Self divisor is the number that can be divided by every digit it contains.
For example, 128 is a self-divisor because 128%1 == 0, 128%2 == 0, 128%8 == 0.
Also, it is not allowed to include 0’s in the self divisor.
Given the upper and lower boundary Numbers, output a list whose elements are all the self-divisor in the boundary (including the boundary).
For example:
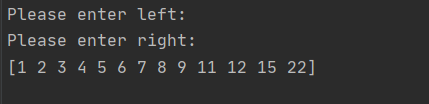
Input: Left on top = 1, right on bottom = 22
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 15, 22]
Note:
The boundary of each input parameter satisfies 1 <= left <= right <= 10000
Train of thought to solve the problem:
The problem requires a self-divisor that divisible the number on each bit. It’s not hard to think of using a recursive algorithm to calculate whether each bit fits the criteria. If it does, it returns true, and the program continues to run, adding qualified Numbers to the output array.If not, false is returned, and the program detects whether the next number matches the requirement. In the go language, you can use the append method to add elements to an array. In the check method, num and tem need to be distinguished, because if num is a two-digit number or a high-digit number, the recursive algorithm will cause the values of the two elements to be different.
Code
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
var left int
var right int
var answer [] int
fmt.Println("Please enter left:")
fmt.Scan(&left)
fmt.Println("Please enter right:")
fmt.Scan(&right)
answer=selfDividingNumbers(left,right)
fmt.Println(answer)
}
func selfDividingNumbers(left int, right int) []int {
answer:=[]int {}
for i:=left;i<=right;i++ {
if check(i) {
answer=append(answer,i)
}
}
return answer
}
func check(num int) bool{
tem:=num
for tem>0 {
d:=tem%10
if d==0 {
return false
}
r:=num%d
if r!=0 {
return false
}
tem/=10
}
return true
}
output