线程可以划分优先级,优先级高的线程得到的CPU资源比较多,也就是CPU优先执行优先级高的线程对象中的任务。
设置线程优先级有助于帮助线程规划器确定下一次选中哪一个线程优先执行。
java中优先级分为1-10个级别
线程优先级的继承特性 例如a线程启迪b线程,则b线程的优先级与a的一样。
代码说话:(很简单)
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("MyThread1 run priority=" + this.getPriority());
MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2();
thread2.start();
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("MyThread2 run priority=" + this.getPriority());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main thread begin priority="
+ Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(6);
System.out.println("main thread end priority="
+ Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1();
thread1.start();
}
优先级具有规则性
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
addResult = addResult + i;
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("★★★★★thread 1 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
addResult = addResult + i;
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("☆☆☆☆☆thread 2 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1();
thread1.setPriority(1);
thread1.start();
MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2();
thread2.setPriority(10);
thread2.start();
}
}
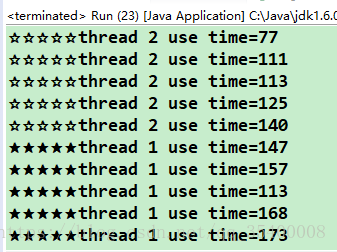
高优先级的线程总是先执行完
线程的优先级和代码的执行顺序没有关系
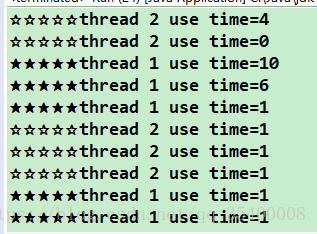
优先级具有随机性
一般优先级较高的线程先执行run()方法,但是这个不能说的但肯定,因为线程的优先级具有 “随机性”也就是较高线程不一定每一次都先执行完。
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("★★★★★thread 1 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("☆☆☆☆☆thread 2 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1();
thread1.setPriority(5);
thread1.start();
MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2();
thread2.setPriority(6);
thread2.start();
}
}
守护线程介绍:
java 中有两种线程 一个是用户线程,一个是守护(Daemon)线程
典型的守护线程就是垃圾回收线程,如果进程中没有非守护线程了,则守护线程自动销毁。
守护线程作用就是为其他线程的运行提供便利的服务,比如GC。
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int i = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
i++;
System.out.println("i=" + (i));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.setDaemon(true);//设置守护线程
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("我离开thread对象也不再打印了,也就是停止了!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}