0x0 引言
比赛时没能做出来这道题,当时我使用OD进行动态调试,分析出启动程序时初始化了0x72数组,并且含有一个12分支的switch被嵌套在循环中,最终没能搞定,今天就复盘这道题。
0x1 查壳
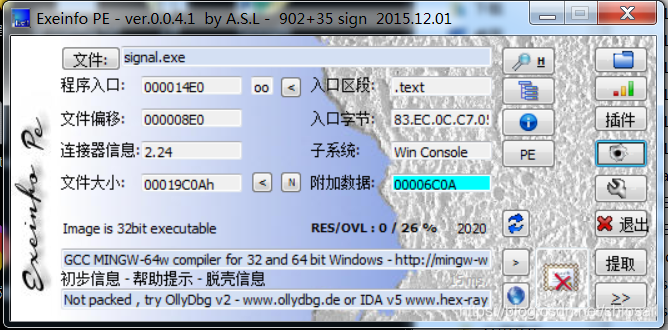
无壳,并且编译时未启用ASLR技术,挺友好哈。
0x2 分析 main
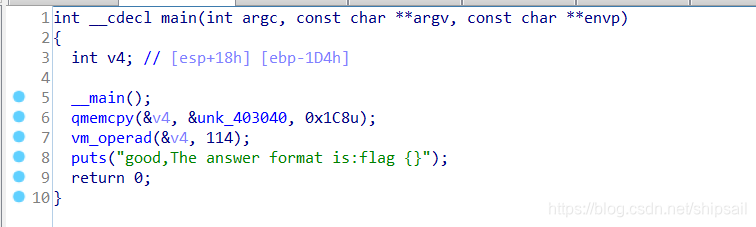
这次学聪明了,先打开反汇编辅助插件查看伪代码(这对理解汇编逻辑有极大的帮助)。
可以看到在 main 函数中先调用了 __main()
随后复制内存到变量v4,随后v4被传入vm_operad()
容易想到,&unk_403040 是通过 __main() 得到的,随后的vm_operad()则是在计算flag,并在puts()中输出。
0x3 瞧一瞧 __main()
GO TO:0x0040176F
通过OD动态调试,F8步过发现寄存器中没有任何的变化,所以我认为之后的操作与__main()函数是无关的。
0x4 内存复制

rep movsd 根据百科上的定义,赋值edx次,即0x72次
其中esi指向的地址为0x403040,如下

再来看反汇编代码。
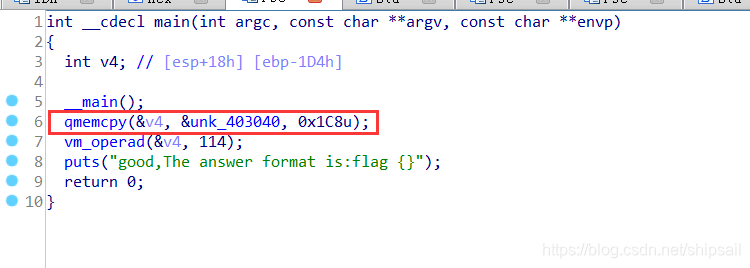
内存复制,从0x403040复制到变量v4,大小为0x1C8个字节。
可能存在疑问,在汇编代码中是0x72,为啥反汇编后是0x1C8呢?

