目录
1、定义
图是由一组顶点和一组能够将两个顶点相连的边组成的。
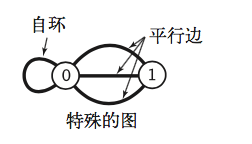
1.1、特殊的图
自环:即一条连接一个顶点和其自身的边;
平行边:连接同一对顶点的两条边称为平行边。
1.2、术语
度数:依附于该点的边的总数。
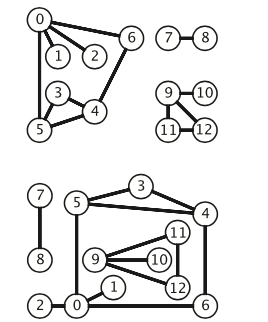
子图:如下图,有三个子图
路径:是由边顺序连接的一系列顶点。
简单路径:是一条没有重复顶点的路径。
环: 是一条至少含有一条边且起点和终点相同的路径。
简单环:是一条(除了起点和终点必须相同之 外)不含有重复顶点和边的环。
路径或者环的长度:为其中所包含的边数。
连通图:如果从任意一个顶点都存在一条路径到达另一个任意顶点,我们称这幅图是连通图。
极大连通子图:一 幅非连通的图由若干连通的部分组成,它们都是其极大连通子图。
树:是一幅无环连通图。
图的密度:已经连接的顶点对占所有可能连接的顶点对的比例。
二分图:是一种能够将所有结点分为两部分的图,其中图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不 同的部分。

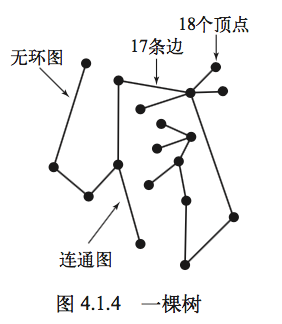
2、无向图的数据结构
对于无向图的代码实现,首先我们需要能保存每个顶点,还要能保存每条边(哪两个顶点相连)。对于这样数据类型,我们有以下3种实现方式。
邻接矩阵:我们可以使用一个 V 乘 V 的布尔 矩阵。当顶点 v 和顶点 w 之间有相连接的边 时,定义 v 行 w 列的元素值为 true,否则为 false。这种方法对于空间(内存)的要求很高。
边的数组:我们可以使用一个 Edge 类,它 保存相连的两个顶点数据。我们要想得到一个顶点的所有邻边,需要遍历数组,效率不高。
邻接表数组:我们可以用一个数组来存储所有的顶点,然后将每个顶点相邻的顶点以链表的形式存储在每个顶点后面。类似散列表。

2.1、数据结构API
无向图数据类型实现了以下函数。

2.2、代码
public class Graph {
private final int V; // 顶点数目
private int E;// 边的数目
private Bag<Integer>[] adj;// 邻接表
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
this.adj = (Bag[]) (new Bag[V]);
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
this.adj[v] = new Bag();
}
}
public Graph(In in) {
this.V = in.readInt();
this.adj = (Bag[]) (new Bag[this.V]);
int E;
for (E = 0; E < this.V; ++E) {
this.adj[E] = new Bag();
}
E = in.readInt();
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
this.addEdge(v, w);
}
}
public int V() {
return this.V;
}
public int E() {
return this.E;
}
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
++this.E;
this.adj[v].add(w);
this.adj[w].add(v);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
return this.adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v) {
return this.adj[v].size();
}
}3、深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索的目的是为了寻找从一个点到所有连通点的路径。
他的思路就和拿着一根绳子走迷宫一样:
- 从起点出发走向下一个没有被标记的路口,在你走过的路上铺上绳子;
- 标记你走过的所有路口和通道;
- 当你来到一个被标记的路口时,往回走,回退到上个路口;
- 当回退的路口已经没有可走的通道是继续回退,知道把所走的路口走完。
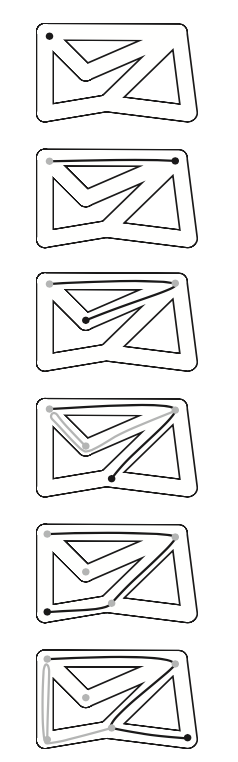
3.1、深度优先搜索代码
public class DepthFirstSearch {
private boolean[] marked; //标记走过顶点
private int count;
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph g, int s) {
marked = new boolean[g.V()];//创建和顶点数量一样大小的标记数组
}
public void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
count++;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked(w)) {// 从v点的其他未被标记的点开始继续向后递归
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
private boolean marked(int w) {
return marked[w];
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
}3.2、深度优先搜索路径代码
public class DepthFirstPaths {
private boolean[] marked;//标记走过的点
private int[] edgeTo;//从起点到一个顶点的已知路径的最后一个顶点
private int s; //起点
public DepthFirstPaths(Graph g, int s) {
marked = new boolean[g.V()];
edgeTo=new int[g.V()];//创建和顶点相同数量大小的数组,记录每个顶点的前一个顶点是啥。
this.s=s;
}
public void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!hasPathTo(w)) {
edgeTo[w]=v; //记录w点前一个点是v,这样就能通过edgeTo倒退来找回整条路径
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
private boolean hasPathTo(int w) {
return marked[w];
}
/**
* 从v点出发,不断倒退,找到从起点到v点的路径
*/
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<Integer> path=new Stack<>();
int w=edgeTo[v];
for (int i=w;i!=s;i=edgeTo[i]) {
path.push(i);
}
path.push(s);
return path;
}
}4、广度优先搜索---寻找最短路径
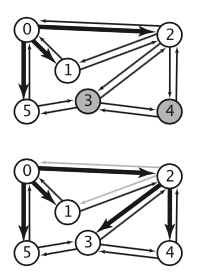
深度优先搜索就好像是一个 人在走迷宫,广度优先搜索则好像是一组人在一起朝各个方向走这座迷宫, 每个人都有自己的绳子。当出现新的叉路时,可以假设一个探索者可以分裂 为更多的人来搜索它们,当两个探索者相遇时,会合二为一(并继续使用先 到达者的绳子)。
这样做的目的可以是从起点出发到达每个顶点的路径是最短的。
下图有深度和广度优先搜索的区别。
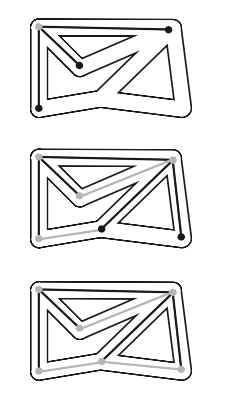

