目录
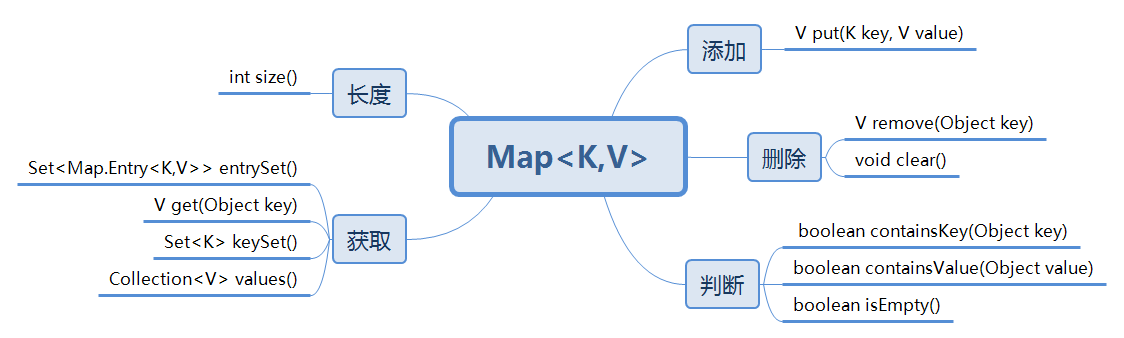
Map接口的常用功能
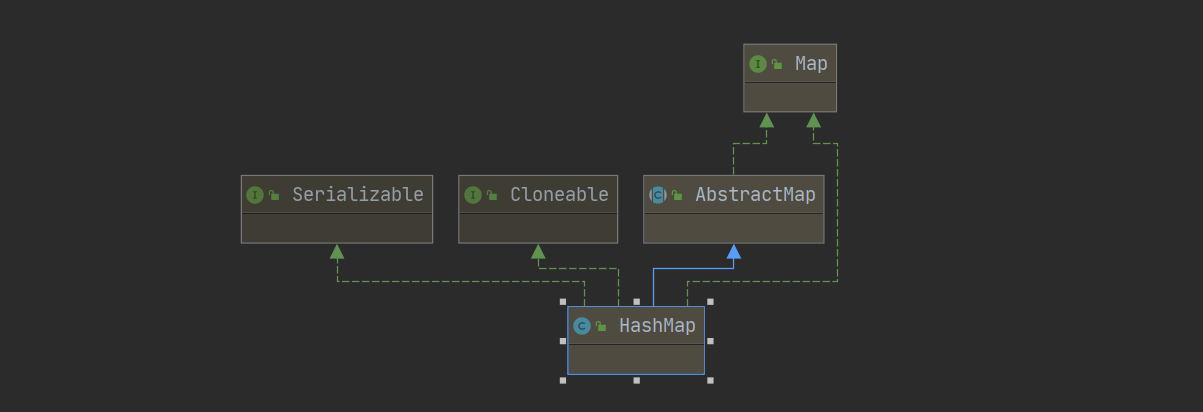
Map接口的常用子类
HashMap<K,V>、Hashtable<K,V>,LinkedHashMap<K,V>,TreeMap<K,V>
HashMap
1、添加功能
如果是第一次存储该键,那么直接存储元素,返回null;
如果键不是第一次存储,就用新value替换以前的旧value,返回旧vlaue。
public String put(K key, V value)
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/17 13:12
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("001", "宝可梦");
map.put("004", "美团");
map.put("002", "奥特曼");
map.put("003", "饿了么");
System.out.println(map);
//{001=宝可梦, 002=奥特曼, 003=饿了么, 004=美团}
//HashMap的存储只与键有关,和值无关
//键相同时,值会进行覆盖
String s = map.put("005", "谭松韵");
System.out.println(s);
//null
//键不同,直接添加,返回null
String s1 = map.put("005", "谭晶晶");
System.out.println(s1);
//谭松韵
//键相同,覆盖原来的value,返回旧value
}
}
Student类型作为键和值
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/17 14:30
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return Objects.equals(name, student.name) &&
Objects.equals(age, student.age);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/17 14:30
*/
public class MyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Student> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("s001", new Student("张三", 23));
hashMap.put("s001", new Student("李四", 24));
hashMap.put("s002", new Student("王五", 25));
hashMap.put("s003", new Student("赵六", 26));
System.out.println(hashMap);
//{s003=Student{name='赵六', age=26}, s002=Student{name='王五', age=25}, s001=Student{name='李四', age=24}}
HashMap<Student, String> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();
hashMap1.put(new Student("张三", 23), "s004");
hashMap1.put(new Student("张三", 23), "s005");
hashMap1.put(new Student("李四", 24), "s006");
hashMap1.put(new Student("王五", 25), "s007");
System.out.println(hashMap1);
//{Student{name='张三', age=23}=s005, Student{name='李四', age=24}=s006, Student{name='王五', age=25}=s007}
}
}
2、删除功能
public V remove(Object key):根据键删除键值对,并把值返回
public void clear():移除所有的键值对元素
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 18:44
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("s001", "151");
map.put("s002", "152");
map.put("s003", "153");
String remove = map.remove("s001");
//删除返回V类型,如果删除失败,返回null
System.out.println(remove);
//151
System.out.println(map);
//{s003=153, s002=152}
boolean s003 = map.remove("s003", "151");
//删除返回boolean类型
System.out.println(s003);
//false
System.out.println(map);
//{s003=153, s002=152}
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
//{}
}
}
3、判断功能
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:05
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(100, "aaa");
hashMap.put(200, "bbb");
hashMap.put(300, "ccc");
boolean b = hashMap.containsKey(200);
System.out.println(b);
//true
boolean ccc = hashMap.containsValue("ccc");
System.out.println(ccc);
//true
boolean empty = hashMap.isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty);
//false
}
}
4、获取功能
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:29
*/
public class MyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(100, "aaa");
hashMap.put(200, "bbb");
hashMap.put(300, "ccc");
hashMap.put(400, "ddd");
//1、通过键找值的方式遍历
Set<Integer> integers = hashMap.keySet();
for (Integer integer : integers) {
String s = hashMap.get(integer);
System.out.println(integer + ":" + s);
}
//400:ddd
//100:aaa
//200:bbb
//300:ccc
//2、通过把所有的键值对对象获取出来
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
//遍历所有的键值对对象
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
//400:ddd
//100:aaa
//200:bbb
//300:ccc
}
entries.forEach(System.out::println);
//400=ddd