其实很简单,因为数据类型为DWORD占4个字节,这从上文中数据硬编码处可以看出。
0x1C8 = 0x72 * 0x4
还有一个很奇怪的现象,puts中只传入了字符串模板,而没有传入存储flag的地址…
0x5 分析 vm_operad
使用IDA自动反汇编 vm_operad(int *a1, int a2)
int * a1传入的是之前的v4首地址,a2为常数114
经过部分的调整与修改我得到了源代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
size_t read(char *a1)
{
size_t result; // eax
printf("string:");
scanf("%s", a1);
result = strlen(a1);
if ( result != 15 )
{
puts("WRONG!\n");
exit(0);
}
return result;
}
int vm_operad(unsigned int *a1, int a2)
{
int result; // eax
char v3[100]; // [esp+13h] [ebp-E5h]
char v4[100]; // [esp+77h] [ebp-81h]
char v5; // [esp+DBh] [ebp-1Dh]
int v6; // [esp+DCh] [ebp-1Ch]
int v7; // [esp+E0h] [ebp-18h]
int v8; // [esp+E4h] [ebp-14h]
int v9; // [esp+E8h] [ebp-10h]
int v10; // [esp+ECh] [ebp-Ch]
v10 = 0;
v9 = 0;
v8 = 0;
v7 = 0;
v6 = 0;
while ( 1 )
{
result = v10;
if ( v10 >= a2 )
return result;
switch ( a1[v10] )
{
case 0:
case 9:
continue;
case 1:
v4[v7] = v5;
++v10;
++v7;
++v9;
break;
case 2:
v5 = a1[v10 + 1] + v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 3:
v5 = v3[v9] - LOBYTE(a1[v10 + 1]);
v10 += 2;
break;
case 4:
v5 = a1[v10 + 1] ^ v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 5:
v5 = a1[v10 + 1] * v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 6:
++v10;
break;
case 7:
if ( v4[v8] != a1[v10 + 1] )
{
printf("what a shame...");
exit(0);
}
++v8;
v10 += 2;
break;
case 8:
v3[v6] = v5;
++v10;
++v6;
break;
case 10:
read(v3);
++v10;
break;
case 11:
v5 = v3[v9] - 1;
++v10;
break;
case 12:
v5 = v3[v9] + 1;
++v10;
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
unsigned int a[] ={0x0A,0x04,0x10,0x08,0x03,0x05,0x01,0x04,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x03,0x01,0x03,0x02,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x04,0x04,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x03,0x21,0x01,0x0B,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x51,0x08,0x04,0x24,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x05,0x02,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x02,0x36,0x08,0x04,0x41,0x01,0x02,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x01,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x41,0x08,0x0C,0x01,0x07,0x22,0x07,0x3F,0x07,0x34,0x07,0x32,0x07,0x72,0x07,0x33,0x7,0x18,0x7,0xffffffa7,0x7,0x31,0x7,0xfffffff1,0x7,0x28,0x7,0xffffff84,0x7,0xffffffc1,0x7,0x1e,0x7,0x7a};
cout << sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
vm_operad(&a,114);
return 0;
}
分析到这里有点懵逼,因为不知道啥是我们要的flag,我们只是拿到了源代码,而且这代码这么多的分支,感觉和我当时用OD调试没啥大的区别。
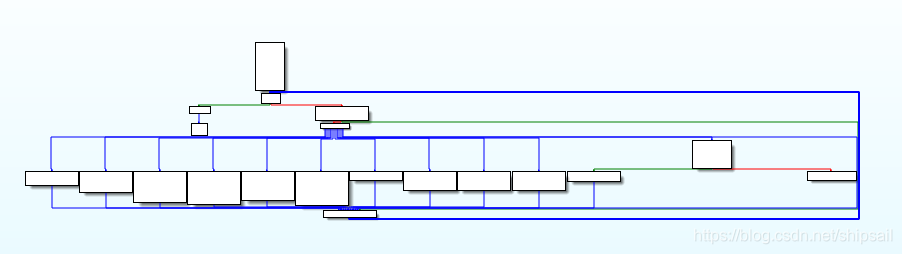
通过可视化,可以知道,如果想反向求解存在一定的困难,因为swich分支太多啦!
