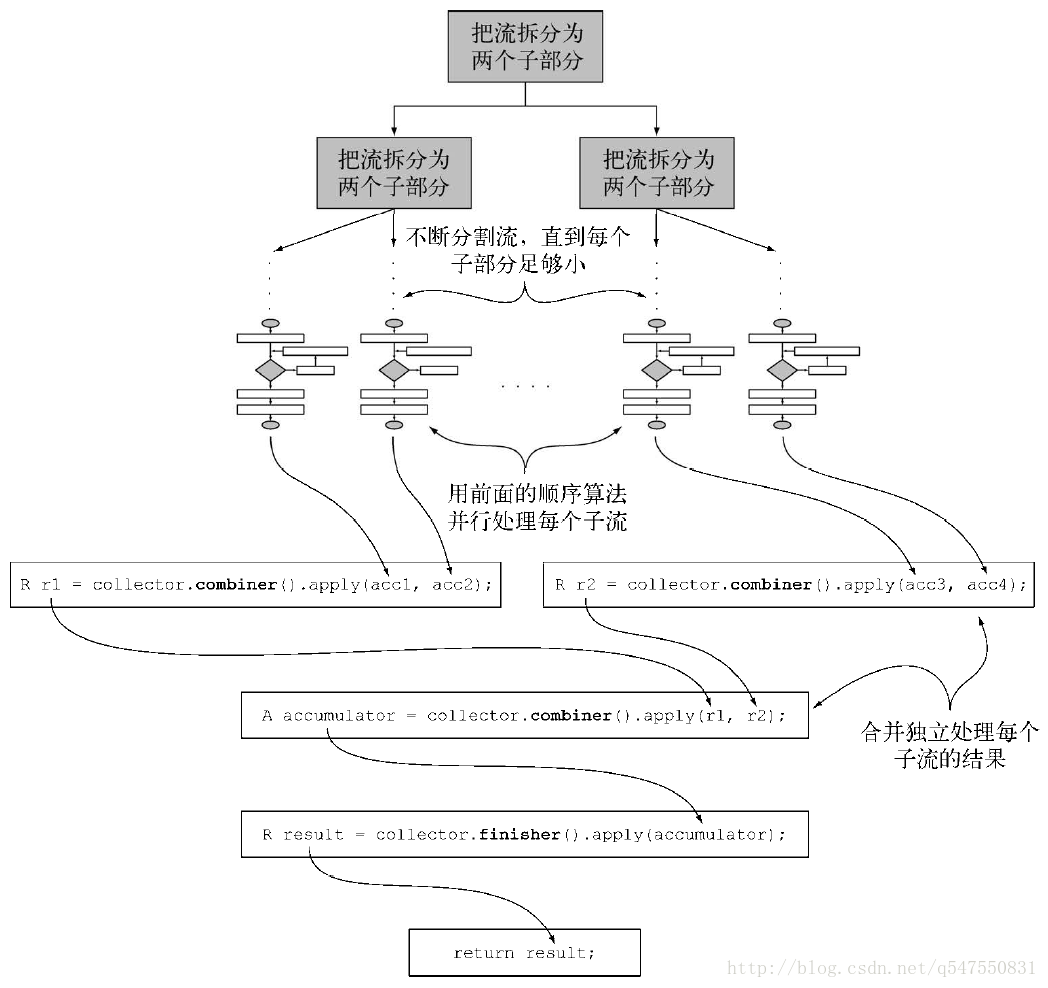
使用combiner方法来并行化归约过程
案例
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.*;
import java.util.stream.Collector;
import static java.util.stream.Collector.Characteristics.*;
public class ToListCollector<T> implements Collector<T, List<T>, List<T>> {
@Override
public Supplier<List<T>> supplier() {
return ArrayList::new;
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<List<T>, T> accumulator() {
return List::add;
}
@Override
public Function<List<T>, List<T>> finisher() {
return Function.indentity();
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<List<T>> combiner() {
return (list1, list2) -> {
list1.addAll(list2);
return list1;
};
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(EnumSet.of(IDENTITY_FINISH, CONCURRENT));
}
}// 进行自定义收集而不去实现Collector
// Supplier<R> supplier, BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator, BiConsumer<R, R> combiner
List<Dish> dishes = menuStream.collect(
ArrayList::new,
List::add,
List::addAll);用Optional取代null
Optional类的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
empty |
返回一个空的Optional实例 |
filter |
如果值存在并且满足提供的谓词,就返回包含该值的Optional对象;否则返回一个空的Optional对象 |
flatMap |
如果值存在,就对该值执行提供的mapping函数调用,返回一个Optional类型的值,否则就返回一个空的Optional对象 |
get |
如果该值存在,将该值用Optional封装返回,否则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常 |
ifPresent |
如果值存在,就执行使用该值的方法调用,否则什么也不做 |
isPresent |
如果值存在就返回true,否则返回false |
map |
如果值存在,就对该值执行提供的mapping函数调用 |
of |
将指定值用Optional封装之后返回,如果该值为null,则抛出一个NullPointerException异常 |
ofNullable |
将指定值用Optional封装之后返回,如果该值为null,则返回一个空的Optional对象 |
orElse |
如果有值则将其返回,否则返回一个默认值 |
orElseGet |
如果有值则将其返回,否则返回一个由指定的Supplier接口生成的值 |
orElseThrow |
如果有值则将其返回,否则抛出一个由指定的Supplier接口生成的异常 |
实战示例
用Optional封装可能为null的值
Optional<Object> value = Optional.ofNullable(map.get("key"));异常与Optional的对比
public static Optional<Integer> stringToInt(String s) {
try {
return Optional.of(Integer.parseInt(s));
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}把所有内容整合起来
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Properties;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
public class OptionalTest {
@Test
public void testOptional() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("a", "5");
props.setProperty("b", "true");
props.setProperty("c", "-3");
assertEquals(5, readDuration(props, "a"));
assertEquals(0, readDuration(props, "b"));
assertEquals(0, readDuration(props, "c"));
assertEquals(0, readDuration(props, "d"));
}
private int readDuration(Properties props, String name) {
return Optional.ofNullable(props.getProperty(name))
.flatMap(OptionalTest::stringToInt)
.filter(i -> i > 0)
.orElse(0);
}
private static Optional<Integer> stringToInt(String s) {
try {
return Optional.of(Integer.parseInt(s));
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
}CompletableFuture组合式异步编程
实现异步API
package com.switchvov.future;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Shop {
private String name;
public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsyncStatic(String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> calculatePrice(product));
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync(String product) {
CompletableFuture<Double> futurePrice = new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
futurePrice.complete(price);
} catch (Exception e) {
futurePrice.completeExceptionally(e);
}
}).start();
return futurePrice;
}
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble()
* product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
private static void delay() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class ShopTest {
@Test
public void testShop() {
Shop shop = new Shop("BestShop");
long start = System.nanoTime();
// Future<Double> futurePrice = shop.getPriceAsync("my favorite produce");
Future<Double> futurePrice = shop.getPriceAsyncStatic("my favorite produce");
long invocationTime = (System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000;
