本文的所有内容均是官方文档的简单翻译和理解。
主要介绍Dart语言[变量、内置类型、函数、类、泛型、异常、库、生成器、元数据(注解)]
本人以实际代码案例为主,可以直接复制Android studio运行学习。
变量
变量的声明
- var
- dynamic
- Object
变量的默认值
- 没有初始化的变量自动获取一个默认值为null
- 一切皆对象,对象的默认值为null
final和const
- 共同点:
- 1.声明的类型可省略
- 2.初始化后不能再赋值
- 3.不能和var同时使用
- 不同点(需要注意的地方)
- 1.类级别常量,使用static const
- 2.const可使用其他const 常量的值来初始化其值
- 3.使用const赋值声明,const可省略
- 4.可以更改非final、非const变量的值,即使曾经具有const值
- 5.const导致的不可变性是可传递的
- 6.相同的const常量不会在内存中重复创建
- 7.const需要是编译时常量
内置类型
num, int, double
- int : 整数值
- double : 64-bit双精度浮点数
- int和double是num的子类
String
- Dart 字符串是 UTF-16 编码的字符序列,可以使用单引号或者双引号来创建字符串
- 可以使用三个单引号或者双引号创建多行字符串对象
- 可以使用 r 前缀创建”原始raw”字符串
- 可以在字符串中使用表达式: ${expression},如果表达式是一个标识符,可以省略 {},如果表达式的结果为一个对象,则 Dart 会调用对象的 toString() 函数来获取一个字符串
bool
- bool对象未初始化的默认值是null
List
- Dart中可以直接打印list包括list的元素,List也是对象。java中直接打印list结果是地址值
- Dart中List的下标索引和java一样从0开始
- 和java一样支持泛型
- 有增删改查,支持倒序,自带排序、洗牌,可使用+将两个List合并
Map
- 跟java类似,不做详解
Set
- set1.difference(set2):返回set1集合里有但set2里没有的元素集合
- set1.intersection(set2):返回set1和set2的交集
- set1.union(set2):返回set1和set2的并集
- set1.retainAll():set1只保留某些元素(要保留的元素要在原set中存在)
Runes路由
Main(){
Runes runes = new Runes('\u{1f605} \u6211‘);
var str1 = String.fromCharCodes(runes);
print(str1);
}
Symbol
- Symbol标识符,主要是反射用,现在mirrors模块已经被移除
函数
- 可在函数内定义
- 定义函数时可省略类型
- 定义函数时可省略类型
可选参数
- 可选命名参数
- 可选位置参数
- 默认参数值
匿名函数
- 可赋值给变量,通过变量调用
- 可在其他函数中直接调用或传递给其他函数
闭包
Function makeAddFunc(int x) {
x++;
