使用:
指定配置文件
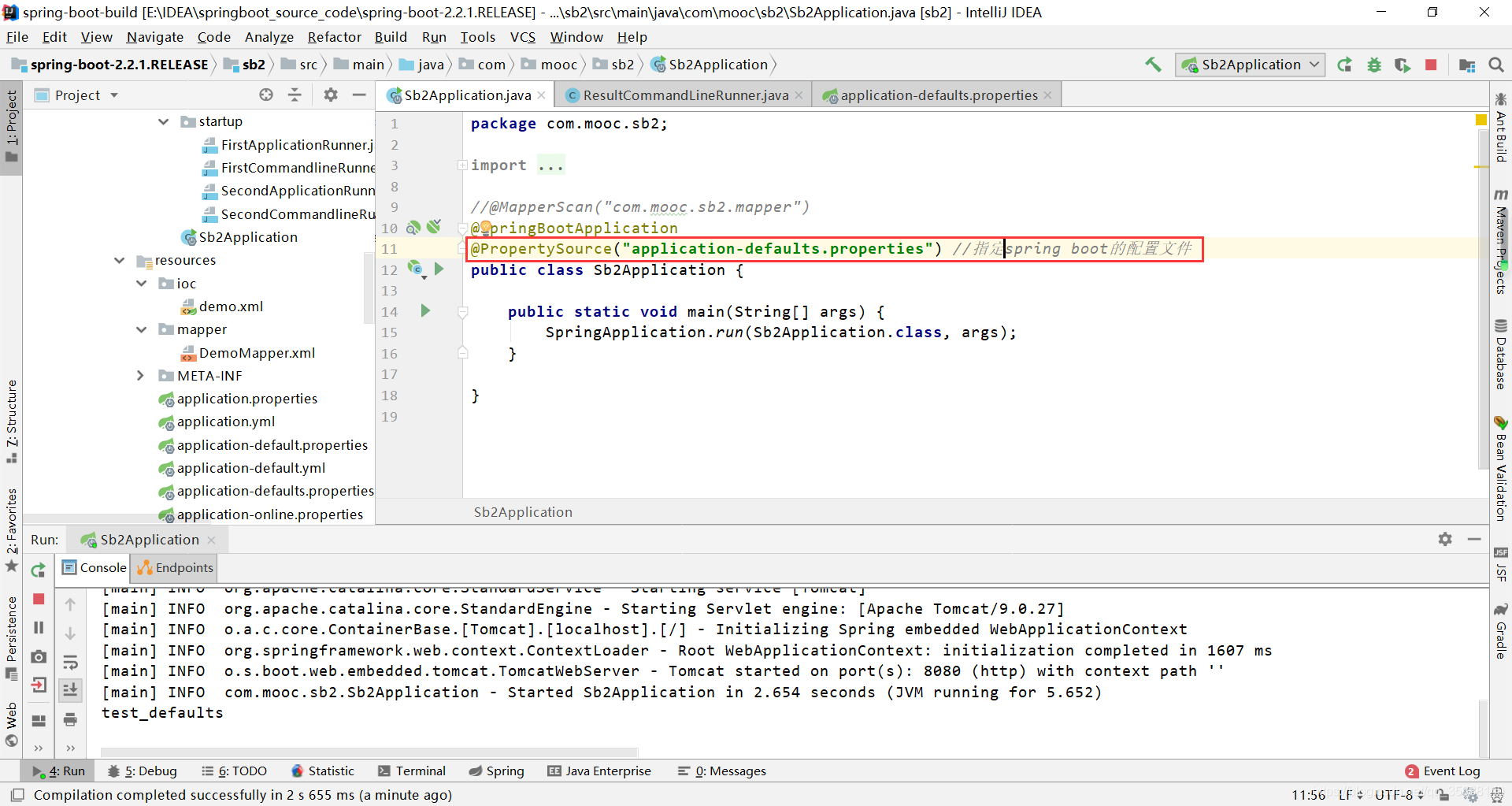
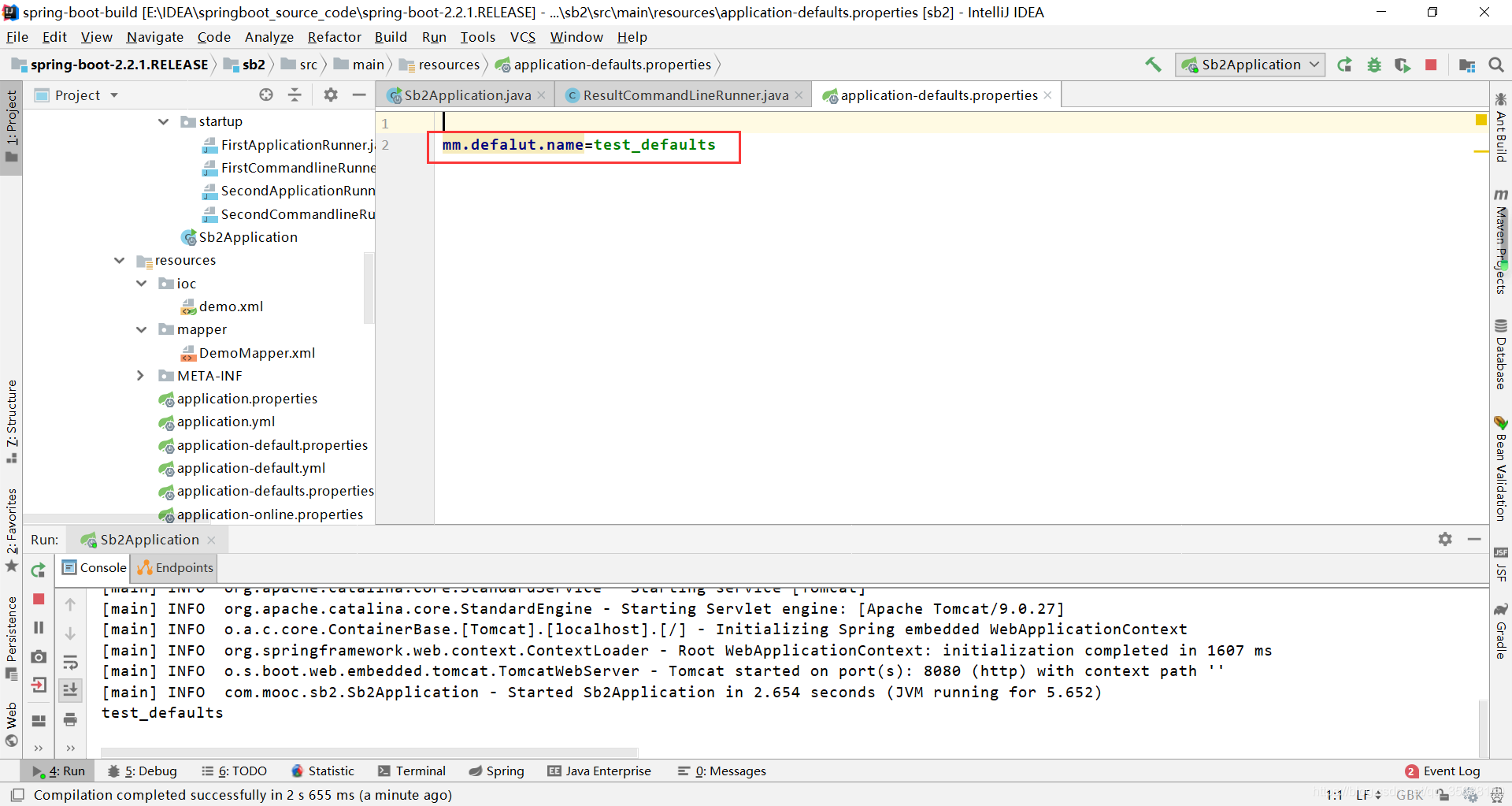
配置文件中配置属性
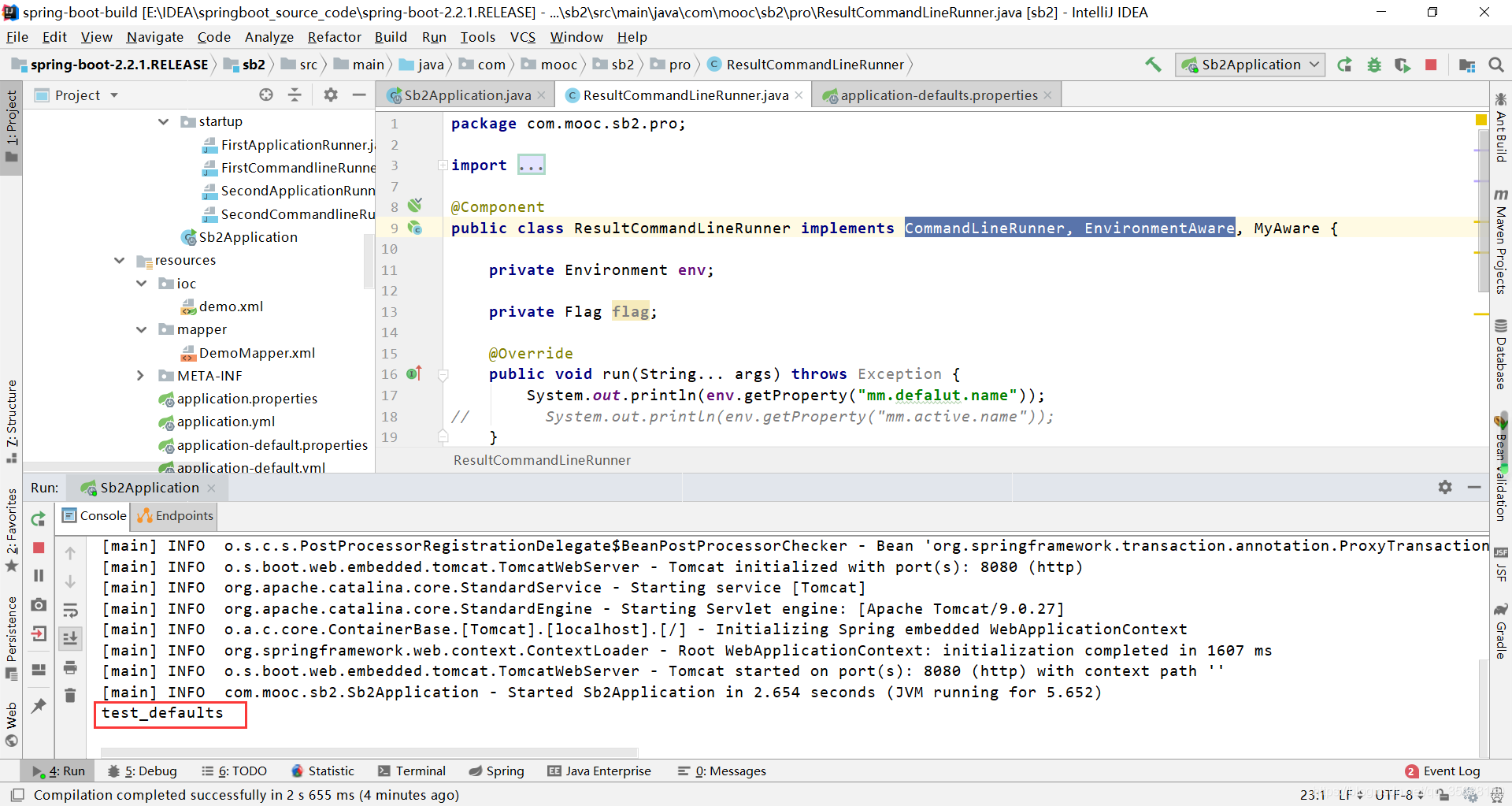
实现CommandLineRunner, EnvironmentAware接口即可
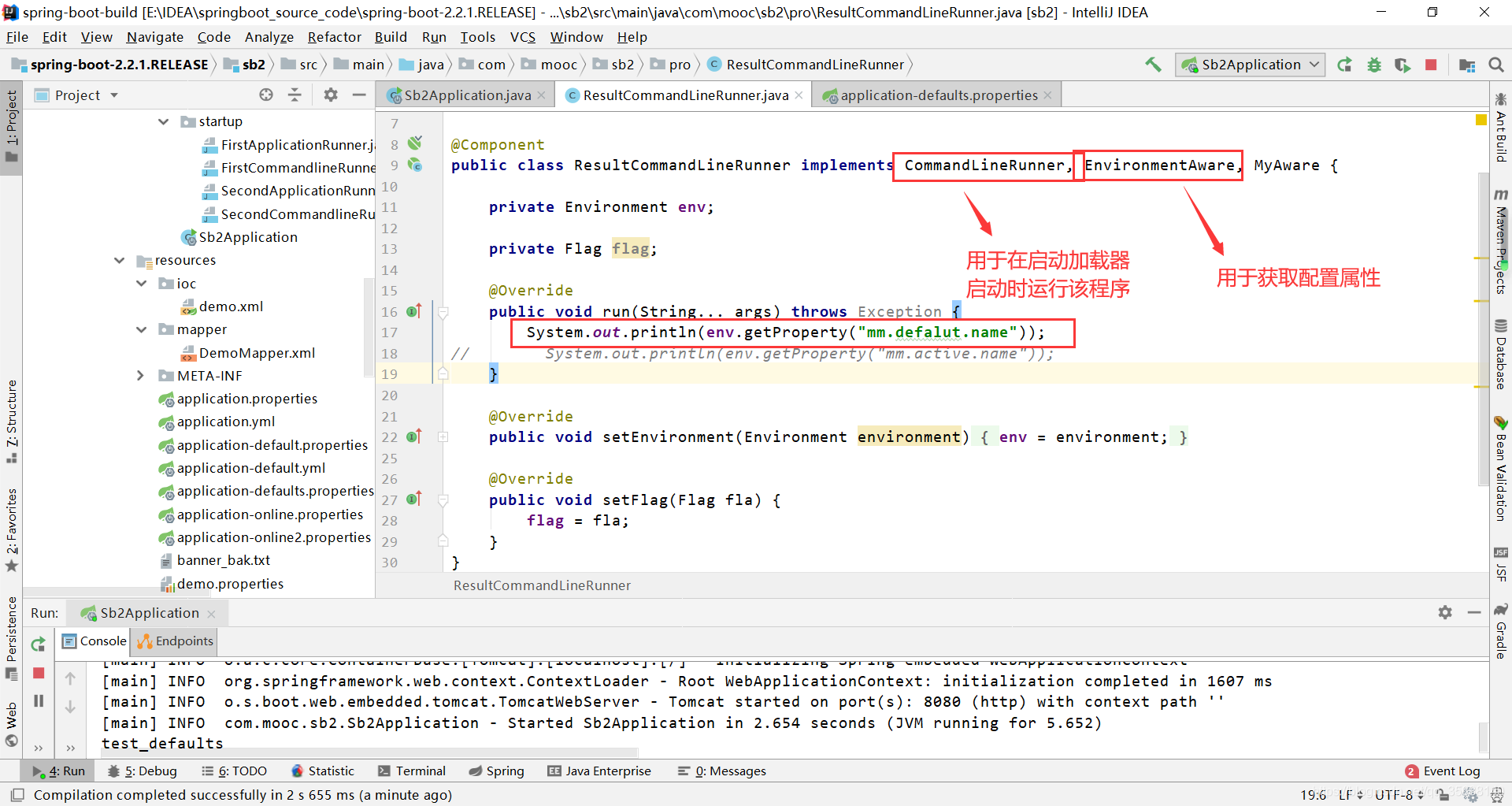
运行程序,打印环境属性:
下面是常见的spring ware
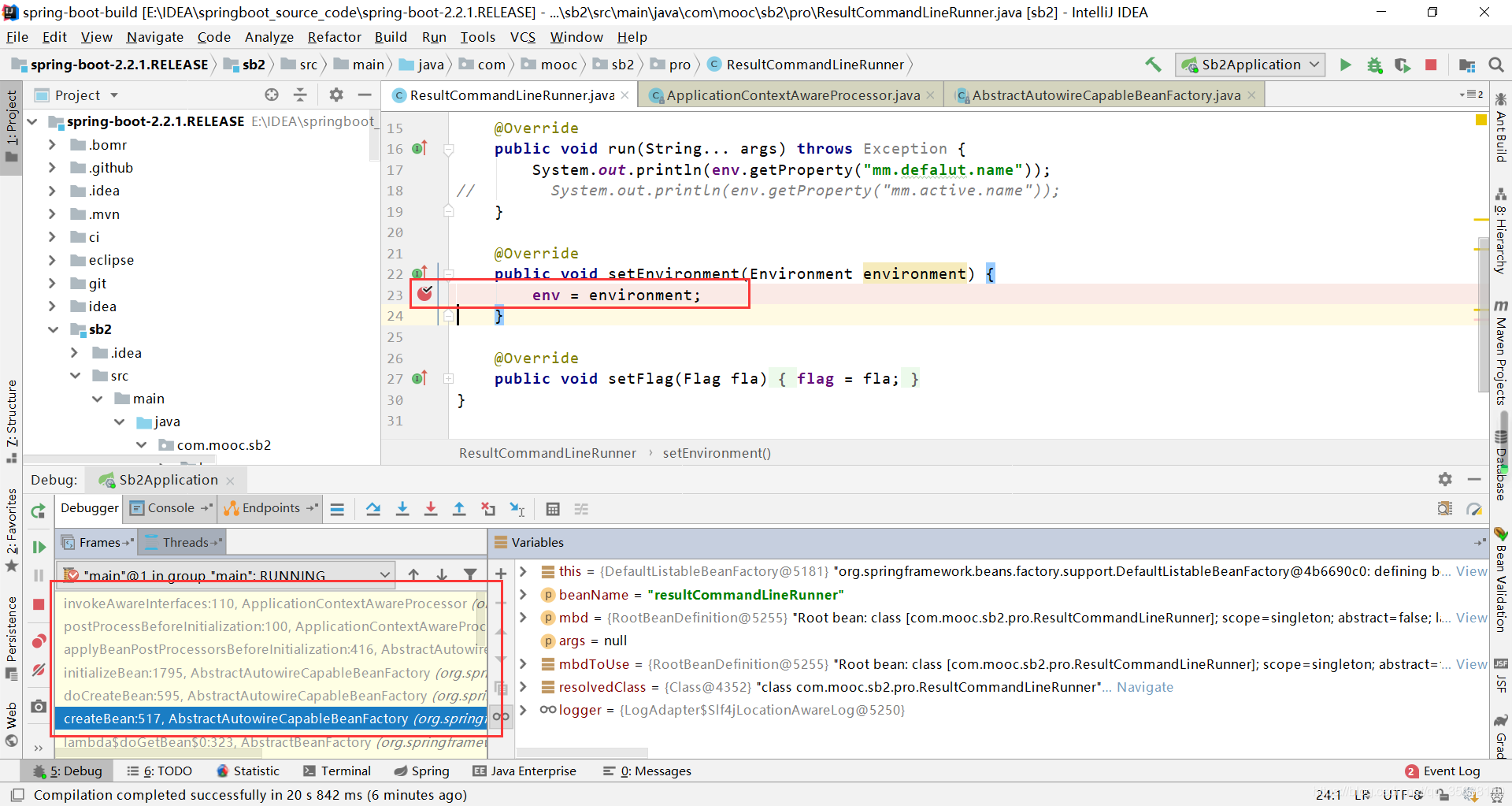
1. 查看aware的调用关系
debug程序,在EnvironmentAware接口的setEnvironment()方法中debug,发现查看左下角的堆的调用关系,由下至上就是调用的关系,看得出来,在application的run方法中,在refresh的最后一步,初始化单例bean的时候使用的finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法,然后调用