初识http
a、超文本传输 、应用层的面向对象的协议,概念介绍网上资源一大堆,关键是基于TCP/IP通信协议来传递数据。
b、一开始接触web项目,都是先接触的servlet,tomcat服务器默认实现的一套http规范,提供了基础服务和组件环境,直接拿到请求、构建正文、响应客户端
然而一个http请求包含:
第一行:请求方式(get、post、put、delete)+“空格”+URI+“空格”+http协议版本(0.9、1.0、1.1) eg:GET /hello.html HTTP/1.1
第二行:我们熟悉的请求头Request Head(请求类型、语言、代理、字符集)
http响应:
第一行:http协议版本+“空格”+状态码+”空格“+描述 eg:HTTP/1.1 200 OK
第二行:Response Head(包含Content-Type等)
第三行:响应正文(一般html)
形象化的了解以上结构,打开熟知的浏览器:
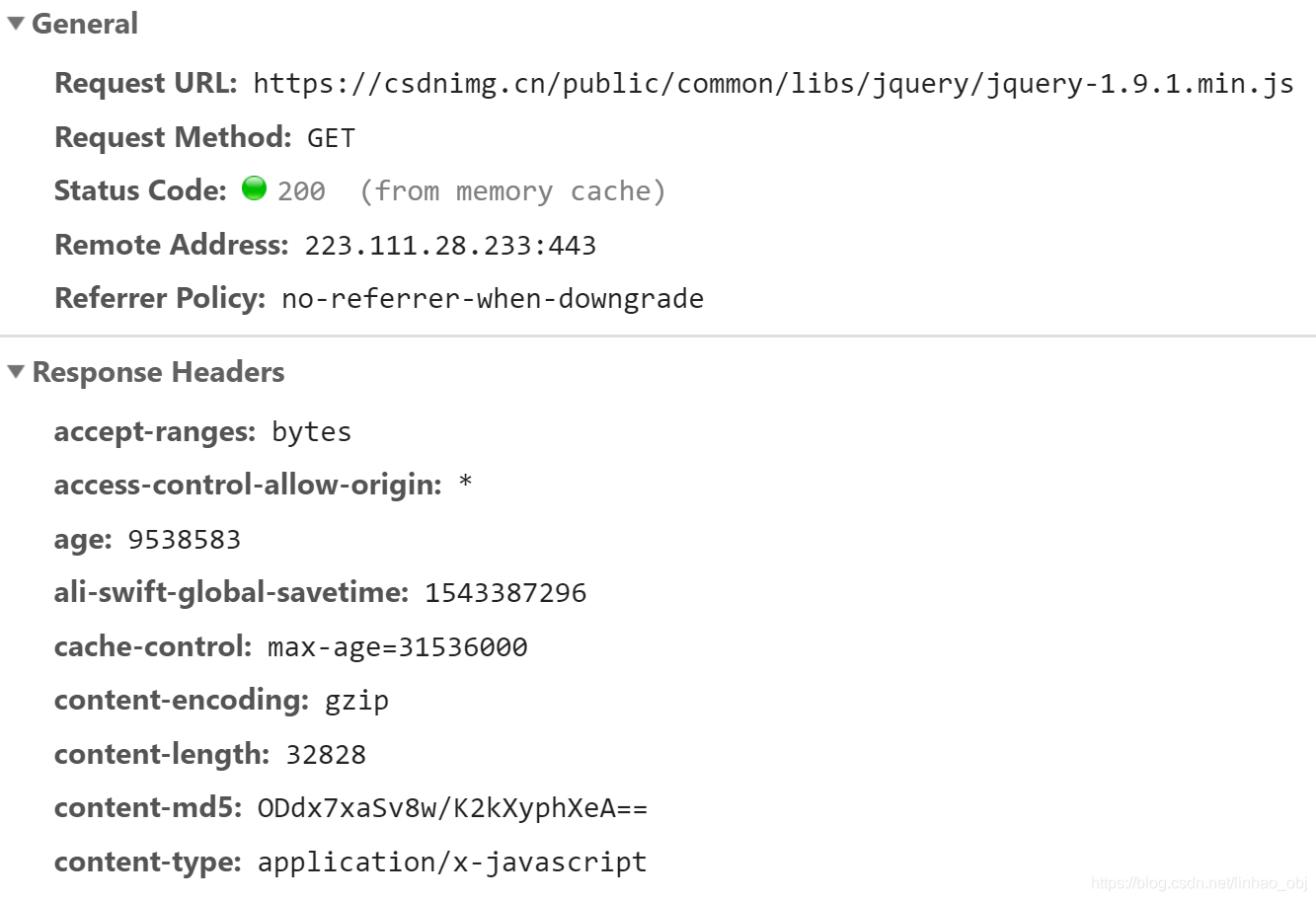
构建http server
现在我们由java代码运用ServerSocket tcp协议模拟构建一个http服务:
public class HttpServer {
public static final int DEFAULT_PORT =8080;//默认8080端口
public static void start(){
ServerSocket serverSocket;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT);
System.out.println("服务器端正在监听端口:"+serverSocket.getLocalPort());
while(true){//死循环时刻监听客户端链接
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("建立了与客户端一个新的tcp连接,客户端地址为:"+socket.getInetAddress()
+":"+socket.getPort());
//开始服务
service(socket);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void service(Socket socket) throws Exception {
