实验二 进程管理
一、目的
本课题实验的目的是,加深对进程概念及进程管理各个部分内容的理解;熟悉进程管理中主要数据结构的设计及进程调度算法,进程控制机构,同步机构,通信机构的实施。
二、题目
进程管理
三、要求及提示
1、要求设置PCB,进程控制原语,进程调度算法,能描述进程调度中不同进程状态之间的转换,设计一个允许n个进程并发运行的进程管理模拟系统。该系统包括有简单的进程控制,同步及通信机构,其进程调度算法可任意选择。每个进程用一个PCB表示,其内容可根据具体情况设置。各进程之间应有一定的同步关系。系统在运行过程中能显示或打印各进程的状态及有关参数的变化情况,以便观察诸进程的运行过程及系统的管理过程。
2、编程实现。
3、工具:C语言或其它高级语言
4、实验时间:2学时
四、实验报告
1、写出进程管理的思想。
2、画出算法流程图和设置的数据结构。
3、写出调试程序出现的问题及解决的方法。
4、打印实验报告及程序清单。
5、报告给出测试的结果。
五、范例
支持多个进程并发运行的简单进程管理模拟系统。
1、问题描述
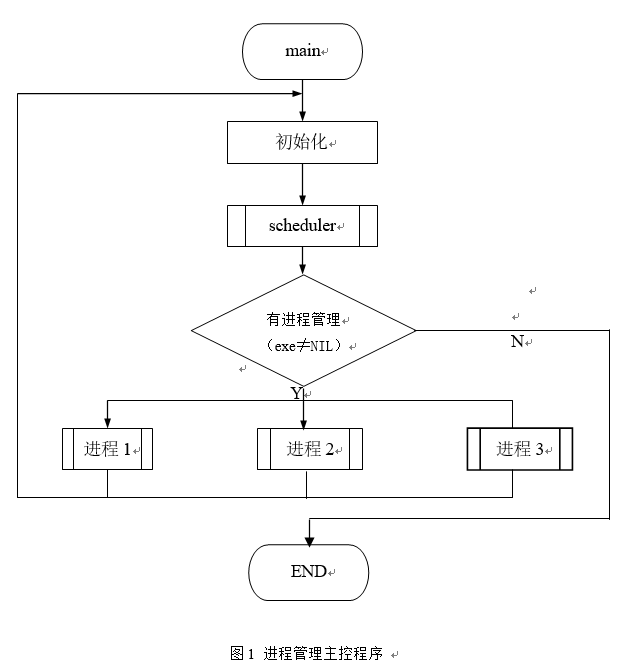
本系统的同步机构采用的是信号量上的P,V操作的机制;控制机构包括阻塞和唤醒操作;时间片中断处理程序处理模拟的时间片中断;进程调度程序负责为各进程分配处理机。系统中设计了3个并发进程。它们之间有如下同步关系:3个进程需要互斥使用临界资源s2,进程1和进程2又需互斥使用临界资源s1。本系统在运行过程中随机打印出各进程的状态变换过程,系统的调度过程及公共变量的变化情况。
2、算法
系统为进程设置了5种运行状态:e-执行态;r-高就绪态;t-低就绪态(执行进程因时间片到限而转入);w-等待态;c-完成态。各进程的初始状态均设置为r。系统分时执行各进程,并规定3个进程的执行概率均为33%。通过产生随机数x来模拟时间片。当进程process1访问随机数x时,若x ≥0.33;当进程process2访问x时,若x<0.33或x≥0.66;当进程process3访问x时,若x<0.66,分别认为各进程的执行时间片到限,产生“时间片中断”而转入低就绪态t。
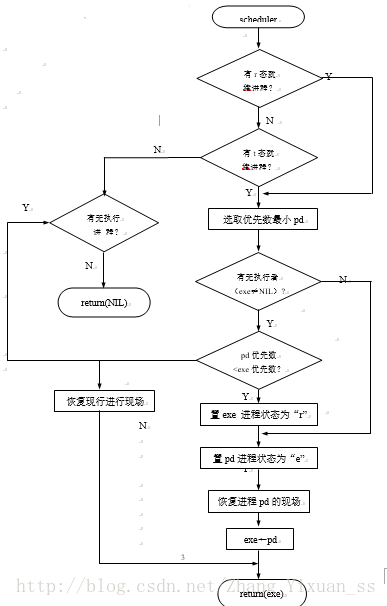
进程调度算法采用剥夺式最高优先数法。各进程的优先数通过键盘输入予以静态设置。调度程序每次总是选择优先数最小(优先权最高)的就绪进程投入执行。先从r状态进程中选择,再从t状态进程中选择。当现行进程唤醒某个等待进程,且被唤醒进程的优先数小于现行进程时,则剥夺现行进程的执行权。
各进程在使用临界资源s1和s2时,通过调用信号量sem1和sem2上的P,V操作来实现同步,阻塞和唤醒操作负责完成从进程的执行态到等待态到就绪态的转换。
系统启动后,在完成必要的系统初始化后便执行进程调度程序。但执行进程因“时间片中断”,或被排斥使用临界资源,或唤醒某个等待资源时,立即进行进程调度。当3个进程都处于完成状态后,系统退出运行。
图1和图2分别示出了系统主控程序和进程调度程序的大致流程。
3 、数据结构
(1)每个进程有一个进程控制块PCB,内容包括:
id 进程控制数,id=0,1,2;
status 进程状态,可为e,r,t,w,c;
priorty 进程优先数;
nexrtwr 等待链指针,只是在同一信号量上等待的下一个进程的标时数。
图2 进程调度程序
(2)信号量semaphore,对于临界资源 s1和s2分别有sem1和sem2均为互斥信号量。内容包括:
value 信号量值,初值为1;
firstwr 等待链首指针,指示该信号量上等待的下一个进程标识数。
(3)现场保留区,用数组savearea[3][4]表示,即每一个进程都有一个大小为4个单元的保留区,用来保存被“中断”时的现场信息,如通用寄存器的内容和断点地址等。此外,系统中还用到下列主要全程变量:
exe 执行进程指针,其值为进程标识数;
i 用来模拟一个通用寄存器;
addr 用来模拟程序计数器;
s1,s2 两个公用变量,与来共享临界资源。
4.程序清单
#include<stdio.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXPRI 100
#define NIL -1
void init();
int find();
void block(int se);
void wakeup(int se);
void eexit(int n);
struct{
int id; //进程标志符
char status; //进程状态,可为e,r,t,w,c;
int nextwr;
int priority;
}pcb[3];
struct{
int value;
int firstwr;
}sem[2];
char savearea[3][4],addr;
int i,s1,s2,seed,exe=NIL;
void init() /*initialization*/
{
int j;
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
pcb[j].id=j;
pcb[j].status='r';
pcb[j].nextwr=NIL;
printf("\n process%d priority?",j+1);