doCreatBean()去实现bean的初始化的过程中完成,在bean初始化前会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation去完成bean的注册(如果注册失败才会让spring去完成注册)。这时在postProcessBeforeInstantiation()初始化完成以后会调用invokeAwareInterfaces()去将系统中的所有的aware接口的实现类全都调用一下,完成参数的注入的过程。
下面由下至上是调用关系:
invokeAwareInterfaces
postProcessBeforeInitialization
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
initializeBean
doCreateBean
getSingleton
doGetBean
getBean
preInstantiateSingletons
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
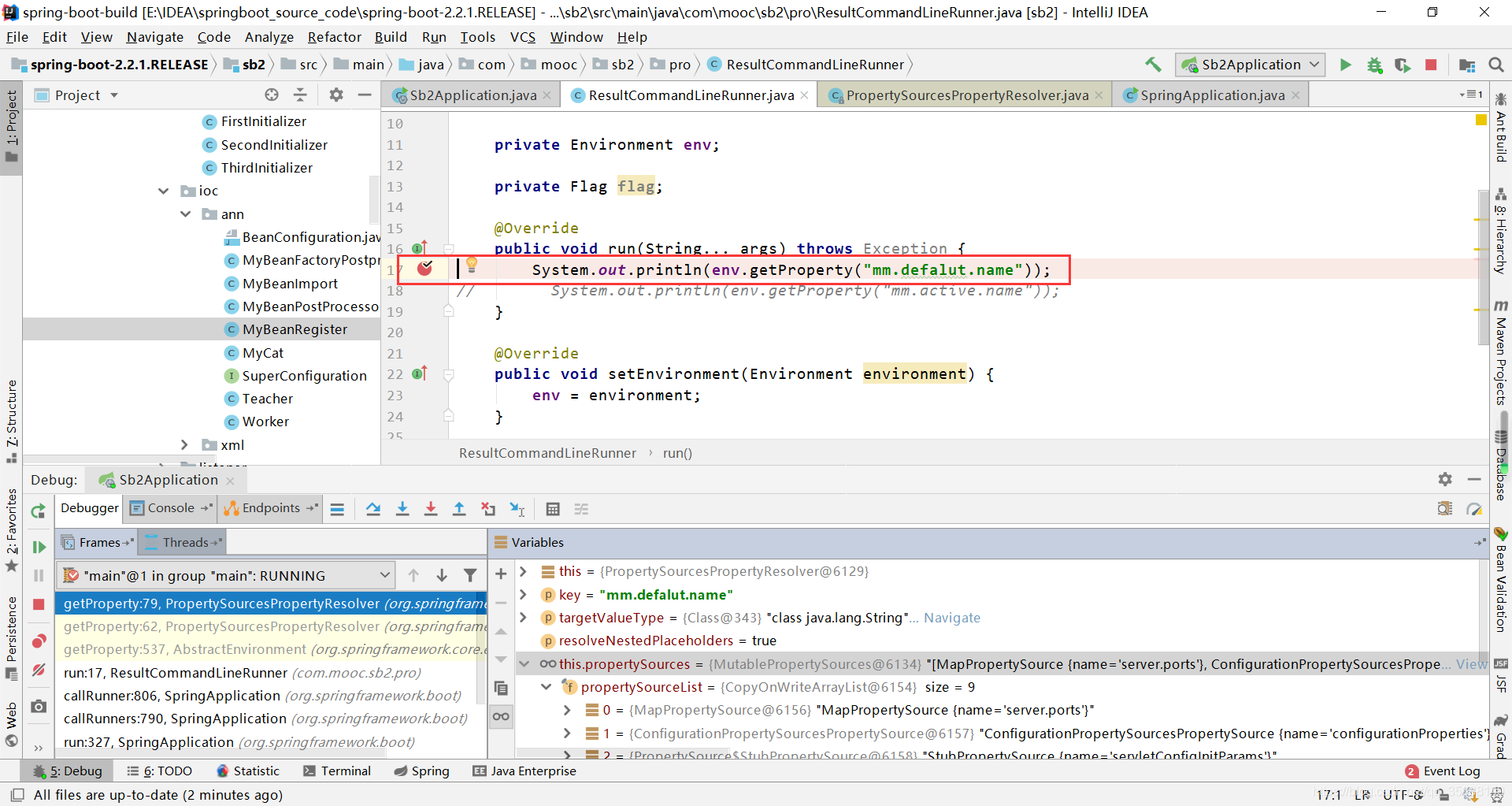
2. 查看PropertySource的属性元
PropertySource的属性元本质上就是一些spring运行参数,比如默认的端口号,或者是application.propertoes中的信息等等。
在代码的env.getProperty("mm.defalut.name")代码处debug
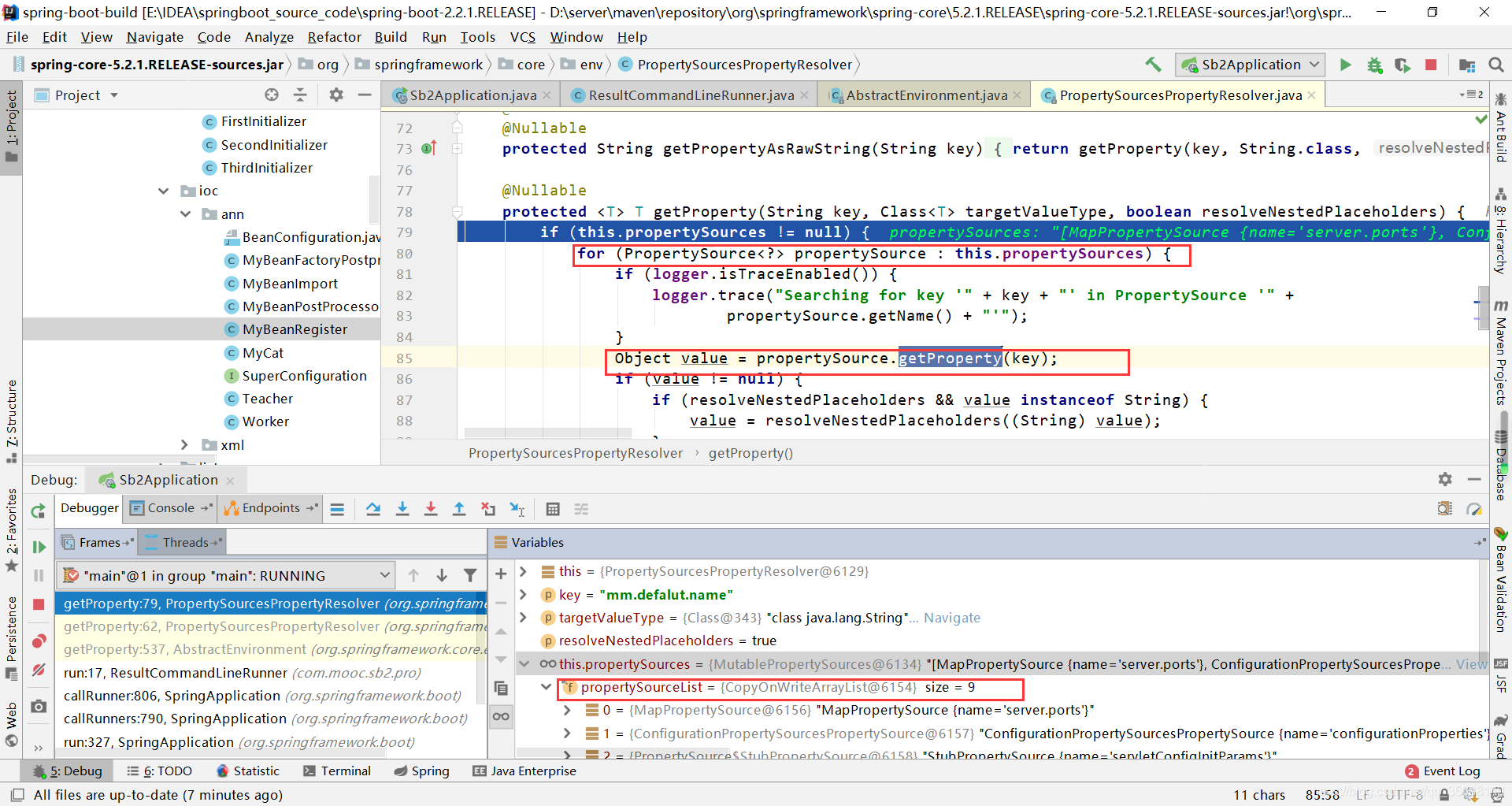
跟进源码发现,存在一个propertySources集合,getProperty()方法会遍历该集合从而拿到我们需要的环境属性
3. PropertySource是在何时被注入到spring的
可以看到,SpringApplication的run()方法里面有一行prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);,跟进源码
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 计时器