return (int y) => x + y;
}
main() {
var addFunc2 = makeAddFunc(2);
var addFunc4 = makeAddFunc(4);
print(addFunc2(3));
print(addFunc4(3));
}
函数别名
typedef Fun1(int a, int b);
typedef Fun2<T, K>(T a, K b);
int add(int a, int b) {
print('a + b');
return a + b;
}
class Demo1 {
Demo1(int f(int a, int b), int x, int y) {
var sum = f(x, y);
print("sum1 = $sum");
}
}
class Demo2 {
Demo2(Fun1 f, int x, int y) {
var sum = f(x, y);
print("sum2 = $sum");
}
}
class Demo3 {
Demo3(Fun2<int, int> f, int x, int y) {
var sum = f(x, y);
print("sum3 = $sum");
}
}
操作符

流程控制语句
- if else
- for, forEach, for-in
- while , do-while
- break ,continue
- switch case
异常
Exception类型
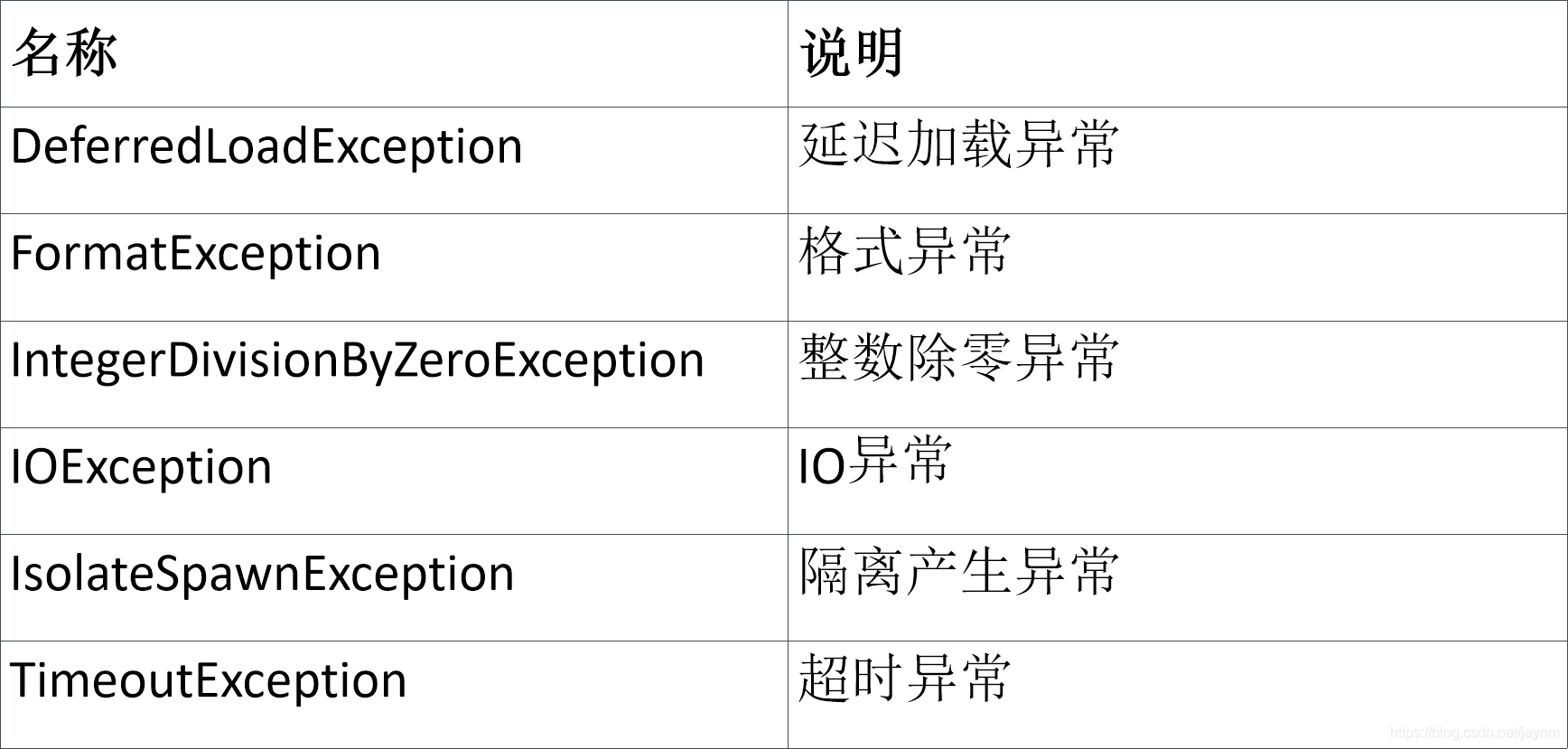
Error类型
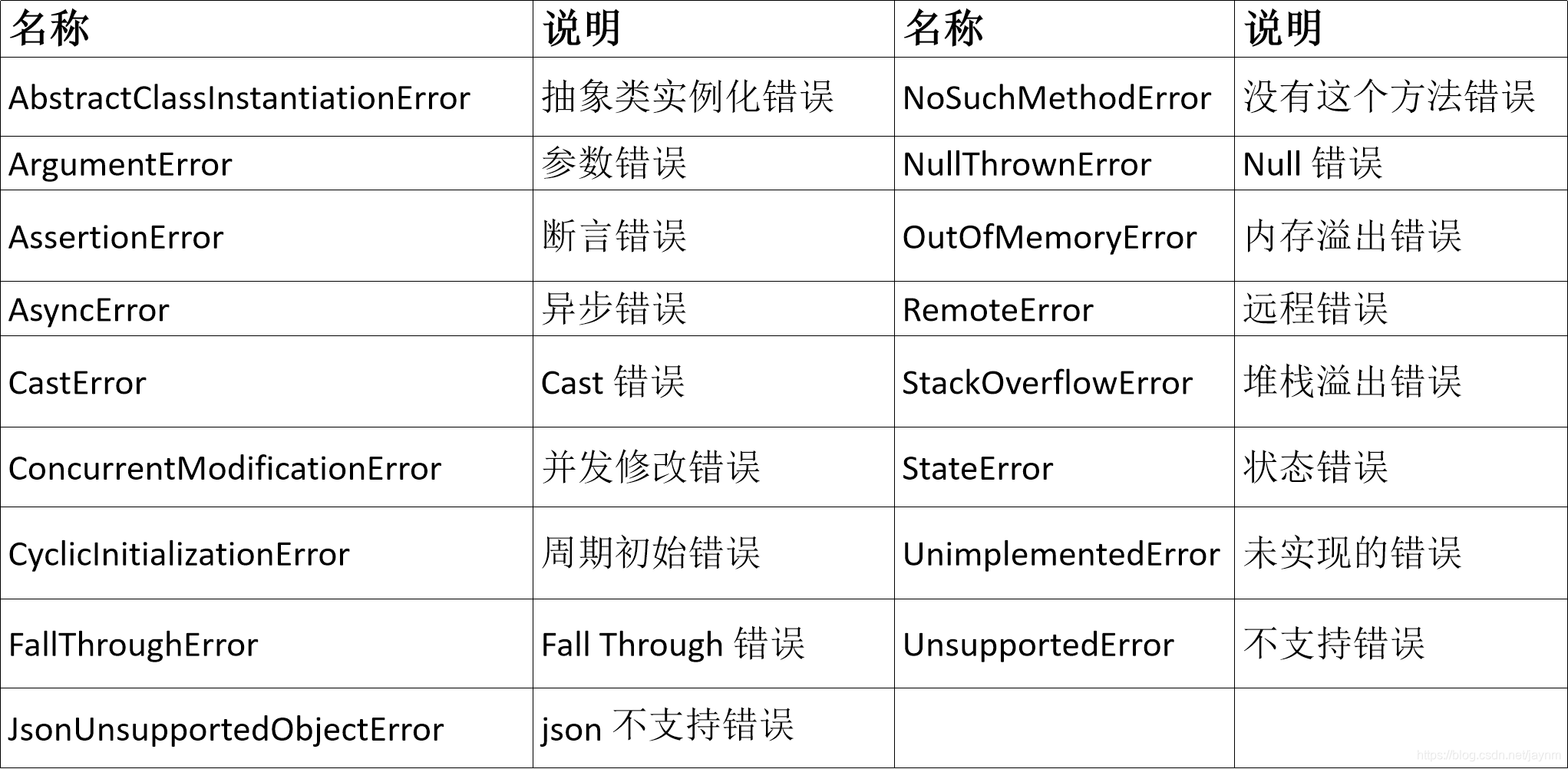
异常抛出
// 抛出Exception 对象
throw new FormatException(‘格式异常');
// 抛出Error 对象
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 抛出任意非null对象
throw '这是一个异常';
异常捕获
try {
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
} on OutOfMemoryError {
print('没有内存了');
} on Error catch(e) {
print('Unknown error: $e');
} catch (e, s) {
print('Exception details: $e');
print('Stack Trace: $s');
} finally {
print('end');
}
类
构造函数
- Java中写法
class Point {
double x;
double y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
- Dart建议写法
class Point {
num x;
num y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
}
命名构造函数
class Point {
num x;
num y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
