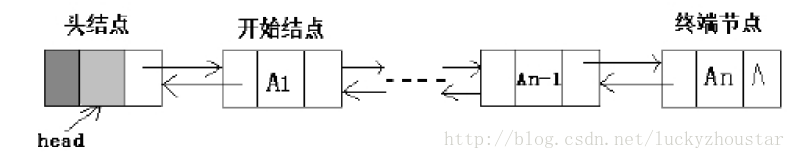
双向链表定义
双链表就是在单链表结点上增添了一个指针域,指向当前结点的前驱。这样就可以方便的由其后继来找到其前驱,而实现输出终端结点到开始结点的数据序列。
同样,双链表也分为带头结点的双链表和不带头结点的双链表,情况类似于单链表。带头结点的双链表 head->next 为null的时候链表为空。不带头结点的双链表head为null的时候链表为空。
代码展示
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLink<String, String> singleLink = new SingleLink<String, String>();
singleLink.addNode("12", "23");
singleLink.addNode("22", "23");
singleLink.addNode("32", "23");
System.out.println(singleLink.get("12"));
System.out.println("开始移除12节点");
singleLink.deleteNode("22");
singleLink.deleteNode("32");
singleLink.print();
}
Node first;
/**
* 首节点操作
*/
private class Node {
Key key;
Value value;
Node next;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 添加节点操作
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void addNode(Key key, Value value) {
Node node = new Node(key, value, null);
/*首先判断首节点*/
if (this.first == null) {
this.first = node;
} else {
//类似于先进后出的操作
/**
* 新添加的默认就添加到header位置
*/
first = new Node(key, value, this.first);
}
}
/**
* 输出内容
*/
public void print() {
//尾节点是null
for (Node node = first; node != null; node = node.next) {
System.out.println(node.key + "--" + node.value);
}
}
public Value get(Key key) {
//查找给定的键,返回相关联的值信息
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
return x.value;
}
}
return null;
}
/*
*删除某个节点操作
* */
public void deleteNode(Key key) {
if (this.first == null) {
return;
}
if (this.first.key.equals(key)) {
this.first = this.first.next;
} else {
if (this.first.next != null) {
delete(this.first, key);
}
}
}
private void delete(Node previous, Key key) {
if (previous.next.key.equals(key)) {
previous.next = previous.next.next;
} else {
//递归删除操作
delete(previous.next, key);
}
}