集合类型
白话学python,就找三岁学编程,用最简谱的话带你从0开始
python集合是什么?
python中也有集合类型(set)
该集合类型与数学的集合基本相似。
概念:包含0个或多个数据项的无序组合。集合元素不可重复。
集合中只包含整数、浮点型、字符串、元组等不可变数据。
无序组合
由于集合的无序性所以没有索引和切片的概念
不能够切片
可以动态添加或删除元素。
元素不可重复
集合里面的元素是单独的唯一的,不可以重复的
使用集合可以把其他数据类型的内容过滤重复元素
set() 函数
set()函数把其他类型的转换成集合。
————————————————————————————
#集合的创建及无序性
>>> s = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18}
>>> s
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18, 'hallo'}
>>> t
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
#set() 函数的使用
>>> w = set('python')
>>> w
{'n', 'y', 'h', 'p', 't', 'o'}
>>> v = set(((13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'))
>>> v
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
#不可重复性
>>> c = {3, 5, 6, 3}
>>> c
{3, 5, 6}
>>> a = 3, 6, 9, 6 #创建元组a
>>> a = set(a)# 将元组转换成列表
>>> a
{9, 3, 6}
集合类型的操作符
集合共有4种基本操作:
交集 (&)
并集 (|)
差集 (-)
补集 (^)
集合类型操作符
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| S-T or S.difference(T) | 返回一个新的集合,包括在集合S但是不包括在T中的元素 |
| S -= T or S.difference_update(T) | 更新集合S ,返回S中有的但是T中没有的元素 |
| S&T or S.intersection(T) | 返回一个新集合,包括在S和T中的相同的元素 |
| S&=T or S.intersection_update(T) | 更新集合S,返回集合S和T中共有的元素 |
| S|T or S.union(T) | 返回一个新的集合,包括S和T中所有的元素 |
| S|=T or S.updat(T) | 更新集合S,返回 S 和 T 的所有元素 |
| S^T or S.symmetric_difference(T) | 返回一个新集合,包含 S 和T 之中所有不同的元素 |
| S^=T or S.symmetric_difference_update(T) | 更新集合 S ,返回集合 S 和 T 集合的不相同值 |
| S<=T or S.issubset(T) | S 与 T相同,或是其子集则返回 True 否则返回 False,用 S<T 判定S 是不是T 的真子集 |
| S>=T or S.issuperset(T) | 与上面的相反,S 与 T 相同或 S 是 T 的子集,返回 True ,否者返回 False,用 S>T 来判断 S 是不是 T 的 真超集 |
差集
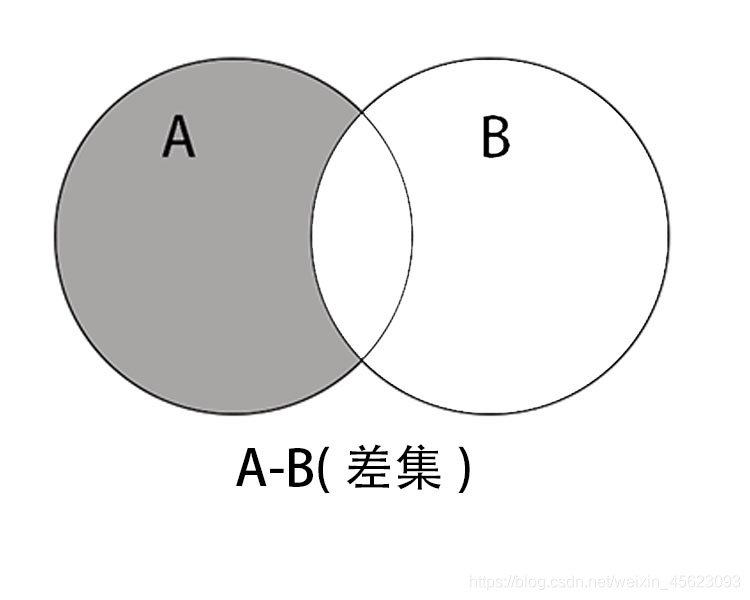
集合A和B的差集就是两者的差
S - T or S.difference(T)
返回一个新的集合,包括在集合S但是不包括在T中的元素
>>> s - t
set()
>>> t-s
{'hallo'}
>>> s.difference(t)
set()
>>> t.difference(s)
{'hallo'}
S -= T or S.difference_update(T)
更新集合S ,返回S中有的但是T中没有的元素
>>> s -= t
>>> s
set()
>>> s = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18}
>>> t = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18, 'hallo'}
>>> t -= s
>>> t
{'hallo'}