System.out.println("Invocation returned after " + invocationTime + " msecs");
// doSomethingElse();
try {
double price = futurePrice.get();
System.out.printf("Price is %.2f%n", price);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
long retrievalTime = (System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000;
System.out.println("Price returned after " + retrievalTime + " msecs");
}
}密集IO任务各种实现间的对比
测试代码
package com.switchvov.future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Shop {
private String name;
public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble()
* product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
private static void delay() {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Warmup(iterations = 1)
@Measurement(iterations = 2)
public class ShopMeasure {
private final String SHOP_PREFIX = "Shop ";
private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 + 1;
private final String PRODUCT_NAME = "Java 8实战";
@Benchmark
public void measureSequential() {
System.out.println(findPricesSequential(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
@Benchmark
public void measureParallelStream() {
System.out.println(findPricesParallelStream(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
@Benchmark
public void measureCompletableFuture() {
System.out.println(findPricesCompletableFuture(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
@Benchmark
public void measureCustomCompletableFuture() {
System.out.println(findPricesCustomCompletableFuture(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
private List<String> findPricesSequential(String product) {
return getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private List<String> findPricesParallelStream(String product) {
return getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).parallelStream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private List<String> findPricesCompletableFuture(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> shop.getName() + " price is " + shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private final Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Math.min(getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).size(), 100), runnable -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
});
private List<String> findPricesCustomCompletableFuture(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> shop.getName() + " price is " + shop.getPrice(product), executor))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private List<Shop> getShops(int shopNumber) {
return IntStream.range(0, shopNumber)
.mapToObj(index -> new Shop(SHOP_PREFIX + index))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options options = new OptionsBuilder()
.forks(1)
.include(ShopMeasure.class.getSimpleName())
.build();
new Runner(options).run();
}
}JMH测试结果
- 商店数:
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
| Benchmark | Mode | Cnt(次数) | Score | Error | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShopMeasure.measureCompletableFuture | avgt | 2 | 1.001 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureCustomCompletableFuture | avgt | 2 | 0.501 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureParallelStream | avgt | 2 | 0.502 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureSequential | avgt | 2 | 4.004 | s/op |
- 商店数:Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 + 1
| Benchmark | Mode | Cnt(次数) | Score | Error | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShopMeasure.measureCompletableFuture | avgt | 2 | 1.502 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureCustomCompletableFuture | avgt | 2 | 0.502 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureParallelStream | avgt | 2 | 1.502 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureSequential | avgt | 2 | 8.506 | s/op |
由此可以看出在IO密集任务中,定制执行器的CompletableFuture效率是最高的。
调整线程池的大小