//命名构造函数
Point.fromJson(Map json) {
x = json['x'];
y = json['y'];
}
}
重定向构造函数
class Point {
num x;
num y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
//重定向构造函数,使用冒号调用其他构造函数
Point.alongXAxis(num x) : this(x, 0);
}
初始化列表
import 'dart:math';
class Point {
//final变量不能被修改,必须被构造函数初始化
final num x;
final num y;
final num distanceFromOrigin;
//初始化列表
Point(x, y)
: x = x,
y = y,
distanceFromOrigin = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
调用超类构造函数
class Parent {
int x;
int y;
//父类命名构造函数不会传递
Parent.fromJson(x, y)
: x = x,
y = y {
print('父类命名构造函数');
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
int x;
int y;
//若超类没有默认构造函数, 需要手动调用超类其他构造函数
Child(x, y) : super.fromJson(x, y) {
//调用父类构造函数的参数无法访问 this
print('子类构造函数');
}
//在构造函数的初始化列表中使用super(),需要把它放到最后
Child.fromJson(x, y)
: x = x,
y = y,
super.fromJson(x, y) {
print('子类命名构造函数');
}
}
常量构造函数
class Point2 {
//定义const构造函数要确保所有实例变量都是final
final num x;
final num y;
static final Point2 origin = const Point2(0, 0);
//const关键字放在构造函数名称之前,且不能有函数体
const Point2(this.x, this.y);
}
工厂构造函数
class Singleton {
String name;
//工厂构造函数无法访问this,所以这里要用static
static Singleton _cache;
//工厂方法构造函数,关键字factory
factory Singleton([String name = 'singleton']) =>
Singleton._cache ??= Singleton._newObject(name);
//定义一个命名构造函数用来生产实例
Singleton._newObject(this.name);
}
Setter和Getter
class Rectangle {
num left;
num top;
num width;
num height;