4.1、代码
public class BreadthFirstSearch {
private boolean[] marked;//标记走过的顶点
private final int[] edgeTo;//记录路径
private int s;//起点
public BreadthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s) {
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
this.s = s;
bfs(G, s);
}
private void bfs(Graph G, int s) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new Queue<>();
marked[s] = true;
queue.enqueue(s); //1、将起点(0)加入到队列中
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int v = queue.dequeue();//2、依次从队尾取出顶点 (0)
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {//3、然后检查该点0时候还有其他相邻点(0-1、0-2、0-3)
if (!marked[w]) {//4、如果有将每个顶点(1、2、3)加入到队列中
edgeTo[w] = v;
marked[w]=true;
queue.enqueue(w);//5、将每个顶点都加入到队头中,然后进行下一次循环
}
}
}
}
private boolean hasPathTo(int w) {
return marked[w];
}
@Nullable
private Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) {
if (!hasPathTo(v))
return null;
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();
for (int w = edgeTo[v]; w != s; w = edgeTo[w]) {
path.push(w);
}
path.push(s);
return path;
}
}5、连通分量
连通分量就相当于子图,如下图就是有三个连通分量。
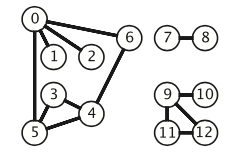
5.1、代码
public class CC {
private boolean[] marked; // 是否被标示过
private int[] id; // 给每个顶点标记在哪个子图中
private int count; // 只有走完一个子图之后才会count++
public CC(Graph G) {
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
id = new int[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (!marked(v)) {
dfs(G, v);
count++;
}
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
id[v] = count;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public boolean connected(int v, int w) {
return id[v] == id[w];
}
public int id(int v) {
return id[v];
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
private boolean marked(int w) {
return marked[w];
}
}
6、检查图中是否有环
public class Cycle {
private boolean[] marked;
private boolean hasCycle;
public Cycle(Graph G) {
marked=new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v=0;v<G.V();v++){
if (!marked(v)){
dfs(G,v,v);
}
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G,int v,int u){
marked[v]=true;
for (int w:G.adj(v)){
if (!marked(w)){
dfs(G,w,v);
}else if (w!=u){
hasCycle=true;
}
}
}
public boolean hasCycle(){
return hasCycle;
}
private boolean marked(int w){
return marked[w];
}
}
7、二分图(二分颜色)
public class TwoColor {
private boolean[] marked;
private boolean[] color;
private boolean isTwoColor=true;
public TwoColor(Graph G) {
marked=new boolean[G.V()];
color=new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v=0;v<G.V();v++){
if (!marked(v)){
dfs(G,v);
}
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G,int v){
marked[v]=true;
for (int w:G.adj(v)){
if (!marked(w)){
color[w]=!color[v];
dfs(G,w);
}else if (color[w]==color[v]){
isTwoColor=false;
}
}
}
public boolean isTwoColor(){
return isTwoColor;
}
private boolean marked(int w){
return marked[w];
}
}
8、符号图(处理String类型的无向图)
/**
* 数据类型如下:用逗号隔开的相邻顶点
* Bacon, Kevin
* Woodsman,The(2004)
* Grier,David Alan
* Bewitched(2005)
* Kidman, Nicole
*/
public class SymbolGraph {
private ST<String, Integer> st; // 红黑树--存储 符号名--索引
private String[] keys; // 将st中的索引放入keys中,用于进行图操作
private Graph G; // 无向图数据存储,用户获取图的一些属性
public SymbolGraph(String stream, String sp) {
st = new ST<>();
In in = new In(stream);
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
// 1、将读取到的数据存储到红黑树的键值对中
String[] edge = in.readLine().split(sp);
for (String point : edge) {
if (!st.contains(point)) {
st.put(point, st.size());
}
}
}
// 2、将符号名--索引 反向存储到keys数组中
keys = new String[st.size()];
for (String key : st.keys()) {
keys[st.get(key)] = key;
}
// 3、
G = new Graph(st.size());
in = new In(stream);
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
String[] edge = in.readLine().split(sp);
int v = st.get(edge[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < edge.length; i++) {
G.addEdge(v, st.get(edge[i]));
}
}
}
public boolean contain(String key) {
return st.contains(key);
}
public int index(String key) {
return st.get(key);
}
public String name(int v) {
return keys[v];
}
public Graph G() {
return G;
}
}