《Java并发编程实战》一书中,Brian Goetz和合著者们为线程池大小的优化提供了不少中肯的建议。这非常重要,如果线程池中线程的数量过多,最终它们会竞争稀缺的处理器和内存资源,浪费大量的时间在上下文切换上。反之,如果线程的数目过少,正如你的应用所面临的情况,处理器的一些核可能就无法充分利用。Brian Goetz建议,线程池大小与处理器的利用率之比可以使用下面的公式进行估算:
Nthreads=NCPU∗UCPU∗(1+WC) 其中:
-NCPU 是处理器的核的数目,可以通过Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()得到
-UCPU 是期望的CPU利用率(该值应该介于0和1之间)
-WC 是等待时间与计算时间的比率,比如说IO操作即为等待时间,计算处理即为计算时间
并行——使用流还是CompletableFutures?
对集合进行并行计算有两种方式:要么将其转化为并行流,利用map这样的操作开展工作,要么枚举出集合中的每一个元素,创建新的线程,在CompletableFuture内对其进行操作。后者提供了更多的灵活性,可以调整线程池的大小,而这能帮助确保整体的计算不会因为线程都在等待I/O而发生阻塞。
使用这些API的建议如下:
- 如果进行的是计算密集型的操作,并且没有I/O,那么推荐使用Stream接口,因为实现简单,同时效率也可能是最高的(如果所有的线程都是计算密集型的,那就没有必要创建比处理器核数更多的线程)。
- 反之,如果并行的工作单元还涉及等待I/O的操作(包括网络连接等待),那么使用CompletableFuture灵活性更好,可以依据等待/计算,或者WC 的比率设定需要使用的线程数。这种情况不使用并行流的另一个原因是,处理流的流水线中如果发生I/O等待,流的延迟特性很难判断到底什么时候触发了等待。
对多个异步任务进行流水线操作
package com.switchvov.future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Shop {
private String name;
public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPrice(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code.values()
[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(Discount.Code.values().length)];
return String.format("%s:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble()
* product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
private static void delay() {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Quote {
private final String shopName;
private final double price;
private final Discount.Code discountCode;
public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code discountCode) {
this.shopName = shopName;
this.price = price;
this.discountCode = discountCode;
}
public static Quote parse(String quoteString) {
String[] split = quoteString.split(":");
String shopName = split[0];
double price = Double.parseDouble(split[1]);
Discount.Code discountCode = Discount.Code.valueOf(split[2]);
return new Quote(shopName, price, discountCode);
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Discount.Code getDiscountCode() {
return discountCode;
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Discount {
public enum Code {
NONE(0), SILVER(5), GOLD(10), PLATINUM(15), DIAMOND(20);
private final int percentage;
Code(int percentage) {
this.percentage = percentage;
}
}
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote) {
return quote.getShopName() + " price is " +
Discount.applyDiscount(quote.getPrice(), quote.getDiscountCode());
}
private static double applyDiscount(double price, Code code) {
delay();
return price * (100 - code.percentage) / 100;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Warmup(iterations = 1)
@Measurement(iterations = 2)
public class ShopMeasure {
private final String SHOP_PREFIX = "Shop ";
private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 + 1;
private final String PRODUCT_NAME = "Java 8实战";
@Benchmark
public void measureSequential() {
System.out.println(findPricesSequential(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
@Benchmark
public void measureCustomCompletableFuture() {
System.out.println(findPricesCustomCompletableFuture(PRODUCT_NAME));
}
private List<String> findPricesSequential(String product) {
return getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice(product))
.map(Quote::parse)
.map(Discount::applyDiscount)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private final Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Math.min(getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).size(), 100), runnable -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
});
private List<String> findPricesCustomCompletableFuture(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse))
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(
quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private List<Shop> getShops(int shopNumber) {
return IntStream.range(0, shopNumber)
.mapToObj(index -> new Shop(SHOP_PREFIX + index))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options options = new OptionsBuilder()
.forks(1)
.include(ShopMeasure.class.getSimpleName())
.build();