//读取HTTP请求信息
InputStream socketIn = socket.getInputStream();
Thread.sleep(500);
int size = socketIn.available();
byte[] b = new byte[size];
socketIn.read(b);
String request = new String(b);
System.out.println(request);
//解析请求方式、uri、协议,获取uri
String typeUriHttp = request.substring(0,request.indexOf("\r\n"));
String uri = typeUriHttp.split(" ")[1];
//简化处理响应头content-Type
String contentType;
if(uri.indexOf("html")!=-1||uri.indexOf("htm")!=-1){
contentType = "text/html";
}else if(uri.indexOf("jpg")!=-1||uri.indexOf("jpeg")!=-1){
contentType = "image/jpeg";
}else if(uri.indexOf("gif")!=-1){
contentType = "image/gif";
}else contentType = "application/octet-stream";
//创建HTTP响应结果
//创建响应协议、状态
String httpStatus = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
//创建响应头
String responseHeader = "Content-Type:" + contentType + "\r\n\r\n";
InputStream in = HttpServer.class.getResourceAsStream("/webRoot"+uri);
OutputStream socketOut = socket.getOutputStream();
//发送响应协议、状态码及响应头、正文
socketOut.write(httpStatus.getBytes());
socketOut.write(responseHeader.getBytes());
int len =0;
b = new byte[1024];
while((len=in.read(b))!=-1){
socketOut.write(b,0,len);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
//socket.close();
}
}
写一个测试类,主方法启动服务
package Http;
/**
* Author:varCode
* Date:2019-03-22 20:55
* Description:<描述>
*/
public class HttpTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开启Http服务端
HttpServer.start();
}
}
在我们项目目录的webRoot文件夹下放入可访问的资源,通过浏览器URI(资源定位符)读取服务端资源,打开我们的浏览器,本地ip+默认端口,
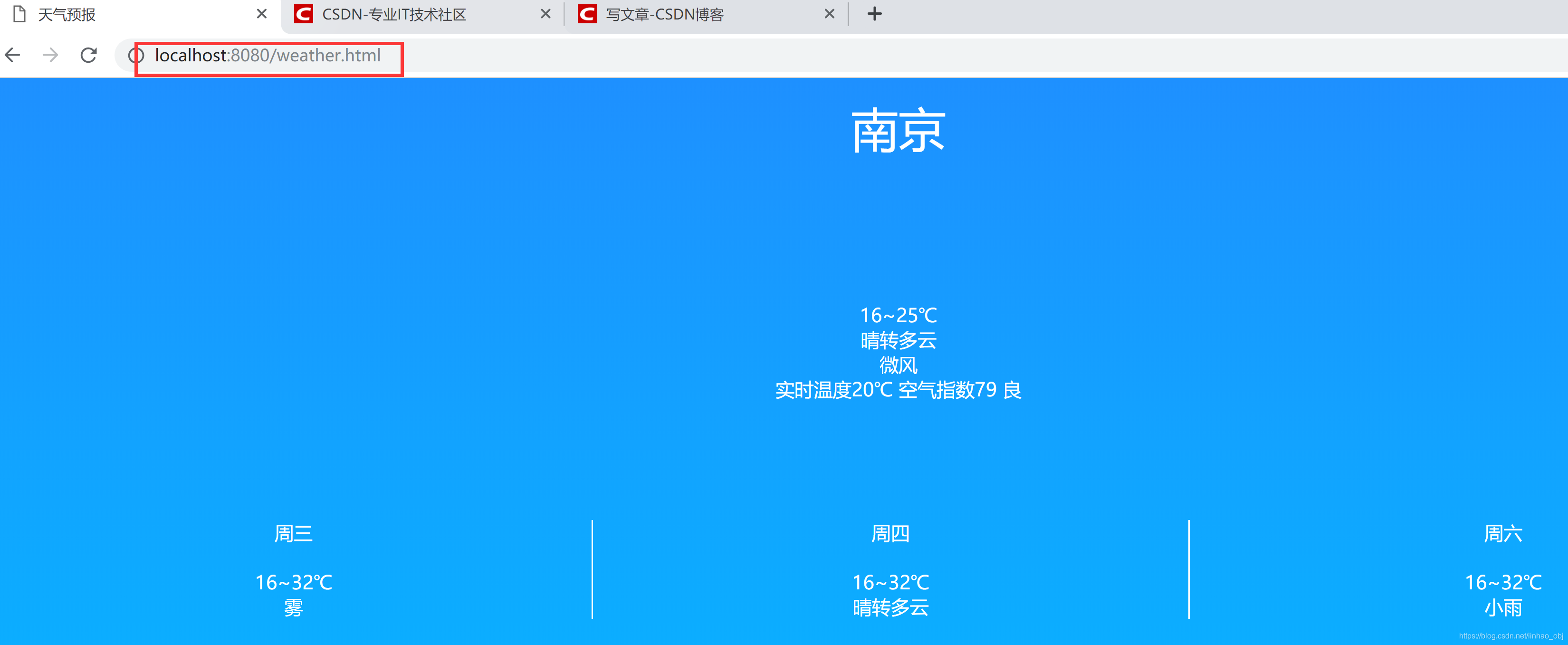
脱离tomcat服务环境的一个web访问页面,是有点小意思啊,下面我们再来脱离客户端浏览器
构建http client
package Http;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* Author:varCode
* Date:2019-03-22 22:20
* Description:<描述>
*/
public class HttpClient {
//实现get方式访问http server
public static void doGet(String host,int port,String uri){
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = new Socket(host,port);
//创建http请求 第一行 注意空格
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("GET "+uri+" HTTP/1.1\r\n");
//构建请求头
sb.append("Accept: */*\r\n");
sb.append("Accept-Language: zh-cn\r\n");