stopWatch.start(); // 开启计时器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// listener事件的触发
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 环境准备
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// bean的注入
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop(); // 停止计时器
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
// 启动加载的启动
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
跟进源码
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
// 创建一个ConfigurableEnvironment对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 将run()方法的agrs传入的ConfigurableEnvironment对象中
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 发送一个environmentPrepared事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 将ConfigurableEnvironment对象配置到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 将environment转化为对应场景下的environment
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 将environment加入到ConfigurationPropertySources
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
3.1 进入getOrCreateEnvironment()方法
查看发现会创建一个StandardServletEnvironment()环境。
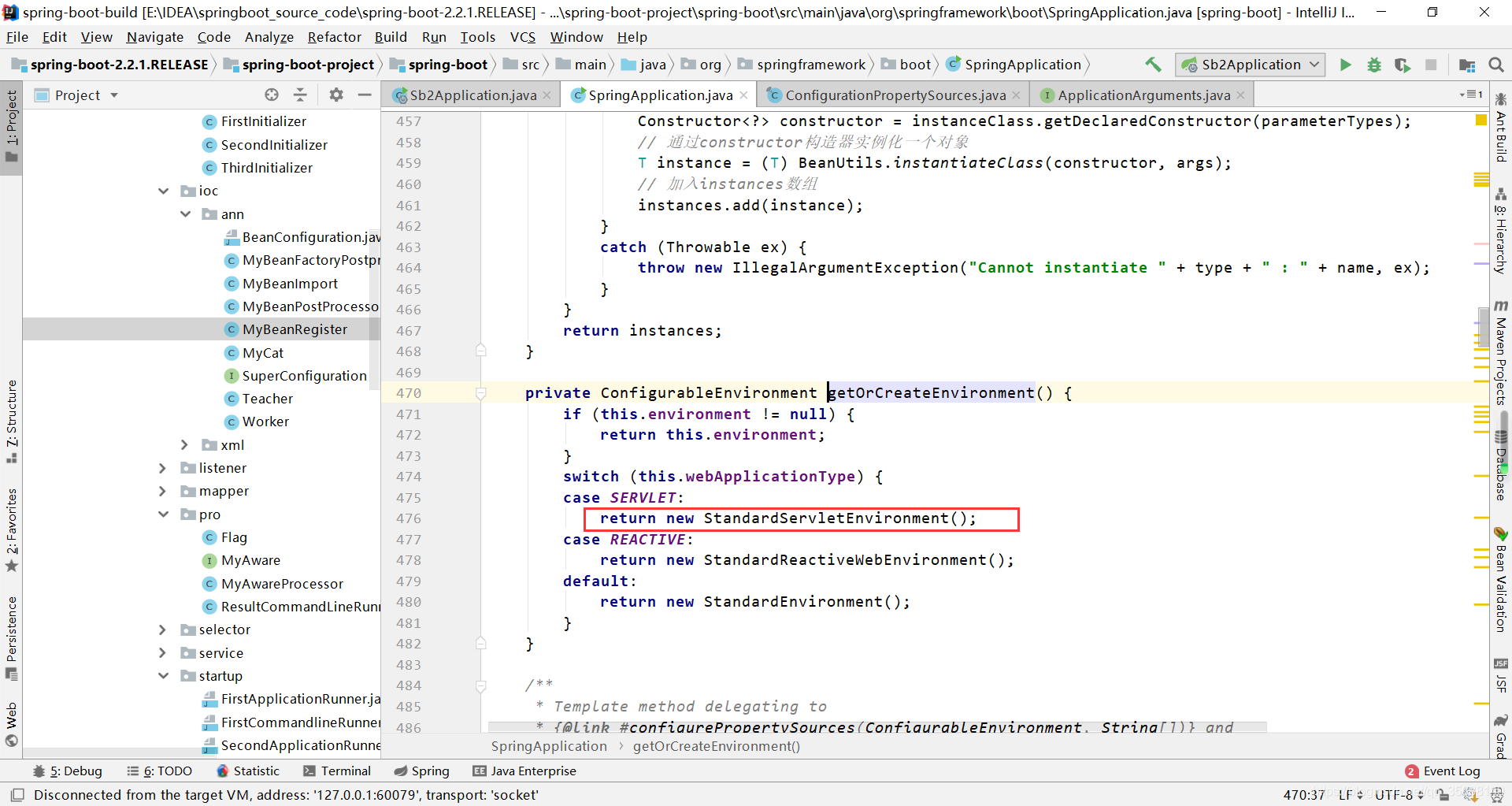 进入
进入StandardServletEnvironment()的构造函数,发现为空,进入其父类的构造函数
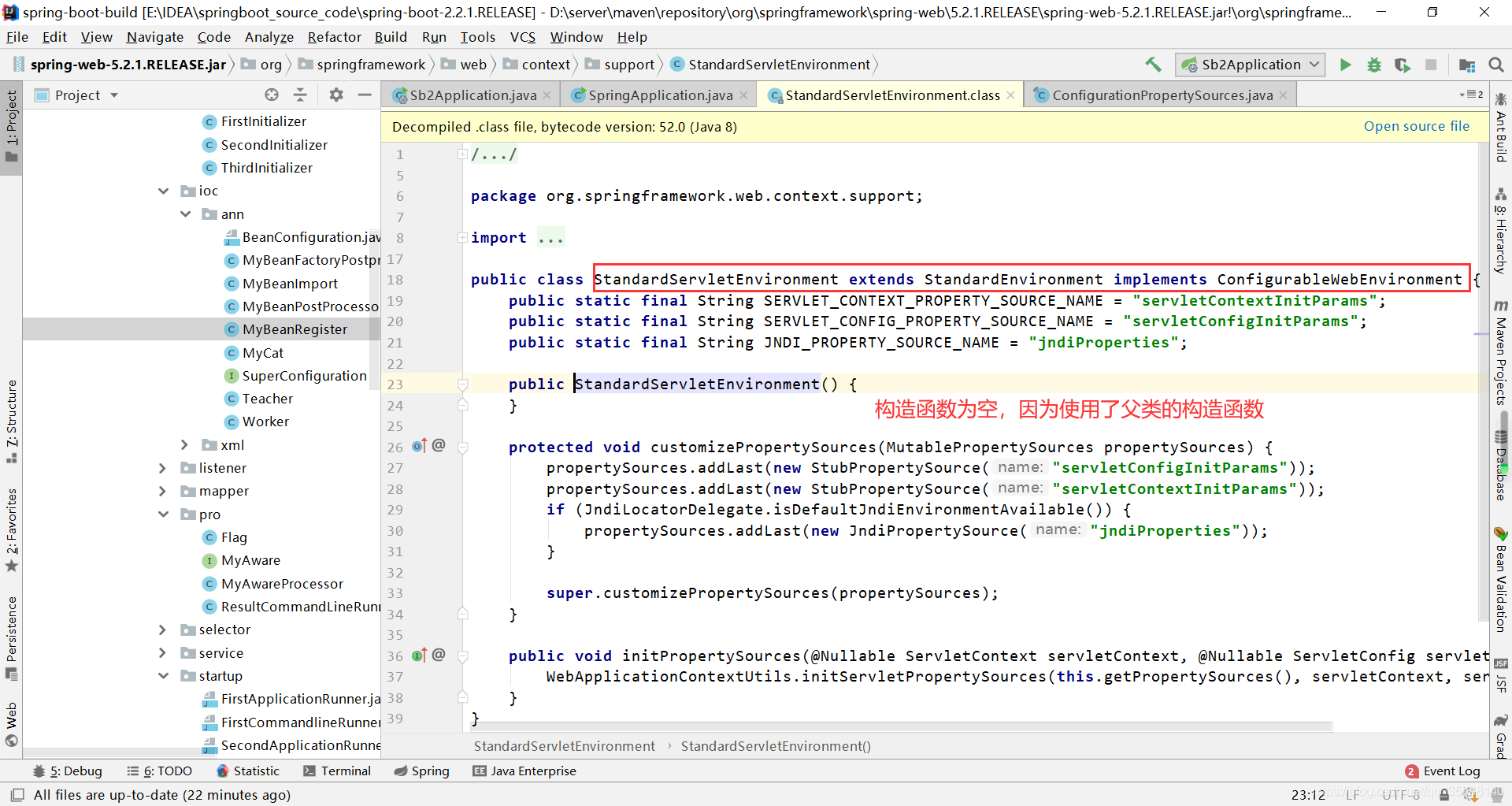
查看发现,StandardServletEnvironment继承于StandardEnvironment,StandardEnvironment继承于AbstractEnvironment,AbstractEnvironment的构造函数中,
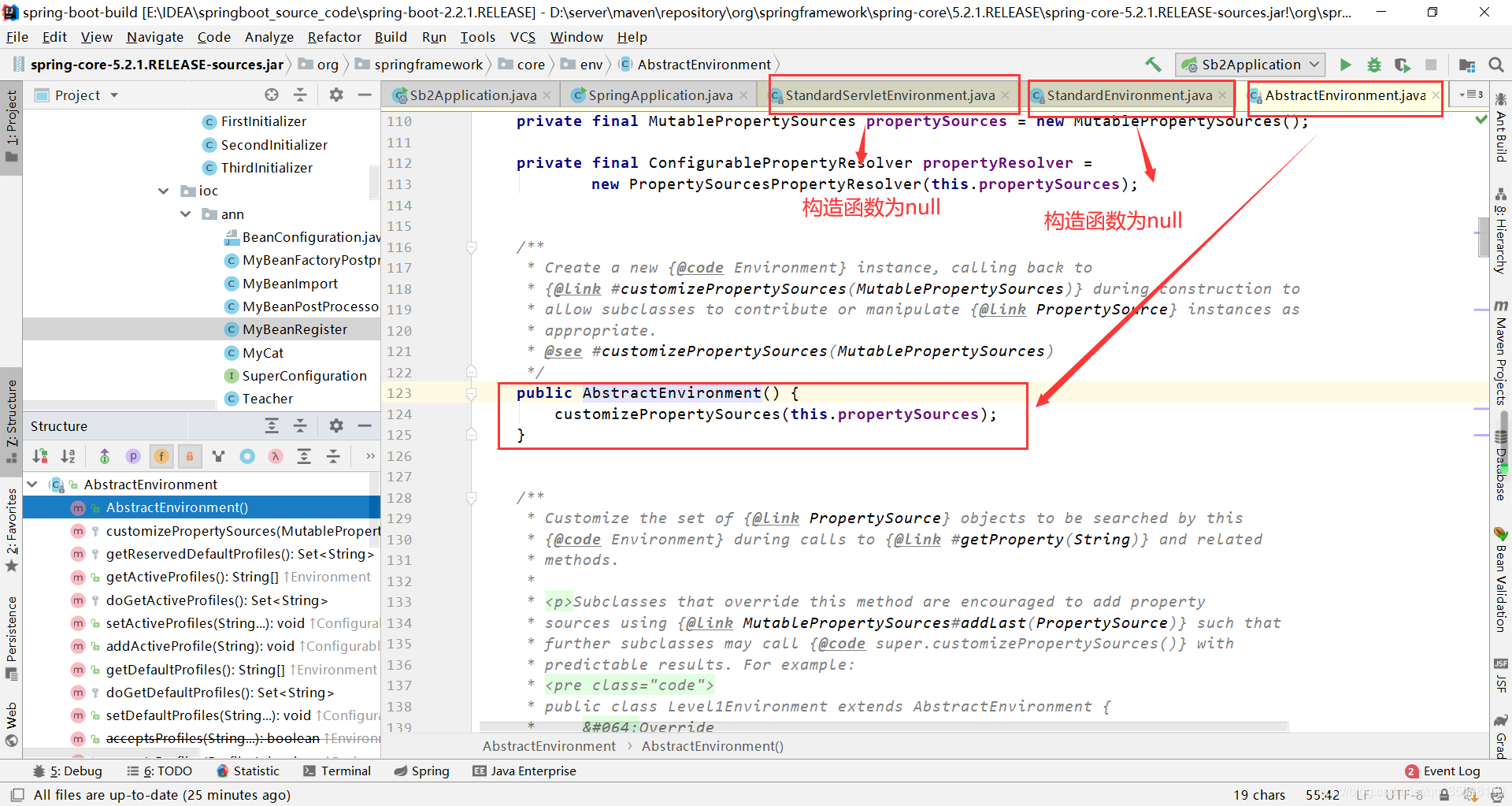
debug发现此时的propertySources为空
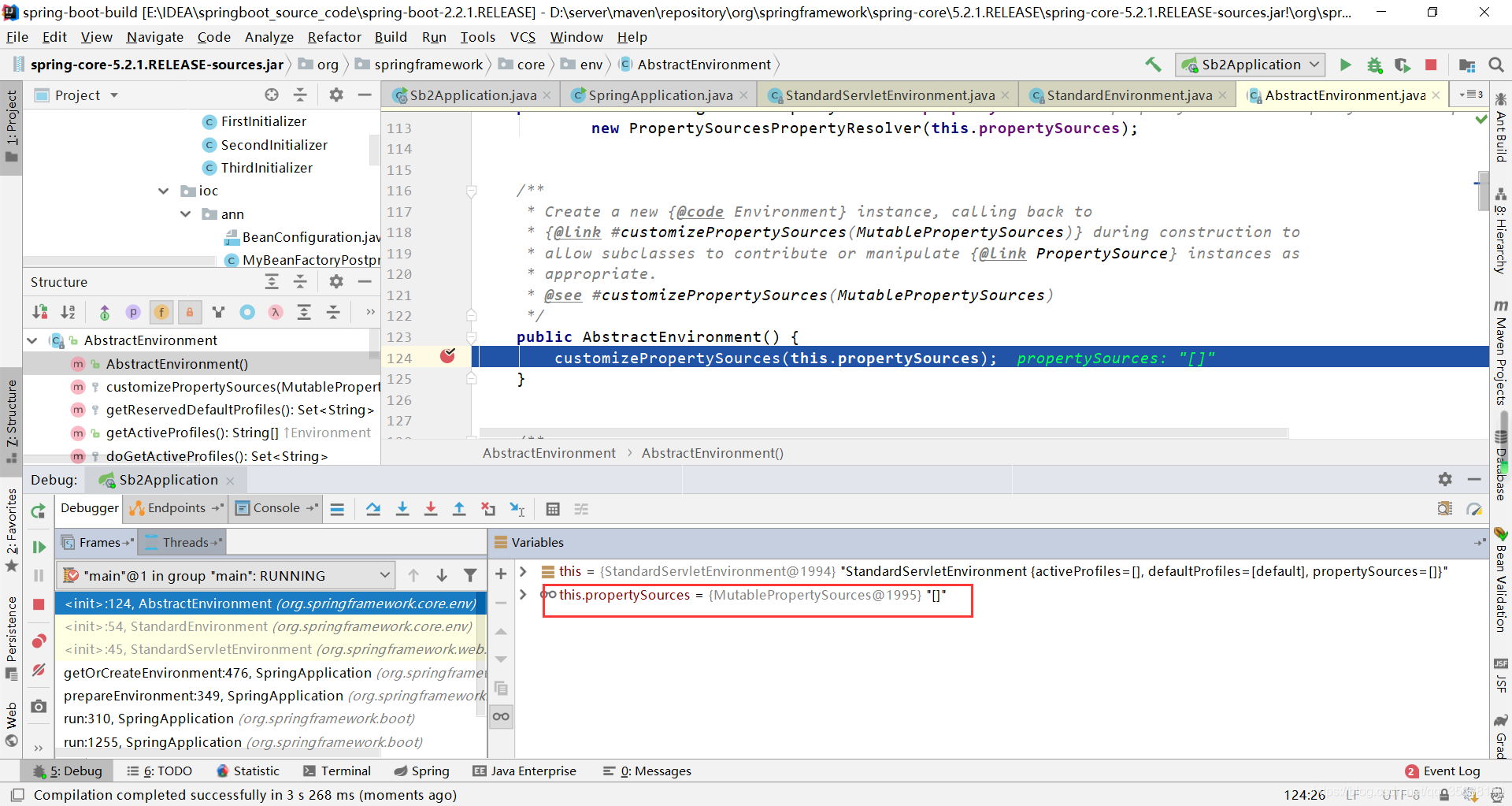
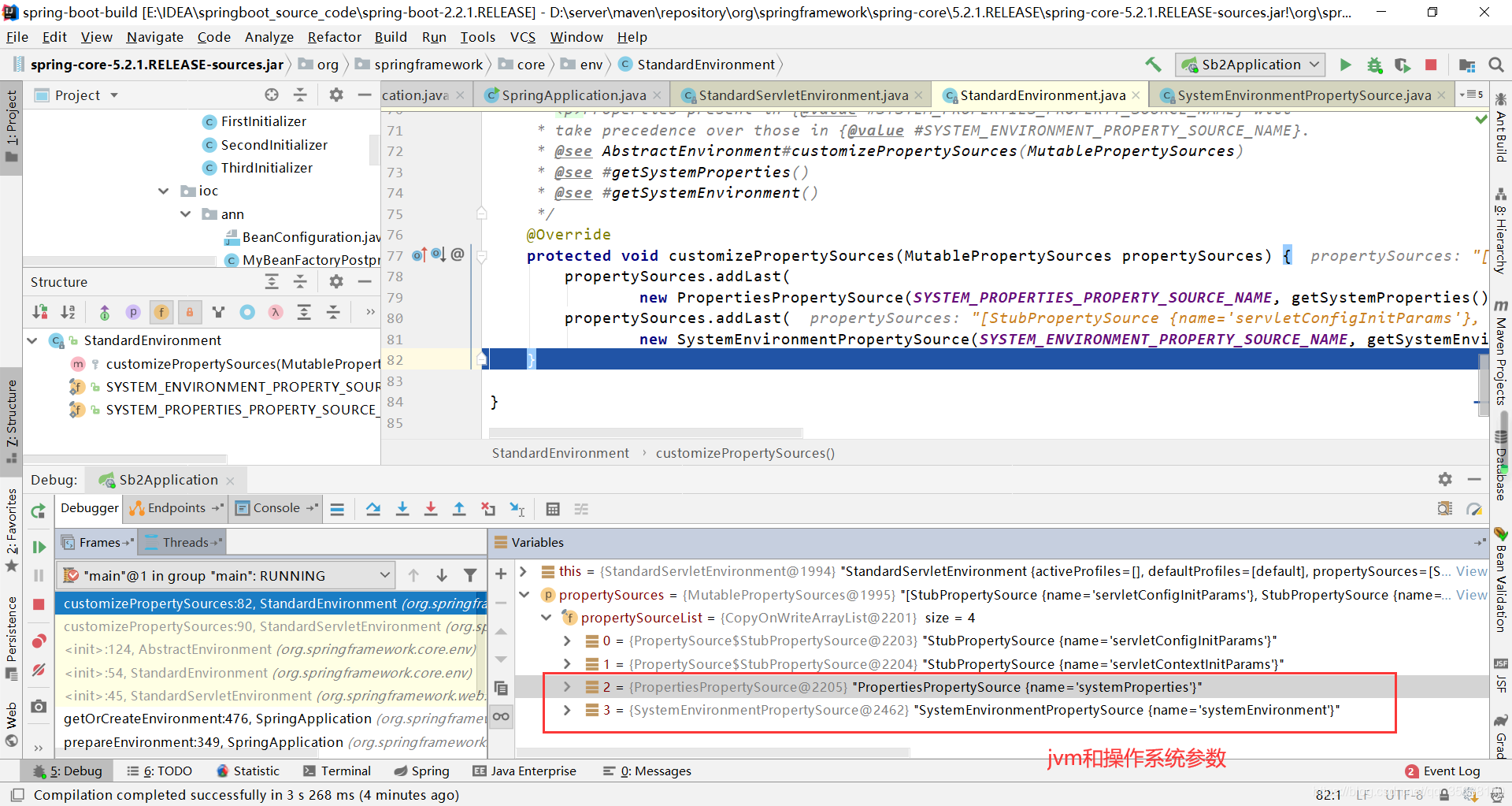
调用子类的customizePropertySources()函数
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