new Runner(options).run();
}
}JMH测试结果
- 商店数:
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
| Benchmark | Mode | Cnt(次数) | Score | Error | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShopMeasure.measureCustomCompletableFuture | avgt | 2 | 2.002 | s/op | |
| ShopMeasure.measureSequential | avgt | 2 | 16.006 | s/op |
合并两个独立的CompletableFuture
private Future<Double> fromCNYToUSD(Shop shop, String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product))
.thenApply(productString -> Quote.parse(productString).getPrice())
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> getRate(Money.CNY, Money.USD)), (price, rate) -> price * rate);
}
enum Money {
CNY(1), USD(0.15);
private double rate;
Money(double rate) {
this.rate = rate;
}
}
private double getRate(Money from, Money to) {
delay();
return to.rate / from.rate;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}响应CompletableFuture的completion事件
package com.switchvov.future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
public class Shop {
private String name;
public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPrice(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code.values()
[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(Discount.Code.values().length)];
return String.format("%s:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
randomDelay();
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
private static void randomDelay() {
int delay = 500 + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(2000);
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}package com.switchvov.future;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* @Author Switch
* @Date 2017/12/10
*/
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Warmup(iterations = 1)
@Measurement(iterations = 2)
public class ShopMeasure {
private final String SHOP_PREFIX = "Shop ";
private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// private final int SHOP_NUMBER = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 + 1;
private final String PRODUCT_NAME = "Java 8实战";
@Benchmark
public void measureFindPricesCustomCompletableFutureStream() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture[] futures = findPricesCustomCompletableFutureStream(PRODUCT_NAME)
.map(future -> future.thenAccept(string ->
System.out.println(string + " (done in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " msecs)")))
.toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new);
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();
System.out.println("All shops have now responded in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " msecs");
}
private final Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.min(getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).size(), 100), runnable -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
});
private Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> findPricesCustomCompletableFutureStream(String product) {
return getShops(SHOP_NUMBER).stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse))
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(
quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)));
}
private List<Shop> getShops(int shopNumber) {
return IntStream.range(0, shopNumber)
.mapToObj(index -> new Shop(SHOP_PREFIX + index))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options options = new OptionsBuilder()
.forks(1)
.include(ShopMeasure.class.getSimpleName())
.build();
new Runner(options).run();
}
}其余类未更改,详见对多个异步任务进行流水线操作
新的日期和时间API
LocalDate、LocalTime、Instant、Duration 以及Period
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2017, 12, 11);
System.out.println(date); // 2017-12-11
System.out.println(date.getYear()); // 2017
System.out.println(date.getMonth()); // DECEMBER
System.out.println(date.getDayOfMonth()); // 11
System.out.println(date.getDayOfWeek()); // MONDAY
System.out.println(date.lengthOfMonth()); // 31
System.out.println(date.isLeapYear()); // false