Rectangle(this.left, this.top, this.width, this.height);
num get right => left + width;
set right(num value) => left = value - width;
num get bottom => top + height;
set bottom(num value) => top = value - height;
}
抽象类
- abstract关键字修饰class
- 继承的方式使用
- 接口的方式使用
可调用类
class ClassFunction {
call(String a, String b, String c) => '$a $b $c!';
}
main() {
var cf = new ClassFunction();
var out = cf("dongnao","flutter","damon");
print('$out');
print(cf.runtimeType);
print(out.runtimeType);
print(cf is Function);
}
泛型
泛型函数
main() {
K addCache<K, V>(K key, V value) {
K temp = key;
print('${key}: ${value}');
return temp;
}
var key = addCache('dongnao', 'damon');
print(key);
}
构造函数泛型
main() {
var p = Phone<String>('123456');
print(p.mobileNumber);
}
class Phone<T> {
final T mobileNumber;
Phone(this.mobileNumber);
}
泛型限制
main() {
var footMassage = FootMassage();
var m = Massage<FootMassage>(footMassage);
m.massage.doMassage();
}
class Massage<T extends FootMassage > {
final T massage;
Massage(this.massage);
}
class FootMassage {
void doMassage() {
print('脚底按摩');
}
}
Dart泛型与Java泛型区别
- Java中的泛型信息是编译时的,泛型信息在运行时是不存在的
- Dart的泛型类型是固化的,在运行时也有可以判断的具体类型
var names = List<String>();
print(names is List<String>);//true
print(names.runtimeType); // List<String>
库
载入第三方库
- 编写pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.0
dio: ^2.1.0
- 调用
import "package:dio/dio.dart";
void main() {
getHttp();
}
void getHttp() async {
try {