//100=aaa
//200=bbb
//300=ccc
//3、通过JDK 1.8的forEach方法
hashMap.forEach((t,u) -> System.out.println(t + ":" + u));
//400:ddd
//100:aaa
//200:bbb
//300:ccc
}
}
package org.westos.demo2;
import org.westos.demo.Student;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:40
*/
public class MyTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Student> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("s001", new Student("张三", 23));
hashMap.put("s002", new Student("王五", 25));
hashMap.put("s003", new Student("赵六", 26));
//1、
Set<String> strings = hashMap.keySet();
for (String string : strings) {
Student student = hashMap.get(string);
System.out.println(string + "---" + student);
}
//s003---Student{name='赵六', age=26}
//s002---Student{name='王五', age=25}
//s001---Student{name='张三', age=23}
//2、
Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> entry : entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
}
//s003:Student{name='赵六', age=26}
//s002:Student{name='王五', age=25}
//s001:Student{name='张三', age=23}
//3、
hashMap.forEach((t,u) -> {
System.out.println(t + "=" + u);
});
//s003=Student{name='赵六', age=26}
//s002=Student{name='王五', age=25}
//s001=Student{name='张三', age=23}
}
}
package org.westos.demo2;
import org.westos.demo.Student;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:45
*/
public class MyTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Student> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("s001", new Student("张三", 23));
hashMap.put("s002", new Student("王五", 25));
hashMap.put("s003", new Student("赵六", 26));
Collection<Student> values = hashMap.values();
System.out.println(values.getClass().getName());
//java.util.HashMap$Values
values.forEach(System.out::println);
//Student{name='赵六', age=26}
//Student{name='王五', age=25}
//Student{name='张三', age=23}
}
}
5、长度功能
HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(100, "aaa");
hashMap.put(200, "bbb");
hashMap.put(300, "ccc");
int size = hashMap.size();
System.out.println(size);
//3
LinkedHashMap
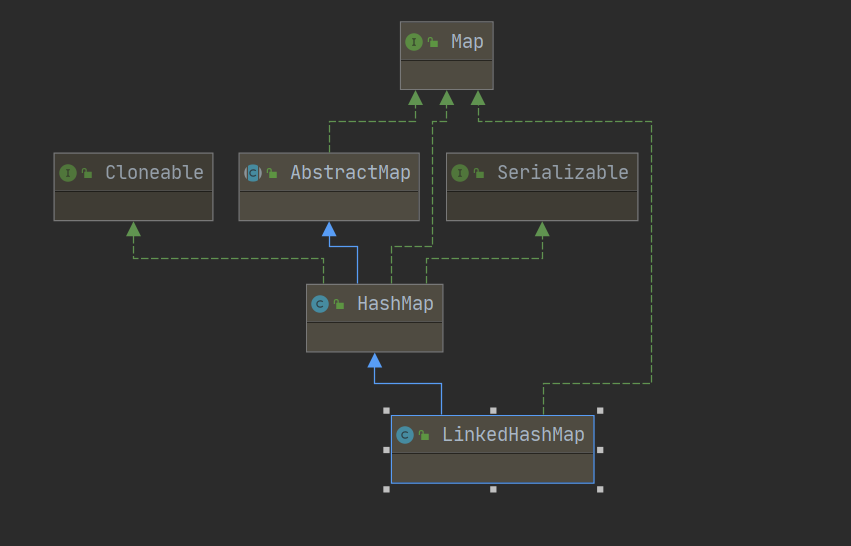
相比HashMap,可以保证元素的添加顺序和迭代顺序一致,通过双向链表实现。
package org.westos.demo3;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:50
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
linkedHashMap.put(100, "aaa");
linkedHashMap.put(200, "bbb");
linkedHashMap.put(400, "ccc");
linkedHashMap.put(300, "ddd");
System.out.println(linkedHashMap);
//{100=aaa, 200=bbb, 400=ccc, 300=ddd}
}
}
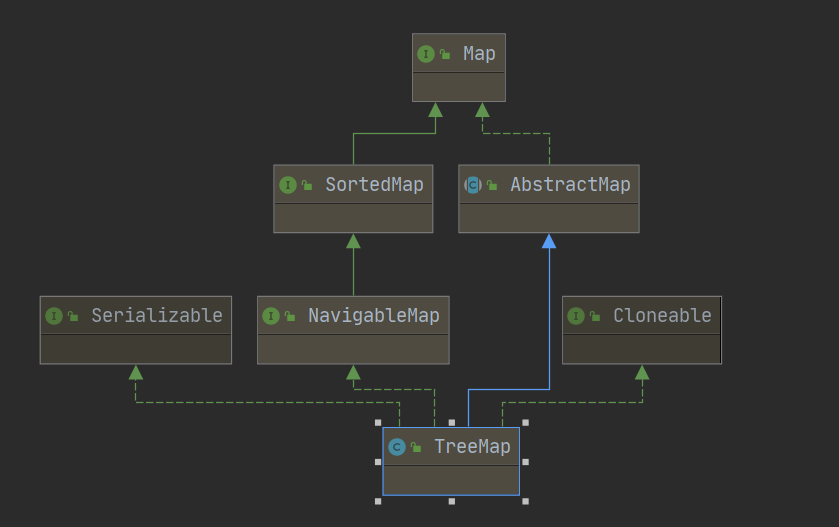
TreeMap
package org.westos.demo3;
import org.westos.demo.Student;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 19:52
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Student, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(((o1, o2) -> {
int compare = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
if (compare != 0) {
return compare;
} else {
return Integer.compare(o1.getAge(), o2.getAge());
}
}));
//自然排序:如果TreeMap是无参构造,那么要求键所在类实现Comparable接口
//比较器排序:如果TreeMap是有参构造,那么要求参数传递一个Comparator接口的子类对象
treeMap.put(new Student("Aaa", 12), 1);
treeMap.put(new Student("Bbb", 11), 2);
treeMap.put(new Student("Aaa", 10), 3);
treeMap.forEach((t,u)-> System.out.println(t+"="+u));
//Student{name='Aaa', age=10}=3
//Student{name='Aaa', age=12}=1
//Student{name='Bbb', age=11}=2
}
}
Hashtable
HashMap允许键和值为null,Hashtable不允许键和值为null。
HashMap线程不安全,Hashtable线程安全。
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/13 23:35
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> stringStringHashMap = new HashMap<>();
stringStringHashMap.put(null, null);