通过已得到的反汇编代码,v3 v4 为长度100的字符数组,由于最后的输出中根本没有flag,所以猜测v3 v4可能就是我们想要的flag。
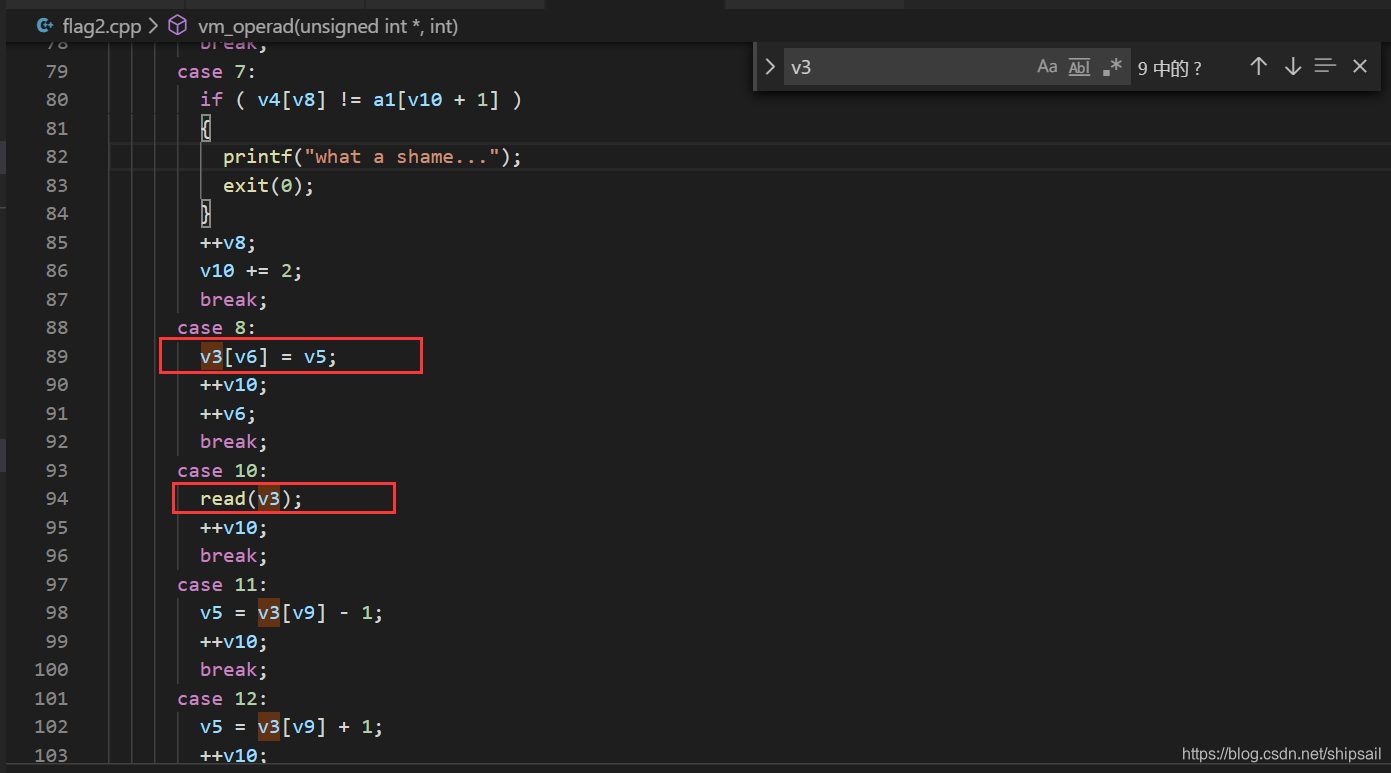
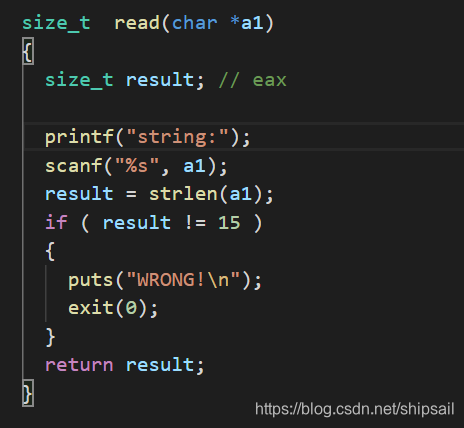
v3 变量在 case8 中被改变,在case10中被输入,输入长度为15
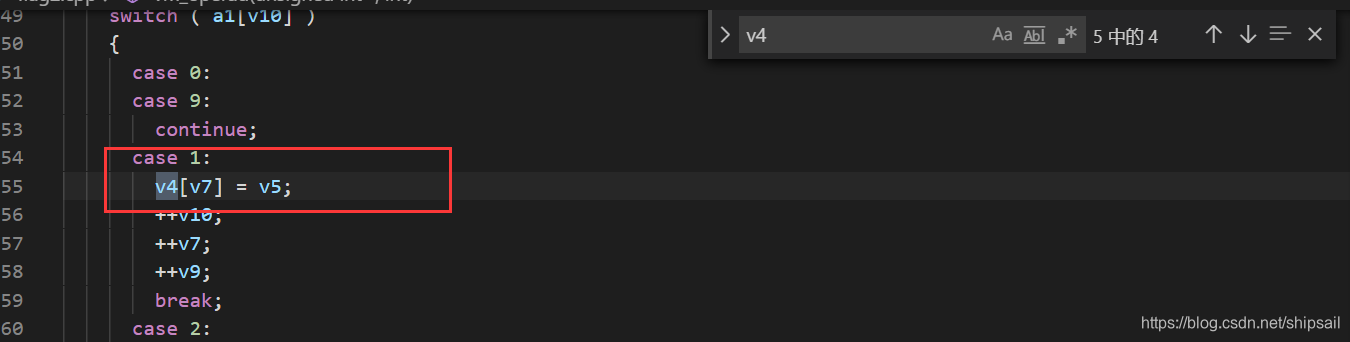
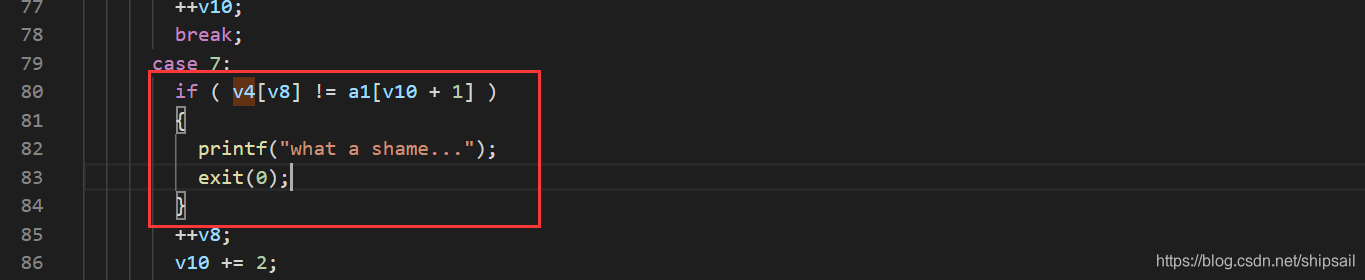
v4 在 case 1 中被改变,case7 中将他与a1元素进行比较,a1中的元素是已知的,为了方便,我把a1改名为array。
这里我将printf() 和 exit() 注释,并在read()中随机输入15个字符
多次执行后发现规律。
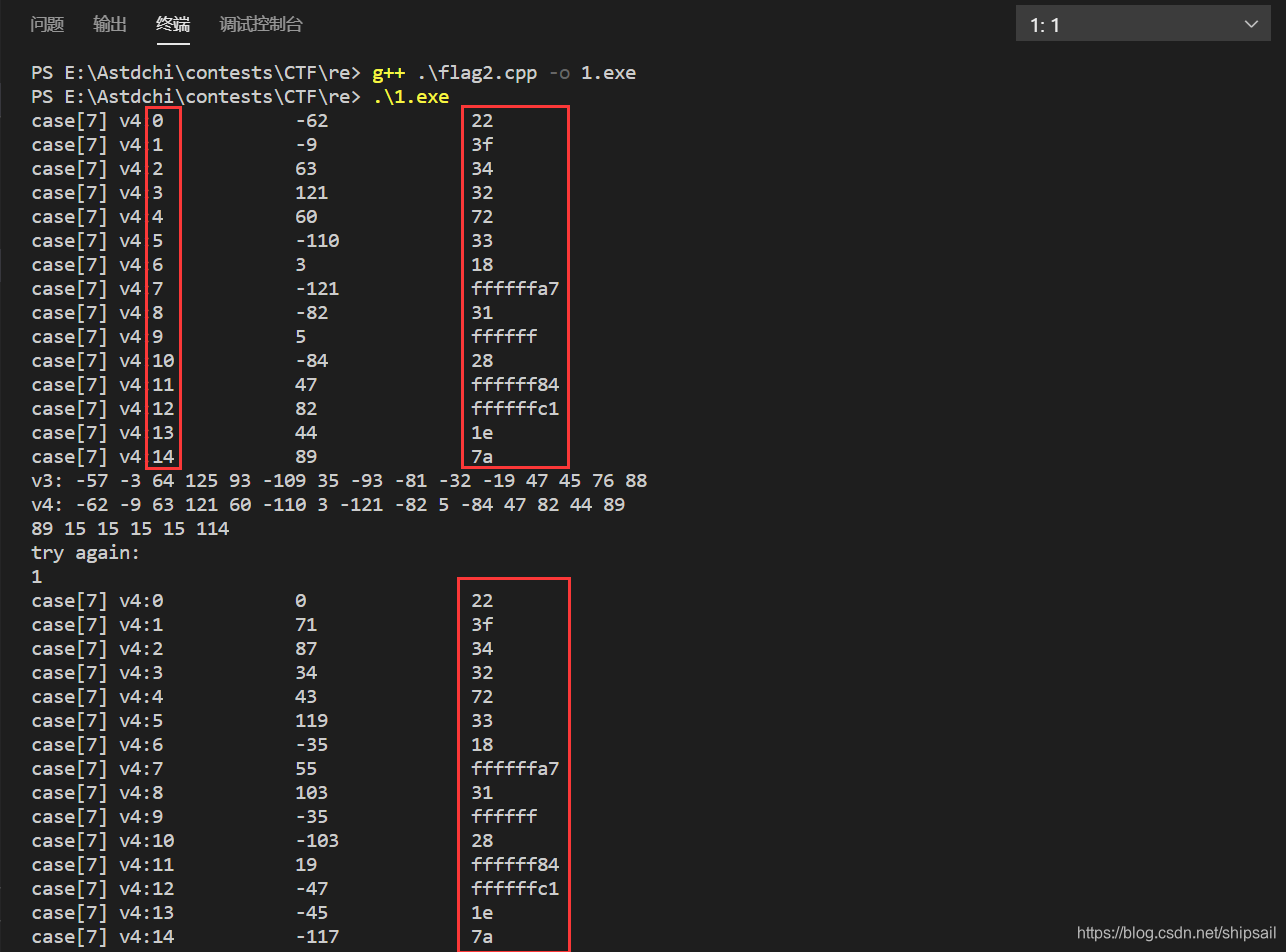
case7 中输出了v4每个元素的验证值 array[v10 + 1] 是常数,这就相当于我们已知了v4数组,而v4是在case 1中赋值为 v5,其中0xffffff不知道为啥显示不全,在OD中他的值为0xfffffff1
v4 = {0x22,0x3f,0x34,0x32,0x72,0x33,0x18,0xffffffa7,0x31,0xf1,0x28,0xffffff84,0xffffffc1,0x1e,0x7a};
现在就得着重研究V5
0x6 调试计算 V5
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
size_t read(char *array)
{
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
array[i] = rand() * 255;
}
return 15;
size_t result; // eax
printf("string:");
scanf("%s", array);
result = strlen(array);
if ( result != 15 )
{
puts("WRONG!\n");
exit(0);
}
return result;
}
void displayV9V10(int _case ,int v9,int v10){
return;
printf("case %d\tv9=%d\tv10=%d\n",_case,v9,v10);
}
int vm_operad(unsigned int *array, int a2)
{
int result; // eax
char v3[100]; // [esp+13h] [ebp-E5h]
char v4[100]; // [esp+77h] [ebp-81h]
char v5; // [esp+DBh] [ebp-1Dh]
int v6; // [esp+DCh] [ebp-1Ch]
int v7; // [esp+E0h] [ebp-18h]
int v8; // [esp+E4h] [ebp-14h]
int v9; // [esp+E8h] [ebp-10h]
int v10; // [esp+ECh] [ebp-Ch]
v10 = 0;
v9 = 0;
v8 = 0;