>>> s = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18}
>>> t = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18, 'hallo'}
>>> t.difference_update(s)
>>> t
{'hallo'}
>>> s = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18}
>>> t = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18, 'hallo'}
>>> s.difference_update(t)
>>> s
set()
交集
A和B相同的部分
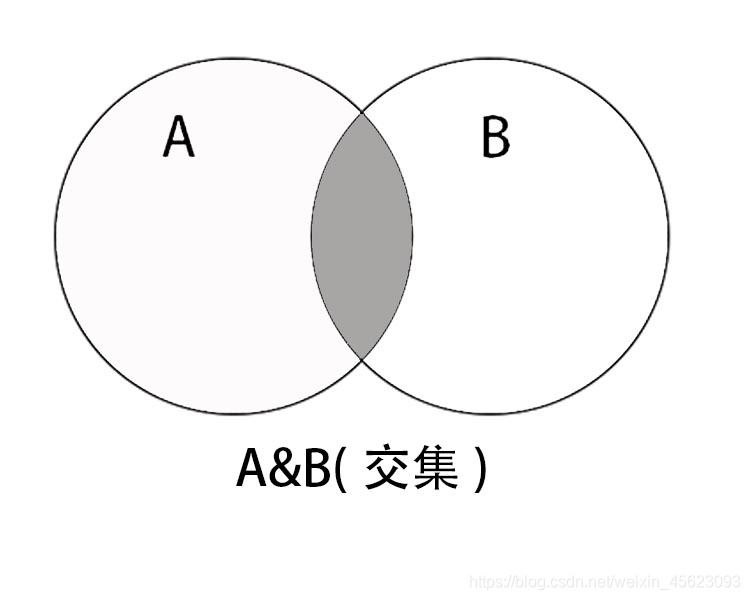
S&T or S.intersection(T)
返回一个新集合,包括在S和T中的相同的元素
>>> s = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18}
>>> t = {123, 'python', (13, 14), 5.18, 'hallo'}
>>> s & t
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t & s
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> s.intersection(t)
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t.intersection(s)
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
这里s和t的顺序无关,结果都一样
S&=T or S.intersection_update(T)
更新集合S,返回集合S和T中共有的元素
>>> s &= t
>>> s
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t &= s
>>> t
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> s.intersection_update(t)
>>> s
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t.intersection_update(s)
>>> t
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
这里要注意s和t的位置,结果是不一样的
并集
A和B的并集是A和B里面所有的元素
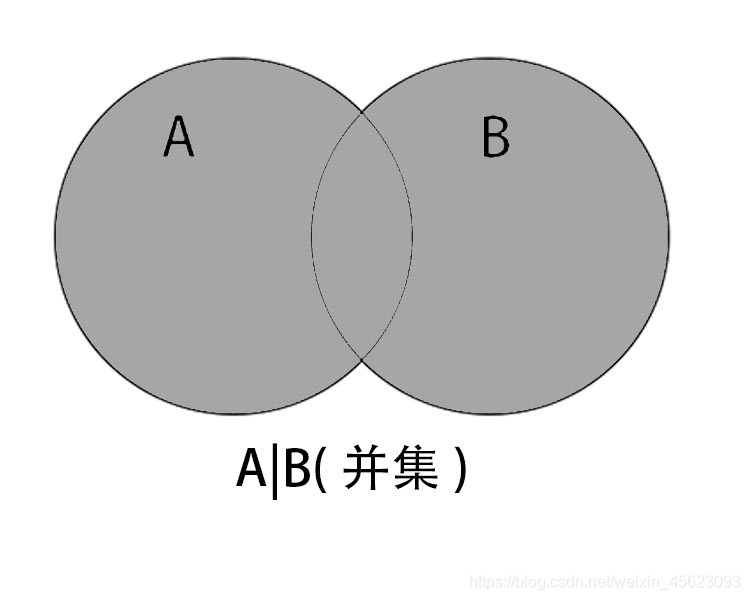
S|T or S.union(T)
返回一个新的集合,包括S和T中所有的元素
>>> s = {(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t = {5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> s | t
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> s.union(t)
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
因为不改变原有代码,s和 t 的顺序不会产生影响
S|=T or S.updat(T)
更新集合S,返回 S 和 T 的所有元素
>>> s |= t
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> t |= s
>>> t
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> s = {(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t.update(s)
>>> t
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> s.update(t)
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
因为会更新原有集合,所以注意顺序
补集
A 和 B 集合中不相同的元素