String s = stringStringHashMap.get(null);
System.out.println(s);
//null
stringStringHashMap.put(null, "abc");
s = stringStringHashMap.get(null);
System.out.println(s);
//abc
}
}
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/13 23:35
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String, String> stringStringHashMap = new Hashtable<>();
stringStringHashMap.put(null, null);
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at java.util.Hashtable.put(Hashtable.java:460)
at org.westos.demo.MyTest.main(MyTest.java:14)
*/
}
}
练习
1、统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数
"aababcabcdabcde",获取字符串中每一个字母出现的次数要求结果:a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)。
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 20:30
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "aababcabcdabcde";
HashMap<Character, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
if (hashMap.containsKey(c)) {
Integer integer = hashMap.get(c);
integer += 1;
hashMap.put(c, integer);
} else {
hashMap.put(c, 1);
}
}
//遍历HashMap
hashMap.forEach((t, u) -> System.out.println(t + "=" + u));
get(str);
}
public static void get(String s) {
int[] nums = new int[26];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
nums[c-'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
System.out.println("字符" + (char)(i + 'a') + "出现" + nums[i] + "次。");
}
}
//字符a出现5次。
//字符b出现4次。
//字符c出现3次。
//字符d出现2次。
//字符e出现1次。
}
}
2、HashMap嵌套HashMap
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 20:46
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
hm1.put("张三", 23);
hm1.put("李四", 24);
HashMap<String, Integer> hm2 = new HashMap<>();
hm2.put("王五", 25);
hm2.put("赵六", 26);
HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put("基础班", hm1);
hm.put("就业班", hm2);
Set<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<String, Integer>>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> entry : entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(key);
HashMap<String, Integer> value = entry.getValue();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries1 = value.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> integerEntry : entries1) {
String key1 = integerEntry.getKey();
Integer value1 = integerEntry.getValue();
System.out.println("\t" + key1 + " " + value1);
}
}
//就业班
// 王五 25
// 赵六 26
//基础班
// 李四 24
// 张三 23
}
}
3、HashMap嵌套ArrayList
package org.westos.demo;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 20:52
*/
public class MyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("吕布", "周瑜"));
ArrayList<String> strings1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("令狐冲", "林平之"));
ArrayList<String> strings2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("郭靖", "黄蓉"));
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put("三国演义", strings);
hm.put("笑傲江湖", strings1);
hm.put("射雕英雄转", strings2);
Set<String> strings3 = hm.keySet();
for (String s : strings3) {
System.out.println(s);
ArrayList<String> strings4 = hm.get(s);
for (String s1 : strings4) {
System.out.println("\t" + s1);
}
}
//射雕英雄转
// 郭靖
// 黄蓉
//三国演义
// 吕布
// 周瑜
//笑傲江湖
// 令狐冲
// 林平之
}
}
4、ArrayList嵌套HashMap
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 20:57
*/
public class MyTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("周瑜", "小乔");
map.put("吕布", "貂蝉");
HashMap<String, String> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map1.put("杨过", "小龙女");
HashMap<String, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("令狐冲", "任盈盈");
map2.put("林平之", "岳灵珊");