v7 = 0;
v6 = 0;
while ( 1 )
{
result = v10;
if ( v10 >= a2 ){
// cout << "v3: ";
// for(int i = 0; v3[i] != '\0';i++){
// cout << int(v3[i]) << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// cout << "v4: ";
// for(int i = 0; v4[i] != '\0';i++){
// cout << int(v4[i]) << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// cout << int(v5) << " "<<v6<<" "<<v7<<" "<<v8<<" "<<v9<<" "<<v10<<endl;
return result;
}
switch ( array[v10] )
{
case 0:
case 9:
continue;
case 1:
displayV9V10(1,v9,v10);
printf("v4[%d] = v5; \n\n\n",v7);
v4[v7] = v5;
++v10;
++v7;
++v9;
break;
case 2:
displayV9V10(2,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = array[%d] + v3[%d]; \n",v10 + 1,v9);
v5 = array[v10 + 1] + v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 3:
displayV9V10(3,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = v3[%d] - LOBYTE(array[%d]); \n",v9 ,v10 + 1);
v5 = v3[v9] - LOBYTE(array[v10 + 1]);
v10 += 2;
break;
case 4:
displayV9V10(4,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = array[%d] ^ v3[%d]; \n",v10 + 1,v9);
v5 = array[v10 + 1] ^ v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 5:
displayV9V10(5,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = array[%d] * v3[%d]; \n",v10 + 1,v9);
v5 = array[v10 + 1] * v3[v9];
v10 += 2;
break;
case 6:
++v10;
break;
case 7:
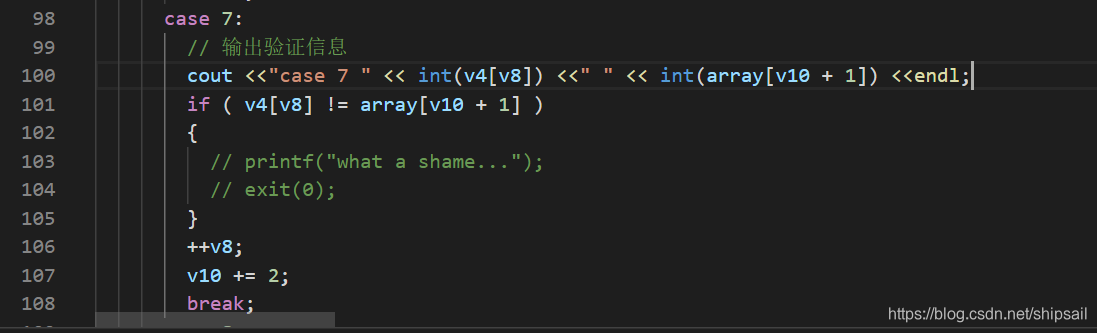
// 输出验证信息
cout << "case[7] " << "v4:" << v8 << "\t\t" << int(v4[v8]) << "\t\t" << int(array[v10 + 1]) <<endl << dec;