Response response = await Dio().get("https://www.baidu.com");
print(response);
} catch (e) {
print(e);
}
}
载入文件
//Mylib1.dart
class MyLib {
String name;
static MyLib _cache;
factory MyLib([String name = 'singleton']) =>
MyLib._cache ??= MyLib._newObject(name);
MyLib._newObject(this.name);
}
import “mylib1.dart";
void main() {
var myLib1 = MyLib();
}
指定库前缀
如果两个库有冲突的标识符,可以为其中一个或两个库都指定前缀:
import 'MyLib1.dart' as lib1;
import 'MyLib2.dart' as lib2;
void main() {
var myLib = lib1.MyLib();
var myLib2 = lib2.MyLib();
}
选择性载入
- show-只载入库的某些部分
- hide-筛选掉库的某些部分
import 'Mylib1.dart' as lib1 show Test;
import 'Mylib2.dart' as lib2 hide Test;
var test = lib1.Test();
var lib = lib2.MyLib();
延迟载入
- 使用deferred as导入
- 使用标识符调用loadLibrary()加载库
import 'MyLib1.dart' deferred as lazyLib;
void main() {
lazyLoad();
}
lazyLoad() async {
await lazyLib.loadLibrary();
var t = lazyLib.Test();
t.test();
}
异步
异步-async和await
void main(){
getName1();
getName2();
getName3();
}
Future getName1() async {
await getStr1();
await getStr2();
print('getName1’);
}
getStr1() {
print('getStr1’);
}
getStr2() {
print('getStr2’);
}
getName2() {
print('getName2’);
}
getName3() {
print('getName3’);
}
异步-then,catchError,whenComplete
void main() {
new Future(() => futureTask())//异步任务的函数
.then((m) => "result:$m")//任务执行完后的子任务
.then((m) => m.length) //其中m为上个任务执行完后的返回的结果
.then((m) => printLength(m))
.catchError(print)