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> hashMaps = new ArrayList<>();
hashMaps.add(map);
hashMaps.add(map1);
hashMaps.add(map2);
for (HashMap<String, String> hashMap : hashMaps) {
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries =
hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
System.out.println("----------------");
}
//吕布=貂蝉
//周瑜=小乔
//----------------
//杨过=小龙女
//郭靖=黄蓉
//----------------
//令狐冲=任盈盈
//林平之=岳灵珊
//----------------
}
}
Collections工具类

Collections是一个操作Set、List和Map等集合的工具类,提供了一系列的静态方法,对集合的元素进行排序、查询和修改,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变,对集合对象实现同步控制等方法。
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list)
//排序,默认按照自然顺序
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c);
//定制排序规则
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 21:04
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 3, 0, -2, -4, 12, 10));
integers.sort(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
}
});
//1、调用集合本身的sort方法
System.out.println(integers);
//[-4, -2, 0, 1, 3, 10, 12]
Collections.sort(integers);
//2、使用元素的自然排序(Comparable接口),默认从小到大排序
System.out.println(integers);
//[-4, -2, 0, 1, 3, 10, 12]
Collections.sort(integers, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return -Integer.compare(o1, o2);
//从大到小排序
}
});
//3、自定义排序逻辑
System.out.println(integers);
//[12, 10, 3, 1, 0, -2, -4]
}
}
public static void reverse(List<?> list);
//反转
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/18 21:06
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7));
Collections.reverse(integers);
System.out.println(integers);
//[7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
}
}
public static void shuffer(List<?> list);
//随机置换
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/19 18:31
*/
public class MyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7));
Collections.shuffle(integers);
Collections.shuffle(integers);
//随机化两次
System.out.println(integers);
//[3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 1, 4]
}
}
public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> c);
//返回集合中的最大值
public static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> c);
//返回集合中的最小值
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/19 18:34
*/
public class MyTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7));
Collections.shuffle(integers);
Integer max = Collections.max(integers);
//自然排序的最大值
System.out.println(max);
//7
Integer min = Collections.min(integers);
//自然排序的最小值
System.out.println(min);
//1
}
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key);
//二分查找,通过自然排序
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/19 18:39
*/
public class MyTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7));
int index = Collections.binarySearch(integers, 3);
//集合的二分查找,通过自然排序
System.out.println(index);
//2
}
}
模拟斗地主
package org.westos.demo3;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/5/19 11:35
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] colors = new String[]{"红桃", "黑桃", "方片", "梅花"};
String[] numbers = new String[]{"2", "A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3"};
HashMap<Integer, String> pokeCards = new HashMap<>();
pokeCards.put(0, "大王");
pokeCards.put(1, "小王");
int index = 2;
for (String number : numbers) {
for (String color : colors) {
pokeCards.put(index++, color.concat(number));
}
}
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = pokeCards.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
}
//0---大王
//1---小王
//2---红桃2
//3---黑桃2
//4---方片2
//5---梅花2
//6---红桃A
//7---黑桃A
//8---方片A
//9---梅花A
//........