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); // 获取今天Date
int year = date.get(ChronoField.YEAR);
int month = date.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR);
int day = date.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(year + " " + month + " " + day); // 2017 12 11
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(20, 14, 30);
System.out.println(time.getHour()); // 20
System.out.println(time.getMinute()); // 14
System.out.println(time.getSecond()); // 30
date = LocalDate.parse("2017-12-11");
System.out.println(date); // 2017-12-11
time = LocalTime.parse("20:14:30");
System.out.println(time); // 20:14:30
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.of(2017, Month.DECEMBER, 11, 20, 14, 30);
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.of(date, time);
LocalDateTime dt3 = date.atTime(20, 14, 30);
LocalDateTime dt4 = date.atTime(time);
LocalDateTime dt5 = time.atDate(date);
date = dt1.toLocalDate();
time = dt1.toLocalTime();
System.out.println(Instant.ofEpochSecond(3)); // 1970-01-01T00:00:03Z
System.out.println(Instant.ofEpochSecond(3, 1)); // 1970-01-01T00:00:03.000000001Z
System.out.println(Instant.ofEpochSecond(2, 1_000_000_000)); // 1970-01-01T00:00:03Z
System.out.println(Instant.ofEpochSecond(4, -1_000_000_000)); // 1970-01-01T00:00:03Z
Duration d1 = Duration.between(time, time.plus(1, ChronoUnit.MINUTES));
System.out.println(d1); // PT1M
Duration d2 = Duration.between(dt1, dt1.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS));
System.out.println(d2); // PT24H
Duration d3 = Duration.between(dt1, dt1.minus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS));
System.out.println(d3); // PT-24H
Duration d4 = Duration.between(Instant.ofEpochSecond(0), Instant.ofEpochSecond(2, 1));
System.out.println(d4); // PT2.000000001S
System.out.println(Duration.ofMinutes(3)); // PT3M
System.out.println(Duration.of(3, ChronoUnit.MINUTES)); // PT3M
System.out.println(Period.ofDays(10)); // P10D
System.out.println(Period.ofWeeks(3)); // P21D
System.out.println(Period.of(2, 6, 1)); // P2Y6M1D日期-时间类中表示时间间隔的通用方法
| 方法名 | 是否是静态方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|---|
| between | 是 | 创建两个时间点之间的interval |
| from | 是 | 由一个临时时间点创建interval |
| of | 是 | 由它的组成部分创建interval的实例 |
| parse | 是 | 由字符串创建interval的实例 |
| addTo | 否 | 创建该interval的副本,并将其叠加到某个指定的temporal对象 |
| get | 否 | 读取该interval的状态 |
| isNegative | 否 | 检查该interval是否为负值,不包含零 |
| isZero | 否 | 检查该interval的时长是否为零 |
| minus | 否 | 通过减去一定的时间创建该interval的副本 |
| multipliedBy | 否 | 将interval的值乘以某个标量创建该interval的副本 |
| negated | 否 | 以忽略某个时长的方式创建该interval的副本 |
| plus | 否 | 以增加某个指定的时长的方式创建该interval的副本 |
| subtractFrom | 否 | 从指定的temporal对象中减去该interval |
操纵、解析和格式化日期
表示时间点的日期-时间类的通用方法
| 方法名 | 是否是静态方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|---|
| from | 是 | 依据传入的Temporal对象创建对象实例 |
| now | 是 | 依据系统时钟创建Temporal对象 |
| of | 是 | 由Temporal对象的某个部分创建该对象的实例 |
| parse | 是 | 由字符串创建Temporal对象的实例 |
| atOffset | 否 | 将Temporal对象和某个时区偏移相结合 |
| atZone | 否 | 将Temporal对象和某个时区相结合 |
| format | 否 | 使用某个指定的格式器将Temporal对象转换为字符串(Instant类不提供该方法) |
| get | 否 | 读取Temporal对象的某一部分的值 |
| minus | 否 | 创建Temporal对象的一个副本,通过将当前Temporal对象的值减去一定的时长创建该副本 |
| plus | 否 | 创建Temporal对象的一个副本,通过将当前Temporal对象的值加上一定的时长创建该副本 |
| with | 否 | 以该Temporal对象为模板,对某些状态进行修改创建该对象的副本 |
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2017, 12, 11);
System.out.println(date1); // 2017-12-11
LocalDate date2 = date1.withYear(2014);
System.out.println(date2); // 2014-12-11
LocalDate date3 = date2.withDayOfMonth(10);
System.out.println(date3); // 2014-12-10
LocalDate date4 = date3.with(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 5);
System.out.println(date4); // 2014-05-10
LocalDate date5 = date4.plusWeeks(1);
System.out.println(date5); // 2014-05-17
LocalDate date6 = date5.minusYears(3);
System.out.println(date6); // 2011-05-17
LocalDate date7 = date6.plus(6, ChronoUnit.MONTHS);
System.out.println(date7); // 2011-11-17TemporalAdjuster类中的工厂方法