运行完该方法以后,propertySources中的内容如下:
3.2 进入configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs())方法
listener发布监听事件,

void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
查看发现有7个监听器
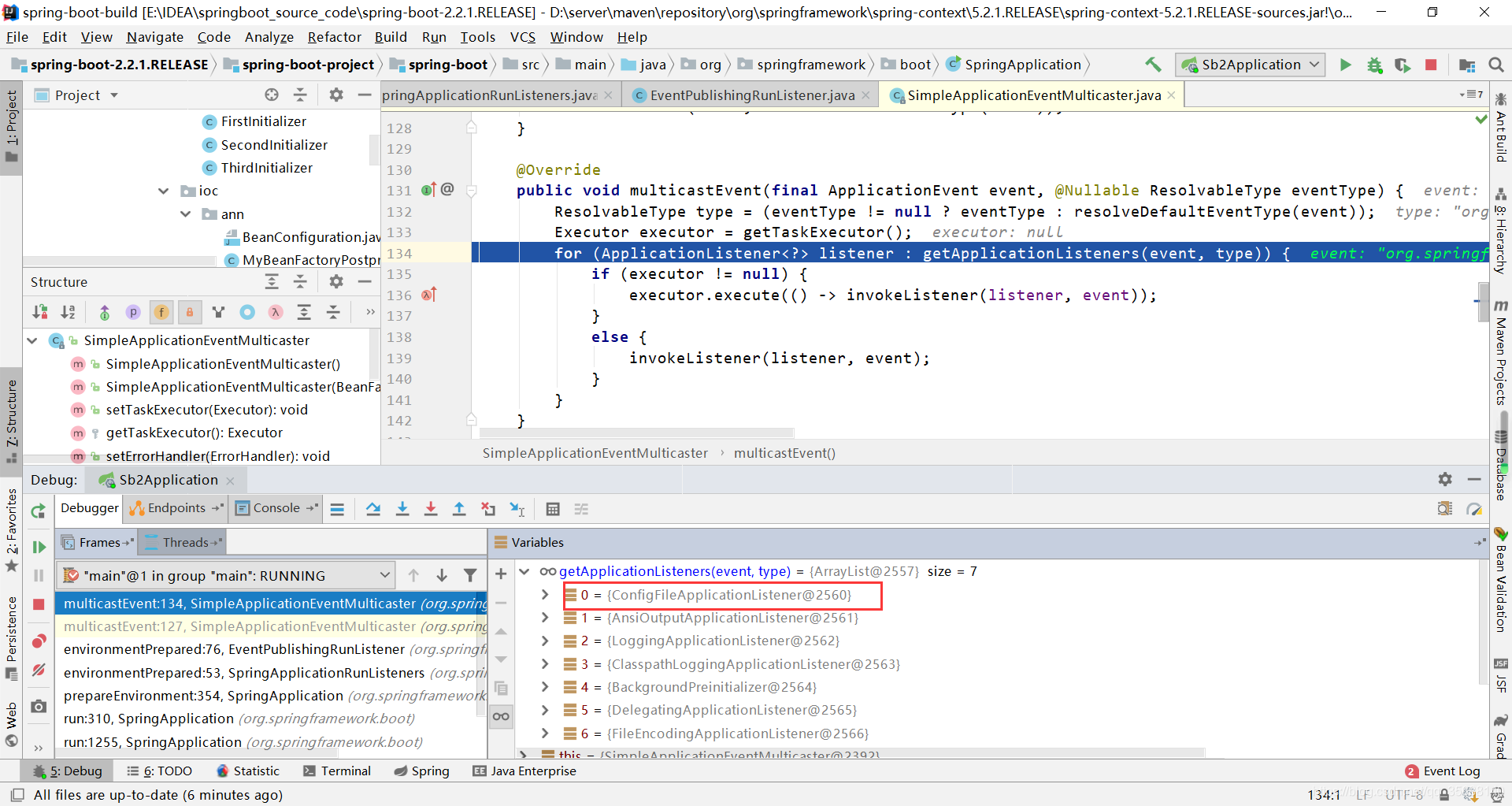
进入ConfigFileApplicationListener
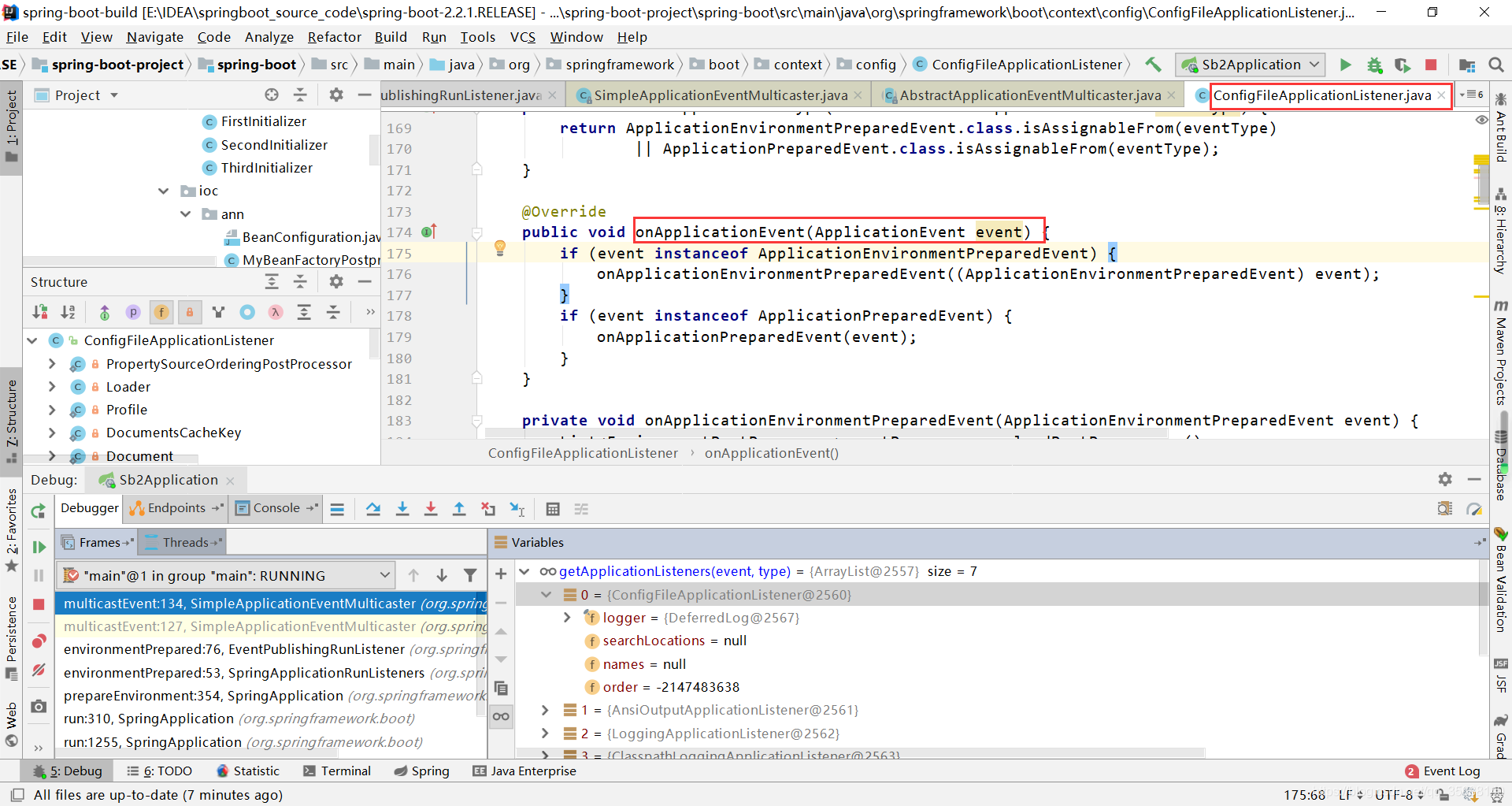
该类会load profile和application.properties的加载
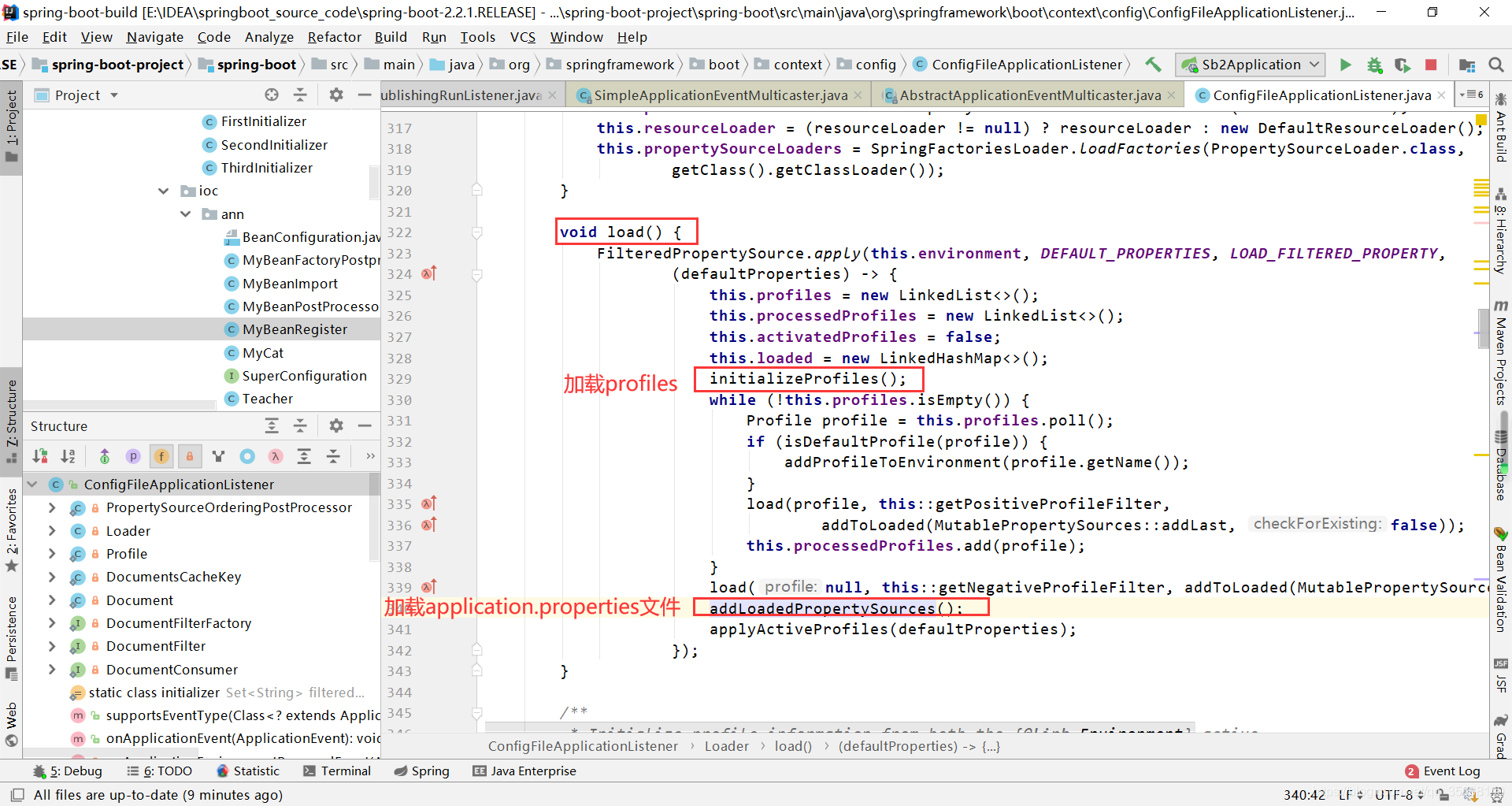
运行该方法结束:新增一个random和application.properties的相关属性
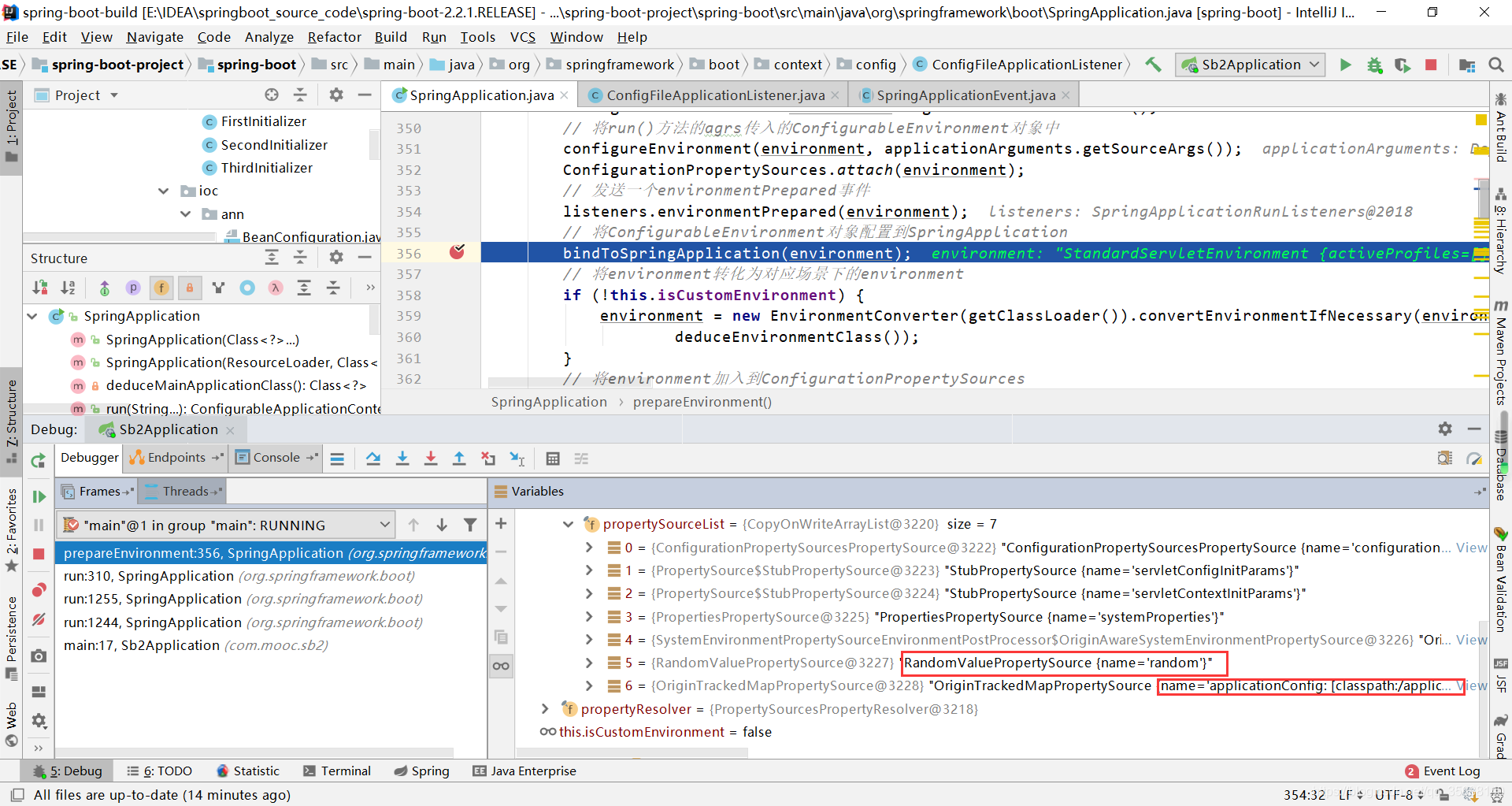
3.3 进入bindToSpringApplication(environment)方法