//获取HashMap的keySet
Set<Integer> integers = pokeCards.keySet();
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(integers);
System.out.println(arrayList);
//[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24,
// 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47,
// 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
//打乱ArrayList
Collections.shuffle(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList);
//[44, 52, 43, 24, 41, 47, 23, 32, 4, 5, 35, 26, 15, 12, 36, 6, 22, 39, 16, 2, 13, 14, 37, 20,
// 28, 34, 3, 11, 10, 21, 50, 8, 51, 49, 9, 25, 0, 17, 1, 48, 31, 53, 7, 18, 45, 46, 30, 33, 27,
// 29, 38, 40, 19, 42]
//将ArrayList的元素循环发给三个人并留三张底牌
List<Integer> holeCards = arrayList.subList(0, 3);
System.out.println("底牌:" + holeCards);
//底牌:[44, 52, 43]
ArrayList<Integer> ming = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> uzi = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> let = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 3;
for (int i = start; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Integer integer = arrayList.get(i);
if (i % 3 == 0) {
ming.add(integer);
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
uzi.add(integer);
} else {
let.add(integer);
}
}
System.out.println("ming的牌:" + ming);
//ming的牌:[24, 23, 5, 15, 6, 16, 14, 28, 11, 50, 49, 0, 48, 7, 46, 27, 40]
System.out.println("uzi的牌:" + uzi);
//uzi的牌:[41, 32, 35, 12, 22, 2, 37, 34, 10, 8, 9, 17, 31, 18, 30, 29, 19]
System.out.println("Let的牌:" + let);
//Let的牌:[47, 4, 26, 36, 39, 13, 20, 3, 21, 51, 25, 1, 53, 45, 33, 38, 42]
//然后开始排序
TreeSet<Integer> mingTreeSet = new TreeSet<>(ming);
TreeSet<Integer> uziTreeSet = new TreeSet<>(uzi);
TreeSet<Integer> letTreeSet = new TreeSet<>(let);
//看牌
ArrayList<String> strings = lookPoke("ming", mingTreeSet, pokeCards);
ArrayList<String> strings1 = lookPoke("uzi", uziTreeSet, pokeCards);
ArrayList<String> strings2 = lookPoke("let", letTreeSet, pokeCards);
System.out.println("ming的牌:" + strings);
//ming的牌:[大王, 梅花2, 红桃A, 黑桃A, 黑桃K, 红桃Q, 黑桃Q, 方片Q, 黑桃10, 方片10, 黑桃9, 方片9, 方片6, 红桃4, 方片4, 梅花4, 红桃3]
System.out.println("乌兹的牌:" + strings1);
//乌兹的牌:[红桃2, 方片A, 梅花A, 红桃K, 方片K, 梅花Q, 红桃J, 黑桃J, 红桃10, 梅花9, 红桃8, 黑桃8, 方片8, 红桃7, 黑桃7, 梅花7, 梅花6]
System.out.println("严君泽的牌:" + strings2);
//严君泽的牌:[小王, 黑桃2, 方片2, 梅花K, 方片J, 梅花J, 梅花10, 红桃9, 梅花8, 方片7, 红桃6, 黑桃6, 红桃5, 梅花5, 黑桃4, 黑桃3, 梅花3]
}
private static ArrayList<String> lookPoke(String name, TreeSet<Integer> treeSet, HashMap<Integer,String> hm) {
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>(treeSet.size());
for (Integer integer : treeSet) {
strings.add(hm.get(integer));
}
return strings;
};
}