if ( v4[v8] != array[v10 + 1] )
{
// printf("what a shame...");
// exit(0);
}
++v8;
v10 += 2;
break;
case 8:
displayV9V10(8,v9,v10);
printf("v3[%d] = v5; \n",v6);
v3[v6] = v5;
++v10;
++v6;
break;
case 10:
read(v3);
++v10;
break;
case 11:
displayV9V10(11,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = v3[%d] - 1; \n",v9);
v5 = v3[v9] - 1;
++v10;
break;
case 12:
displayV9V10(12,v9,v10);
printf("v5 = v3[%d] + 1; \n",v9);
v5 = v3[v9] + 1;
++v10;
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
unsigned int a[] ={0x0A,0x04,0x10,0x08,0x03,0x05,0x01,0x04,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x03,0x01,0x03,0x02,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x04,0x04,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x03,0x21,0x01,0x0B,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x51,0x08,0x04,0x24,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x05,0x02,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x02,0x36,0x08,0x04,0x41,0x01,0x02,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x01,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x41,0x08,0x0C,0x01,0x07,0x22,0x07,0x3F,0x07,0x34,0x07,0x32,0x07,0x72,0x07,0x33,0x7,0x18,0x7,0xffffffa7,0x7,0x31,0x7,0xffffff,0x7,0x28,0x7,0xffffff84,0x7,0xffffffc1,0x7,0x1e,0x7,0x7a};
int test;
while(1){
unsigned int *b = new unsigned int[114];
for(int i = 0; i < 114;i++)
b[i] = a[i];
vm_operad(b,114);
delete [] b;