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| dayOfWeekInMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为同一个月中每一周的第几天 |
| firstDayOfMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为当月的第一天 |
| firstDayOfNextMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为下月的第一天 |
| firstDayOfNextYear | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为明年的第一天 |
| firstDayOfYear | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为当年的第一天 |
| firstInMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为同一个月中,第一个符合星期几要求的值 |
| lastDayOfMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为当月的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfNextMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为下月的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfNextYear | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为明年的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfYear | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为今年的最后一天 |
| lastInMonth | 创建一个新的日期,它的值为同一个月中,最后一个符合星期几要求的值 |
| next/previous | 创建一个新的日期,并将其值设定为日期调整后或者调整前,第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期 |
| nextOrSame/previousOrSame | 创建一个新的日期,并将其值设定为日期调整后或者调整前,第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期,如果该日期已经符合要求,直接返回该对象 |
LocalDate date8 = date7.with(TemporalAdjusters.nextOrSame(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY));
System.out.println(date8); // 2011-11-20
LocalDate date9 = date8.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(date9); // 2011-11-30TemporalAdjuster接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TemporalAdjuster {
Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal);
}定制的TemporalAdjuster
public class NextWorkingDay implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
DayOfWeek dow = DayOfWeek.of(temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK));
int dayToAdd = 1;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.FRIDAY) dayToAdd = 3;
else if (dow == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY) dayToAdd = 2;
return temporal.plus(dayToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
}
} date = date.with(temporal -> {
DayOfWeek dow = DayOfWeek.of(temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK));
int dayToAdd = 1;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.FRIDAY) dayToAdd = 3;
else if (dow == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY) dayToAdd = 2;
return temporal.plus(dayToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
}); TemporalAdjuster nextWorkingDay = TemporalAdjusters.ofDateAdjuster(temporal -> {
DayOfWeek dow = DayOfWeek.of(temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK));
int dayToAdd = 1;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.FRIDAY) dayToAdd = 3;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY) dayToAdd = 2;
return temporal.plus(dayToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
});
date =date.with(nextWorkingDay);打印输出及解析日期-时间对象
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2017, 12, 11);
String s1 = date.format(DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE); // 20171211
String s2 = date.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE); // 2017-12-11
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.parse("20171211", DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse("2017-12-11", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd/MM/yyyy");
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2017, 12, 11);
String formattedDate = date1.format(formatter);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse(formattedDate, formatter);构造一个DateTimeFormatter
DateTimeFormatter italianFormatter = new DateTimeFormatterBuilder()
.appendText(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH)
.appendLiteral(". ")
.appendText(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR)
.appendLiteral(" ")
.appendText(ChronoField.YEAR)
.parseCaseInsensitive()
.toFormatter(Locale.ITALIAN);———–参考《Java 8 实战》