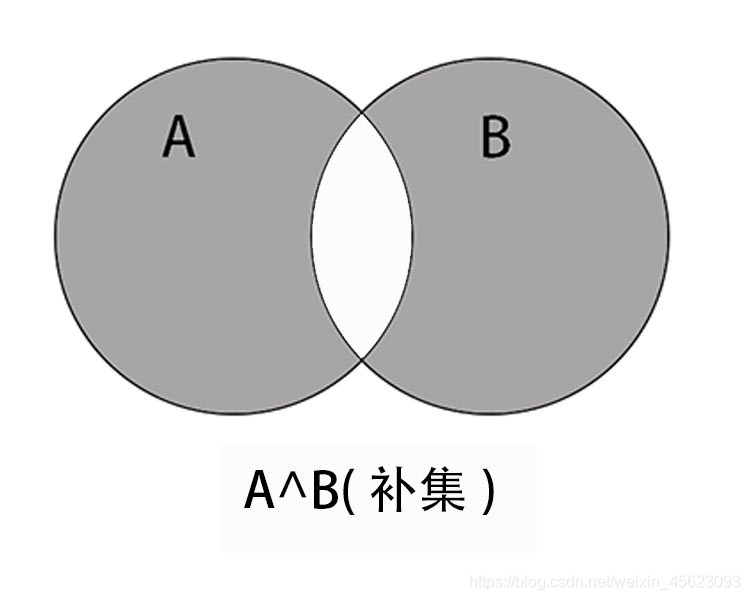
S^T or S.symmetric_difference(T)
返回一个新集合,包含 S 和T 之中所有不同的元素
>>> s = {(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> s ^ t
{'hallo'}
>>> s.symmetric_difference(t)
{'hallo'}
返回新集合,s 和 t 的位置无关
S^=T or S.symmetric_difference_update(T)
更新集合 S ,返回集合 S 和 T 集合的不相同值
>>> s ^= t
{'hallo'}
>>> t ^= s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 123}
>>>s.symmetric_difference_update(t)
>>> s
{'hallo'}
>>> t.symmetric_difference_update(s)
>>> t
{'hallo'}
更新了数组,注意顺序和位置
S和T数组比较
S<=T or S.issubset(T)
S 与 T相同,或是其子集则返回 True 否则返回 False
用 S<T 判定S 是不是T 的真子集
>>> s = {(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
>>> t={5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 'hallo', 123}
>>> s <= t
True
>>> s.issubset (t)
True
>>> t <= s
False
>>> t.issubset(s)
False
S>=T or S.issuperset(T)
与上面的相反,S 与 T 相同或 S 是 T 的子集,返回 True ,否者返回 False
用 S>T 来判断 S 是不是 T 的 真超集
>>> s >= t
False
>>> s.issuperset(t)
False
>>> t >= s
True
>>> t.issuperset(s)
True
集合类型的操作函数或方法
| 操作函数及方法 | 描 述/解 释 |
|---|---|
| S.add(X) | 如果 元素 X 不在 S 集合中则添加到集合 S |
| S.clear() | 移除 S 中的所有数据项 |
| S.copy() | 返回一个集合的副本 |
| S.pop() | 随机返回集合的一个元素,若S为空则报错! |
| S.discard(X) | 如果元素 X 在集合 S 中,则删除,不在也不报错 |
| S.remove(X) | 如果元素 X 在集合 S 中,则删除,不在则报错(keyError异常) |
| S.isdisjoint(T) | 若 S 和 T 没有相同的元素则返回True |
| X in S | 如果X 是S的元素返回 True 否则返回False |
| X not in S | 如果X 不是S的元素返回 True 否则返回False |
S.add(X)
如果 元素 X 不在 S 集合中则添加到集合 S
>>> s.add(250)
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250, 123}
S.clear()
移除 S 中的所有数据项
>>> s = {5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250, 123}
>>> s.clear()
>>> s
set()
注:移除数据项,不是删除整个集合
S.copy()
返回一个集合的副本
注:这里是副本,不是返回集合
>>> s.copy()
{(13, 14), 123, 5.18, 'python'}
S.pop()
随机返回集合的一个元素,若S为空则报错!
>>> s.pop()
(13, 14)
>>> s.pop()
123
#报错测试
>>> b = set()
>>> b.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#94>", line 1, in <module>
b.pop()
KeyError: 'pop from an empty set'
S.discard(X) or S.remove(X)
S.discard(X) | 如果元素 X 在集合 S 中,则删除,不在也不报错
S.remove(X) | 如果元素 X 在集合 S 中,则删除,不在则报错(keyError异常)