cout <<"input a int to try again:"<<endl;
cin >> test;
}
return 0;
}
打印运算V5的case 和 case 1
由于V4已知,所以可以求出对应的V3,以下为打印获取计算过程
v5 = array[2] ^ v3[0];
v3[0] = v5;
v5 = v3[0] - LOBYTE(array[5]);
v4[0] = v5;
v5 = array[8] ^ v3[1];
v3[1] = v5;
v5 = array[11] * v3[1];
v4[1] = v5;
v5 = v3[2] - LOBYTE(array[14]);
v3[2] = v5;
v5 = v3[2] - 1;
v4[2] = v5;
v5 = v3[3] + 1;
v3[3] = v5;
v5 = array[21] ^ v3[3];
v4[3] = v5;
v5 = array[24] * v3[4];
v3[4] = v5;
v5 = v3[4] - LOBYTE(array[27]);
v4[4] = v5;
v5 = v3[5] - 1;
v3[5] = v5;
v5 = v3[5] - 1;
v4[5] = v5;
v5 = array[34] ^ v3[6];
v3[6] = v5;
v5 = v3[6] - LOBYTE(array[37]);
v4[6] = v5;
v5 = array[40] + v3[7];
v3[7] = v5;
v5 = array[43] ^ v3[7];
v4[7] = v5;
v5 = v3[8] + 1;
v3[8] = v5;
v5 = v3[8] - 1;
v4[8] = v5;
v5 = array[50] * v3[9];
v3[9] = v5;
v5 = array[53] + v3[9];
v4[9] = v5;
v5 = array[56] + v3[10];
v3[10] = v5;
v5 = array[59] ^ v3[10];
v4[10] = v5;
v5 = array[62] + v3[11];
v3[11] = v5;
v5 = array[65] * v3[11];
v4[11] = v5;
v5 = array[68] * v3[12];
v3[12] = v5;
v5 = array[71] + v3[12];
v4[12] = v5;
v5 = array[74] ^ v3[13];
v3[13] = v5;
v5 = v3[13] - LOBYTE(array[77]);
v4[13] = v5;
v5 = array[80] + v3[14];
v3[14] = v5;
v5 = v3[14] + 1;
v4[14] = v5;
根据上面每一块内容写脚本计算V3
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