.whenComplete(() => whenTaskCompelete());//所有任务完成后的回调函数
}
Event-Looper
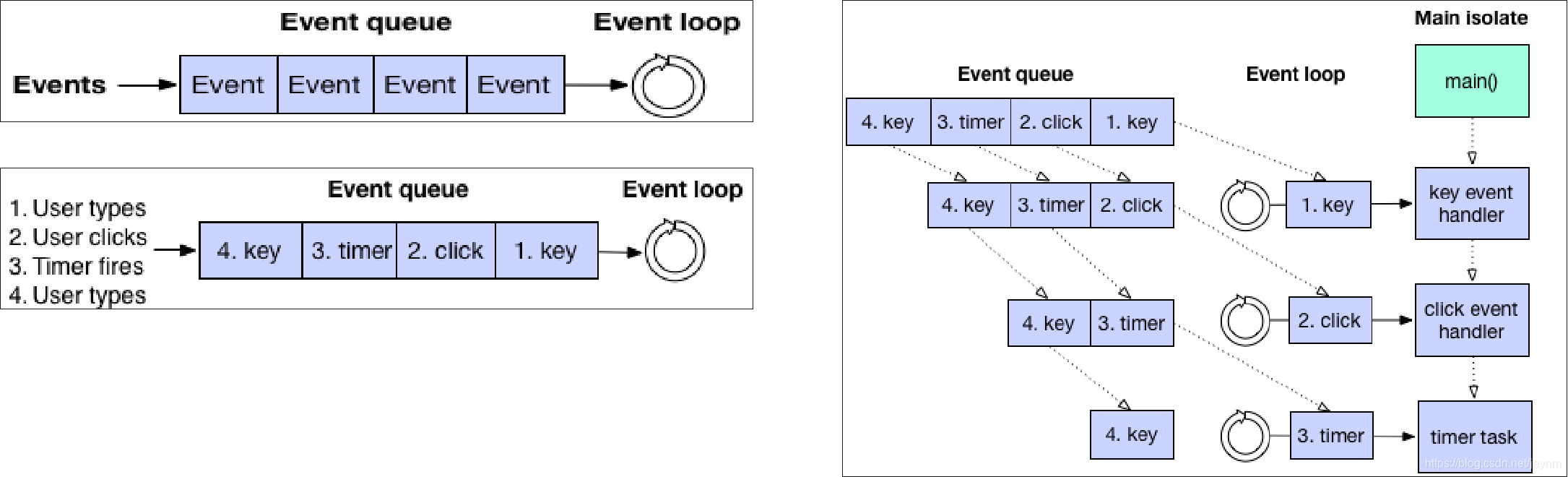
异步-Event Queue和Microtask Queue
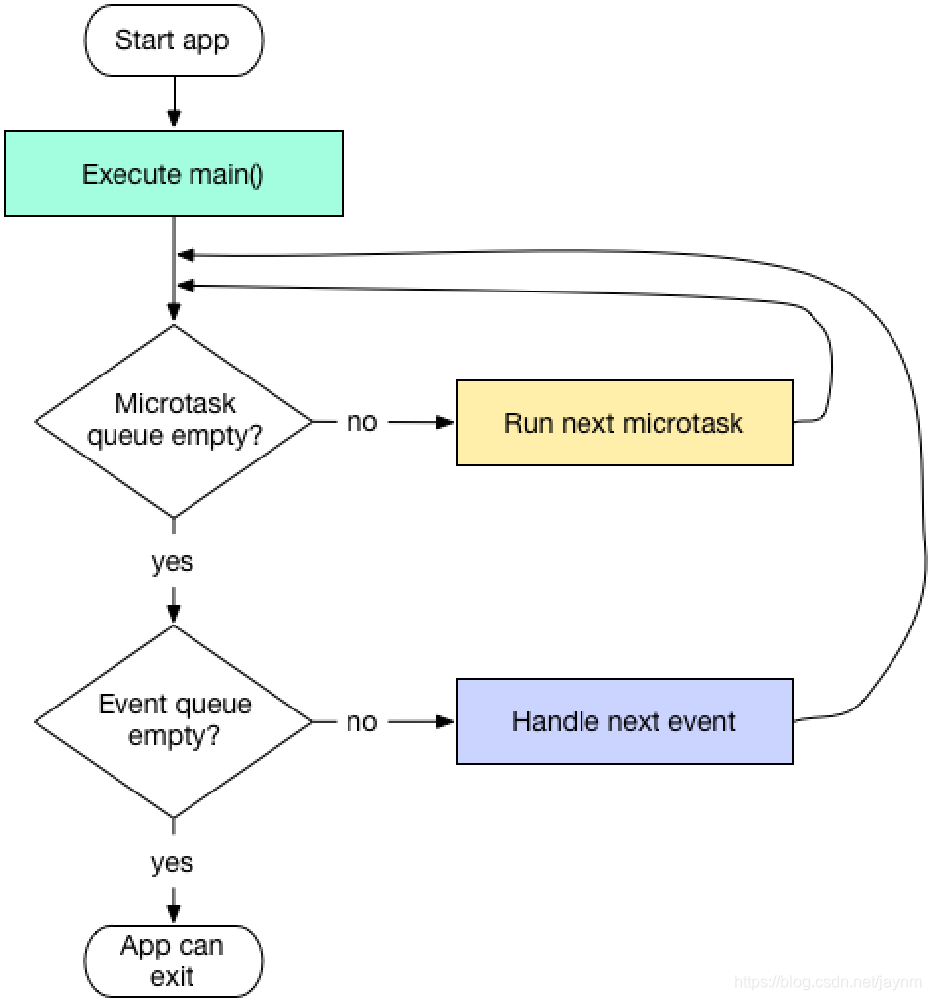
异步-任务调度
- 使用Future类,可以将任务加入到Event Queue的队尾
- 使用scheduleMicrotask函数,将任务加入到Microtask Queue队尾
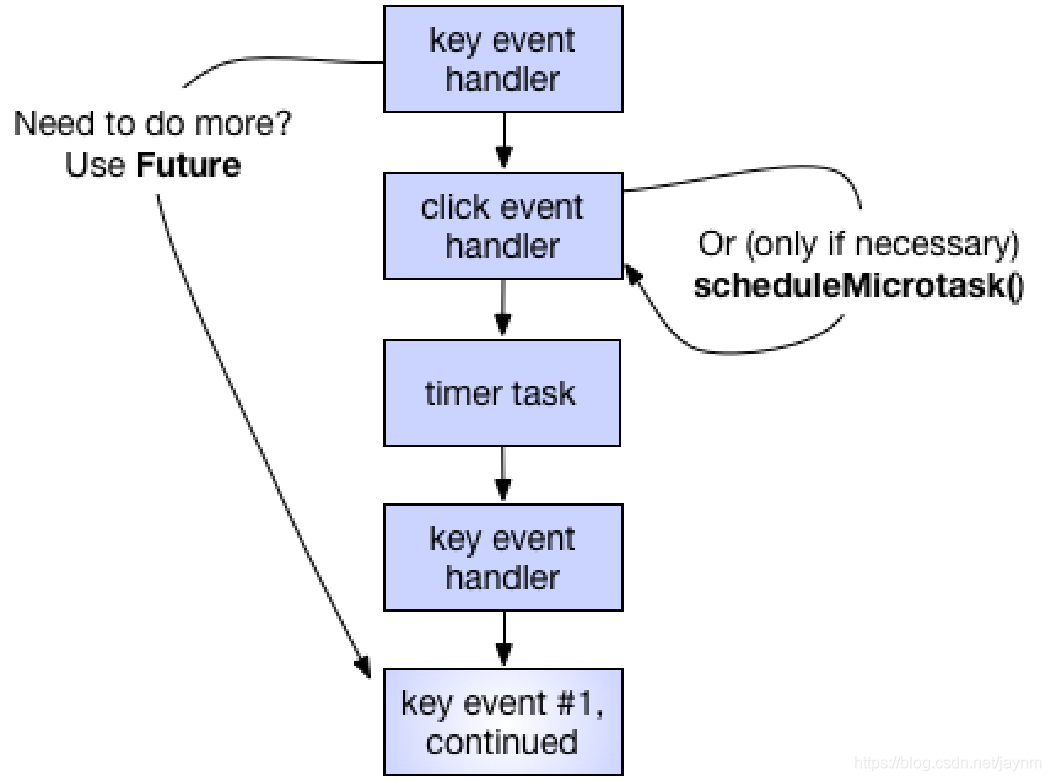
异步-new Future()
void main(){
testFuture();
}
void testFuture() {
Future f = new Future(() => print('f1'));
Future f1 = new Future(() => null);
//Future f1 = new Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1) ,() => null);
Future f2 = new Future(() => null);
Future f3 = new Future(() => null);
f3.then((_) => print('f2'));
f2.then((_) {
print('f3');
new Future(() => print('f4'));
f1.then((_) {
print('f5');
});
});
f1.then((m) {
print('f6');
});
print('f7');
}
异步-scheduleMicrotask()
import 'dart:async';
void main(){
testFuture();
}
void testScheduleMicrotask(){
scheduleMicrotask(() => print('s1'));
new Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 1), () => print('s2'));
new Future(() => print('s3')).then((_) {
print('s4');
scheduleMicrotask(() => print('s5'));
}).then((_) => print('s6'));
new Future(() => print('s7'));
scheduleMicrotask(() => print('s8'));
print('s9');
}
生成器
生成器-同步生成器
Main(){
var it = getSyncGenerator(5).iterator;
while (it.moveNext()) {
print(it.current);
}
}
Iterable<int> getSyncGenerator(int n) sync* {
print('start');
int k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield k++;