# S.discard(X)
>>> s = {5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250, 123}
>>> s.discard(123)
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250}
>>> s.discard(6)
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250}
#S.remove(X)
>>> s = {5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250, 123}
>>> s.remove(123)
>>> s
{5.18, 'python', (13, 14), 250}
>>> s.remove(12)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#105>", line 1, in <module>
s.remove(12)
KeyError: 12
S.isdisjoint(T)
若 S 和 T 没有相同的元素则返回True
>>> s.isdisjoint(t)
False
X in S or X not in S
X in S | 如果X 是S的元素返回 True 否则返回False
X not in S | 如果X 不是S的元素返回 True 否则返回False
>>> 'python' in s
True
>>> 'python' not in s
False
>>> 'hallo' in s
False
>>> 'hallo' not in s
True
优势
集合的单一性,不包括重复的元素是特色
所以有需要数据去重的可以用集合来完成
冰冻的集合
冰冻的被冻住了那么久无法修改了,这是一个特殊的集合又叫不可变集合
frozenset()
定义冰冻的集合(不可变集合)
>>> a = frozenset('pythopn')
>>> a
frozenset({'y', 'p', 'h', 't', 'n', 'o'})
既然是不可变的集合那么上面的
添加、删除就不存在了
没有add()、remove()、clear()、pop()等函数
>>> a.add('c') #add()报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#2>", line 1, in <module>
a.add('c')
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'add'
>>> a.clear('h')#clear() 报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#3>", line 1, in <module>
a.clear('h')
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'clear'
>>> a.remove('h')#remove()报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#4>", line 1, in <module>
a.remove('h')
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'remove'
>>> a.pop()# pop()报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module>
a.pop()
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'pop'
>>> a.discard('h')#discard()报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#7>", line 1, in <module>
a.discard('h')
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'discard'
以上函数均不适用于冰冻集合,估计是他太高冷,没有那么平易近人。
他有哈希值,可以作为字典的键,也可以作为元素,就是不能够修改,比较硬核。
集合的整理就告一段落了,有问题记得留言,好的记得收藏
点个赞,给小编一点,鼓励,整理不易啊
谢谢大家!!!