unsigned long array[] ={0x0A,0x04,0x10,0x08,0x03,0x05,0x01,0x04,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x03,0x01,0x03,0x02,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x04,0x04,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x03,0x21,0x01,0x0B,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x51,0x08,0x04,0x24,0x01,0x0C,0x08,0x0B,0x01,0x05,0x02,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x02,0x36,0x08,0x04,0x41,0x01,0x02,0x20,0x08,0x05,0x01,0x01,0x05,0x03,0x08,0x02,0x25,0x01,0x04,0x09,0x08,0x03,0x20,0x01,0x02,0x41,0x08,0x0C,0x01,0x07,0x22,0x07,0x3F,0x07,0x34,0x07,0x32,0x07,0x72,0x07,0x33,0x7,0x18,0x7,0xffffffa7,0x7,0x31,0x7,0xfffffff1,0x7,0x28,0x7,0xffffff84,0x7,0xffffffc1,0x7,0x1e,0x7,0x7a};
unsigned long v4[] = {0x22,0x3f,0x34,0x32,0x72,0x33,0x18,0xffffffa7,0x31,0xf1,0x28,0xffffff84,0xffffffc1,0x1e,0x7a};
unsigned long v3[15];
v3[0] = (v4[0] + LOBYTE(array[5])) ^ array[2];
v3[1] = (v4[1] / array[11]) ^ array[8];
v3[2] = (v4[2] + 1) + LOBYTE(array[14]);
v3[3] = (v4[3] ^ array[21]) - 1;
v3[4] = (v4[4] + LOBYTE(array[27])) / array[24];
v3[5] = (v4[5] + 1) + 1;
v3[6] = (v4[6] + LOBYTE(array[37])) ^ array[34];
v3[7] = (v4[7] ^ array[43]) - array[40];
v3[8] = (v4[8] + 1) - 1;
v3[9] = (v4[9] - array[53]) / array[50];
v3[10] = (v4[10] ^ array[59]) - array[56];
v3[11] = (v4[11] / array[65]) - array[62];
v3[12] = (v4[12] - array[71]) / array[68];
v3[13] = (v4[13] + LOBYTE(array[77])) ^ array[74];
v3[14] = (v4[14] - 1) - array[80];
cout << "flag{";
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
cout <<char(v3[i]);
}
cout<<"}";
return 0;
}

得到 Flag
0x7 总结
这道题不像往常刷的题那样去破解算法本身,由于他分支复杂,所以应该有内在的规律。