}
print('end');
}
生成器-异步生成器
Main(){
//getAsyncGenerator(5).listen((value) => print(value));
StreamSubscription subscription = getAsyncNumIterator(5).listen(null);
subscription.onData((value) {
print(value);
if(value>=2){
subscription.pause();
}
});
}
Stream<int> getAsyncGenerator(int n) async* {
print('start');
int k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield k++;
}
print('end');
}
生成器-递归生成器
Main(){
var it = getSyncRecursiveGenerator(5).iterator;
while (it.moveNext()) {
print(it.current);
}
}
Iterable<int> getSyncRecursiveGenerator(int n) sync* {
if (n > 0) {
yield n;
yield* getSyncNumDownFrom(n - 1);
}
}
元数据
(注解)-@deprecated
main() {
dynamic tv = new Television();
tv.activate();
tv.turnOn();
}
class Television {
@deprecated
void activate() {
turnOn();
}
void turnOn() {
print('Television turn on!');
}
}
(注解)-@override
main() {
dynamic tv = new Television();
tv.activate();
tv.turnOn();
tv.turnOff();
}
class Television {
@deprecated
void activate() {
turnOn();
}
void turnOn() {
print('Television turn on!');
}
@override
noSuchMethod(Invocation mirror) {
print('没有找到方法');
}
}
(注解)-自定义
//todo.dart
class Todo {
final String who;
final String what;
const Todo({this.who, this.what});
}
import 'todo.dart’;
main() {
dynamic tv = new Television();
tv.doSomething();
}
class Television {
@Todo(who: 'damon', what: 'create a new method')
void doSomething() {
print('doSomething');
}
}