sb.append("Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\n");
sb.append("User-Agent: HTTPClient\r\n");
sb.append("Host: localhost:8080\r\n");
sb.append("Connection: Keep-Alive\r\n");
//发送http请求
OutputStream socketOut = socket.getOutputStream();
socketOut.write(sb.toString().getBytes());
Thread.sleep(2000);
InputStream socketIn = socket.getInputStream();
int size = socketIn.available();
byte[] b = new byte[size];
socketIn.read(b);
//将相应结果输出到控制台 模拟浏览器界面
System.out.println(new String(b));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
再来一个客户端测试类:要先启动上述的HttpTest服务测试类,再运行下面客户端主程序测试:
package Http;
/**
* Author:varCode
* Date:2019-03-22 22:41
* Description:<描述>
*/
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//客户端发请求
HttpClient.doGet("localhost",8080,"/weather.html");
}
}
且将控制台当作页面打印如下:
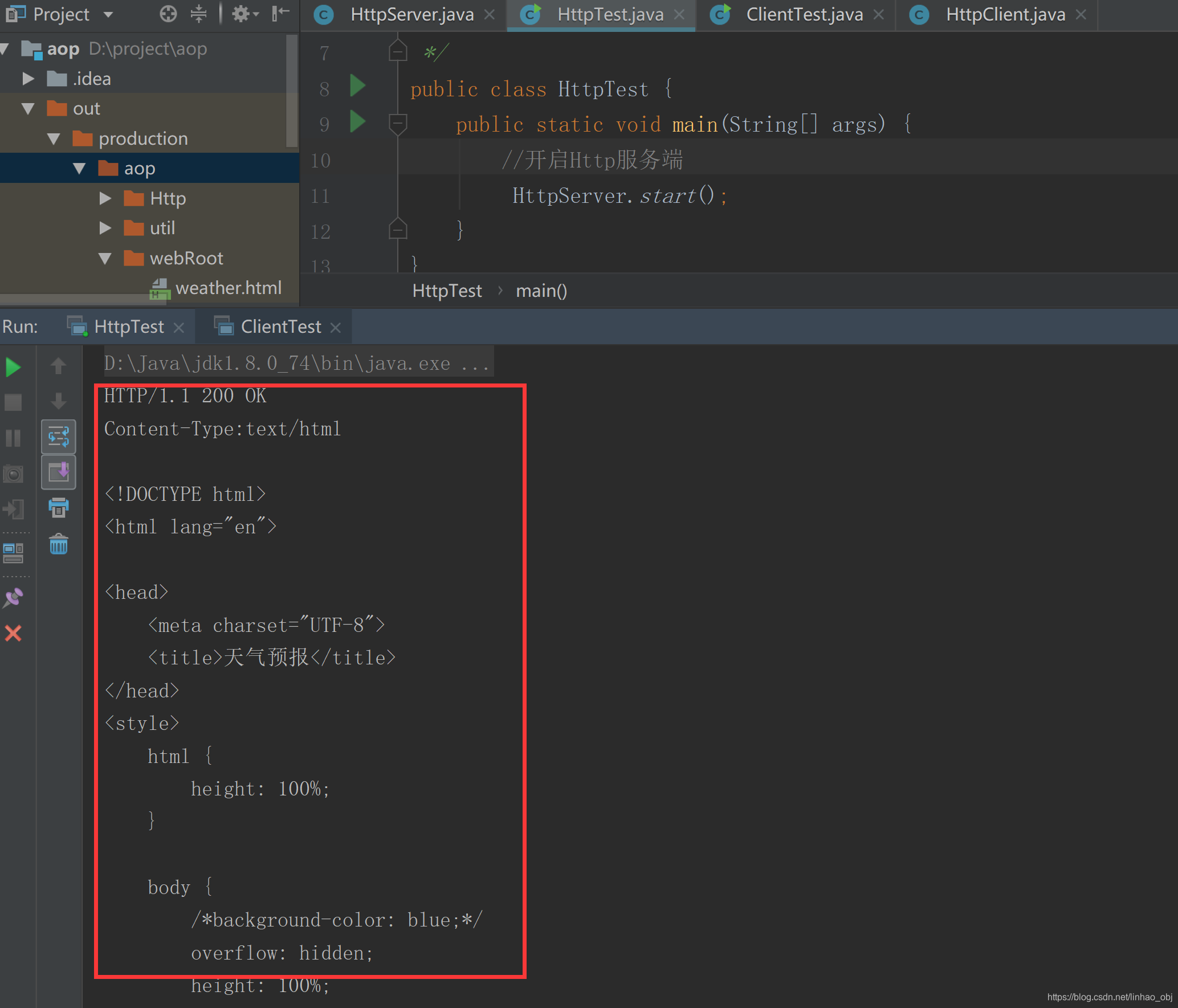
好了,至此完全可以由HttpClient客户端类——>HttpServer服务类上请求及响应,可以由浏览器——>HttpServer发送请求(上面已经测试了),HttpClient——>tomcat来相应请求(有兴趣的可以自己来,tcp协议只能监听一个端口的主机服务,开启tomcat,关闭HttpServer测试类)
浏览器和tomcat都是实现了http规范,都能解析请求和构建响应,更何况tomcat还是java编写的服务器,哈哈!