该方法会将application中spring.main开头的属性,与一些系统类的属性关联起来。
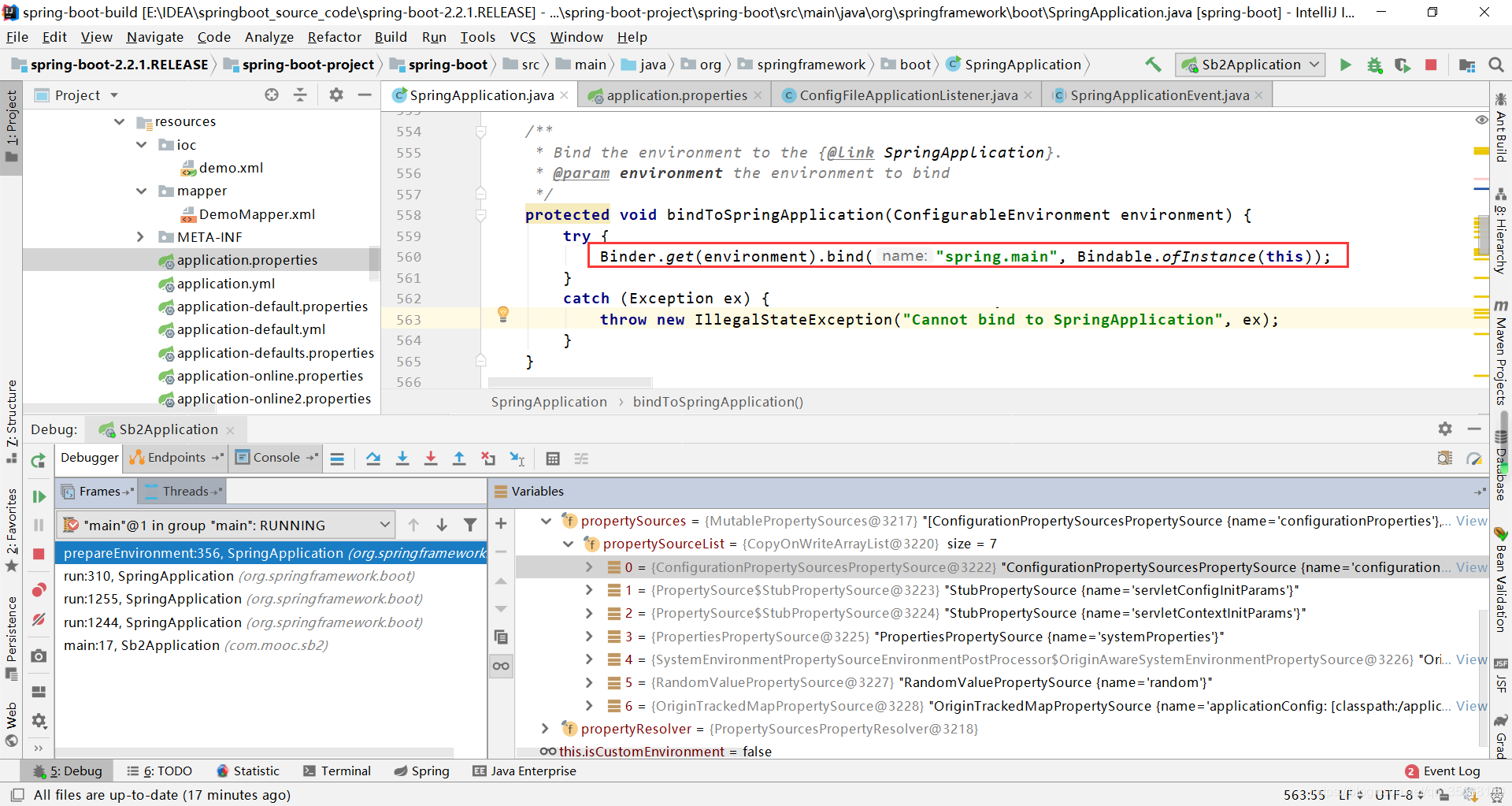
3.4 new EnvironmentConverter();
该方法主要是判断当前环境于Environment类是否相符和,不符合就实现不同Environment之间的一个转化,下面是三种不同的Environment
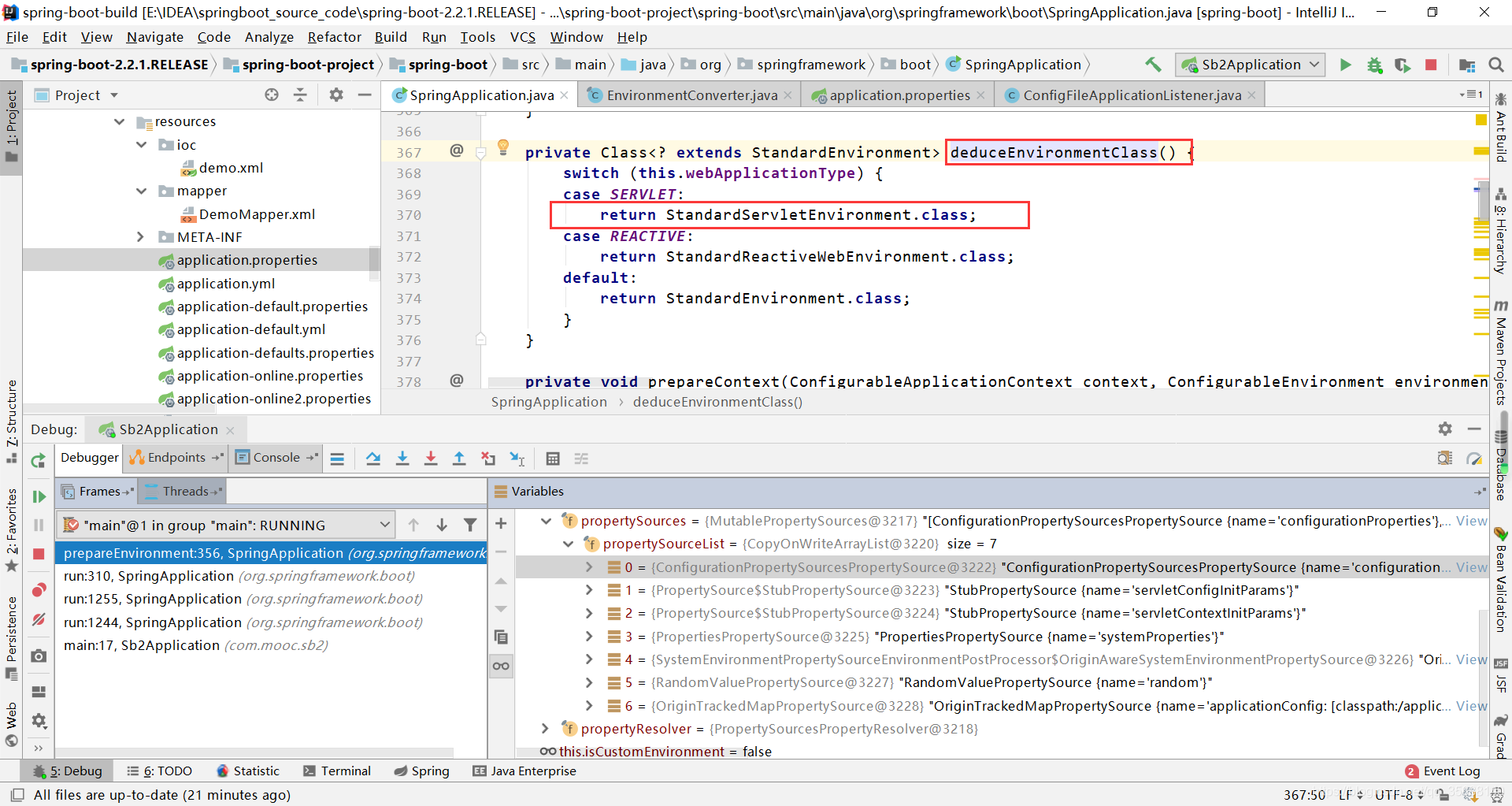
3.5 ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment)
该方法主要用于建立ConfigurationPropertySources于environment之间的绑定关系
总结:SpringApplication的run()方法里面有一行prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);主要是根据当前环境初始化Environment,然后向其中注入PropertySource参数,