scanf("%d",&i);
pcb[j].priority=i;
}
sem[0].value=1;
sem[0].firstwr=NIL;
sem[1].value=1;
sem[1].firstwr=NIL;
for(i=1;i<3;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
savearea[i][j]='0';
}
float random()
{
int m;
if (seed<0)
m=-seed;
else
m=seed;
seed=(25173*seed+13849)%65536;
return(m/(float)32767.0);
}
timeint(char ad) /*time slice interrupt */
{
float x;
x=random();
if((x<0.33)&&(exe==0))
return(FALSE);
if((x<0.66)&&(exe==1))
return(FALSE);
if((x<1.0)&&(exe==2))
return(FALSE);
savearea[exe][0]=i;
savearea[exe][1]=ad;
pcb[exe].status='t';
printf("Time silce interrupt'\nprocess%d enter into ready.\n",exe+1);
exe=NIL;
return(TRUE);
}
int scheduler()
{
int pd;
if((pd=find())==NIL&&exe==NIL)
return(NIL); /*quit system*/
if(pd!=NIL)
{
if(exe==NIL)
{
pcb[pd].status='e';
exe=pd;
printf("process%d is executing.\n",exe+1);
}
else if(pcb[pd].priority<pcb[exe].priority)
{
pcb[exe].status='r';
printf("process%d enter into ready\n",exe+1);
pcb[pd].status='e';
exe=pd;
printf("process%d is executing\n",exe+1);
}
}
i=savearea[exe][0];
addr=savearea[exe][1];
return(exe);
}
int find()
{
int j,pd=NIL,w=MAXPRI;
for (j=0;j<3;j++)
if(pcb[j].status=='r')
if (pcb[j].priority<w)
{
w=pcb[j].priority;pd=j;
}
if (pd==NIL)
for (j=0;j<3;j++)
if(pcb[j].status=='t')
if(pcb[j].priority<w)
{
w=pcb[j].priority;pd=j;
}
return (pd);
}
p(int se,char ad)
{
if(--sem[se].value>=0)
return(FALSE);
block(se);
savearea[exe][0]=i;
savearea[exe][1]=ad;
exe=NIL;
return(TRUE);
}
void block(int se)
{
int w;
printf("process%d is blocked\n",exe+1);
pcb[exe].status='w';
pcb[exe].nextwr=NIL;
if((w=sem[se].firstwr)==NIL)
sem[se].firstwr=exe;
else
{
while(pcb[w].nextwr!=NIL)
w=pcb[w].nextwr;
pcb[w].nextwr=exe;
}
}
v(int se,char ad)
{
if(++sem[se].value>0) return(FALSE);
wakeup(se);
savearea[exe][1]=ad;
savearea[exe][0]=i;
return (TRUE); /* scheduler*/
}
void wakeup(int se)
{
int w;
w=sem[se].firstwr;
if(w!=NIL)
{
sem[se].firstwr=pcb[w].nextwr;
pcb[w].status='r';
printf("process%d is waken up\n",w+1);
}
}
void process1()
{
if(addr=='a')goto a1;
if(addr=='b')goto b1;
if(addr=='c')goto c1;
if(addr=='d')goto d1;
if(addr=='e')goto e1;
if(addr=='f')goto f1;
for(i=1;i<6;i++)
{
printf("process1 calls P on the semaphore 1\n");
if(p(0,'a')) break; /* process 1 is blocked*/
a1:
printf("process1 is executing in the cretical section 1\n");
if(timeint('b'))
break;
b1:
printf("s1=%d\n",++s1);
printf("process1 calls V on semaphore1 and quit cretical section 1.\n");
if(v(0,'c'))
break;
c1:
printf("process1 calls P on semaphore1 2.\n");
if(p(1,'d'))
break;
d1:
printf("process1 is executing cretical section 2.\n");
if(timeint ('e'))
break;
e1:
printf("s2=%d\n",++s2);
printf("process1 calls V on semephore2 and quit cretical section2.\n");
if(v(1,'f') )
break;
f1:
printf("process1 cycle count=%d\n",i);
}
if(i<6) return;
eexit(0);
}
void process2()
{
if(addr=='a')goto a2;
if(addr=='b')goto b2;
if(addr=='c')goto c2;
if(addr=='d')goto d2;
if(addr=='e')goto e2;
if(addr=='f')goto f2;
for(i=1;i<6;++i)
{
printf("process2 calls Pon semephore2\n");
if(p(1,'a')) break;
a2: printf("process2 is executing on the cretical section2\n");
if(timeint('b')) break;
b2: printf("s2=%d\n",++s2);
printf("process2 calls V on semephore2 and quit cretical section2.\n");
if(v(1,'c')) break;
c2: printf("process2 calls P on semaphore1.\n");
if(p(0,'d')) break;
d2: printf("process2 is executing cretical section1.\n");
if(timeint('e')) break;
e2: printf("s1=%d\n",++s1);
printf("process2 calls V on semephore1 and quit cretical section1.\n");
if(v(0,'f')) break;
f2: printf("process2 cycle count=%d\n",i);
}
if(i<6) return;
eexit(1);
}
void process3()
{
if(addr=='a')goto a3;
if(addr=='b')goto b3;
if(addr=='c')goto c3;
for(i=1;i<6;++i)
{
printf("process3 calls P on semaphore2\n");
if(p(1,'a')) break;
a3: printf("process3 is executing on the cretical section \n");
if(timeint('b')) break;
b3: printf("s2=%d\n",++s2);
printf("process3 calls V on semaphore2 and quit cretical section.\n");
if(v(1,'c')) break;
c3: printf("process3 cycle count=%d\n");
}
if(i<6) return;
eexit(2);
}
void eexit(int n)
{
pcb[n].status='c';
printf("process%d is completed !\n",n+1);
exe=NIL;
}
void main()
{
int k;
printf("****process management*******\n\n");
init();
printf("s1=%d,s2=%d\n",s1,s2);
printf("process1,process2,process3 are all in ready1\n");
for( ; ;)
{
if((k=scheduler())!=NIL)
{
switch(k)
{
case 0: process1(); break;
case 1: process2(); break;
case 2: process3(); break;
default: printf("process identifer error\n"); break;
}
}
else
break;
}
printf("s1=%d,s2=%d\n",s1,s2);
printf("\n ******END*******\n");
}