1.概述
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的 #doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) 方法,主要干三件事情:
- 实例化 bean 对象:
#createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args)方法。 - 属性注入:
#populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw)方法。 - 初始化 bean 对象:
#initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)方法。
而初始化 bean 对象时,也是干了三件事情:
- 激活 Aware 方法
- 后置处理器的应用
- 激活自定义的 init 方法
接下来三篇文章将会详细分析这三件事情,这篇主要分析 Aware 接口。
2.Aware接口
org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware 接口,定义如下:
/** * A marker superinterface indicating that a bean is eligible to be notified by the * Spring container of a particular framework object through a callback-style method. * The actual method signature is determined by individual subinterfaces but should * typically consist of just one void-returning method that accepts a single argument. * * <p>Note that merely implementing {@link Aware} provides no default functionality. * Rather, processing must be done explicitly, for example in a * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor}. * Refer to {@link org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor} * for an example of processing specific {@code *Aware} interface callbacks. * * @author Chris Beams * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 3.1 */ public interface Aware { }
Aware 接口为 Spring 容器的核心接口,是一个具有标识作用的超级接口,实现了该接口的 bean 是具有被 Spring 容器通知的能力,通知的方式是采用回调的方式。
Aware 接口是一个空接口,实际的方法签名由各个子接口来确定,且该接口通常只会有一个接收单参数的 set 方法,该 set 方法的命名方式为 set + 去掉接口名中的 Aware 后缀,即 XxxAware 接口,则方法定义为 setXxx(),例如 BeanNameAware(setBeanName),ApplicationContextAware(setApplicationContext)。
Aware 的子接口需要提供一个 setXxx 方法,我们知道 set 是设置属性值的方法,即 Aware 类接口的 setXxx 方法其实就是设置 xxx 属性值的。 Aware 的含义是感知的、感应的,那么在 Spring 容器中是如何实现感知并设置属性值得呢?我们可以从初始化 bean 中的激活 Aware 的方法 #invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) 中看到一点点,代码如下:
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { // BeanNameAware if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } // BeanClassLoaderAware if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); if (bcl != null) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); } } // BeanFactoryAware if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } }
- 首先,判断 bean 实例是否属于 Aware 接口的范畴,如果是的话,则调用实例的
setXxx()方法给实例设置 xxx 属性值,在#invokeAwareMethods(...)方法,主要是设置 beanName,beanClassLoader、BeanFactory 中三个属性值。
3.Aware子类
Spring 提供了一系列的 Aware 接口,如下图(部分):

上面只是一部分子类,从这里我们可以看到Spring提供的Aware接口是何其多,同事从上图我们也看到了几个比较熟悉的接口,如BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware、BeanNameAware,下面就这三个接口来做一个简单的演示:
public interface BeanClassLoaderAware extends Aware { /** * 将 BeanClassLoader 提供给 bean 实例回调 * 在 bean 属性填充之后、初始化回调之前回调, * 例如InitializingBean的InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法或自定义init方法 */ void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader); } public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware { /** * 将 BeanFactory 提供给 bean 实例回调 * 调用时机和 setBeanClassLoader 一样 */ void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; } public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware { /** * 在创建此 bean 的 bean工厂中设置 beanName */ void setBeanName(String name); } public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware { /** * 设置此 bean 对象的 ApplicationContext,通常,该方法用于初始化对象 */ void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException; }
3.1 示例
下面简单演示下上面四个接口的使用方法
public class MyApplicationAware implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,ApplicationContextAware{ private String beanName; private BeanFactory beanFactory; private ClassLoader classLoader; private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) { System.out.println("调用了 BeanClassLoaderAware 的 setBeanClassLoader 方法"); this.classLoader = classLoader; } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("调用了 BeanFactoryAware 的 setBeanFactory 方法"); this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("调用了 BeanNameAware 的 setBeanName 方法"); this.beanName = name; } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("调用了 ApplicationContextAware 的 setApplicationContext 方法"); this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public void display(){ System.out.println("beanName:" + beanName); System.out.println("是否为单例:" + beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)); System.out.println("系统环境为:" + applicationContext.getEnvironment()); } }
测试方法:
public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("spring.xml"); DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); MyApplicationAware applicationAware = (MyApplicationAware) factory.getBean("myApplicationAware"); applicationAware.display(); }
运行结果:
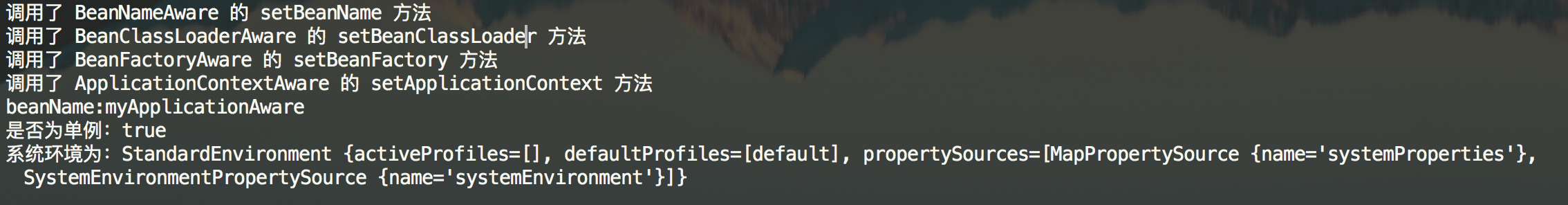
从这我们基本上可以了解Aware的含义是什么了? 感知,其实是Spring容器在初始化中主动监测当前Bean是否实现了Aware接口,如果实现了则回调其set方法将相应的参数设置给Bean,这个时候该Bean就从Spring容器中获取相应的资源。