0 环境准备
1、数据库环境准备
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user_info
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_info`;
CREATE TABLE `user_info` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`userName` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_unicode_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user_info
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES (1, 'yang', '123456');
2、实体类
package com.snow.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@ToString
public class UserEntity {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String password;
}
3、
UserMapper
package com.snow.mapper;
import com.snow.entity.UserEntity;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user_info WHERE userName=#{userName} AND password=#{password}")
public UserEntity login(UserEntity userEntity);
}
4、
controller
package com.snow.controller;
import com.snow.entity.UserEntity;
import com.snow.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(UserEntity userEntity) {
System.out.println("账号密码信息:userEntity:" + userEntity.toString());
UserEntity login = userMapper.login(userEntity);
return login == null ? "登陆失败!" : "登陆成功!";
}
}
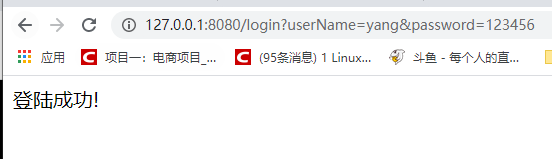
5、测试
启动项目,浏览器访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/login?userName=yang&password=123456
1 什么是 SQL 注入
SQL 注入:利用现有应用程序,将(恶意)的SQL命令注入到后台数据库执行一些恶意的代码。
造成 SQL 注入的原因是因为程序没有有效过滤用户的输入,使攻击者成功的向服务器提交恶意的 SQL 查询代码,程序在接收后错误的将攻击者的输入作为查询语句的一部分执行,导致原始的查询逻辑被改变,额外的执行了攻击者精心构造的恶意代码。
2 演示 SQL 注入攻击
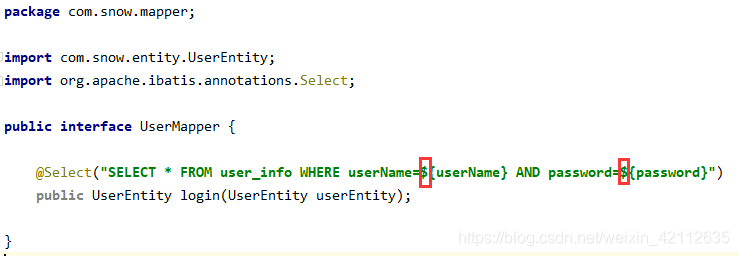
修改
UserMapper
package com.snow.mapper;
import com.snow.entity.UserEntity;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user_info WHERE userName=${userName} AND password=${password}")
public UserEntity login(UserEntity userEntity);
}
启动项目,浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:8080/login?userName=yang&password=123456
报错:
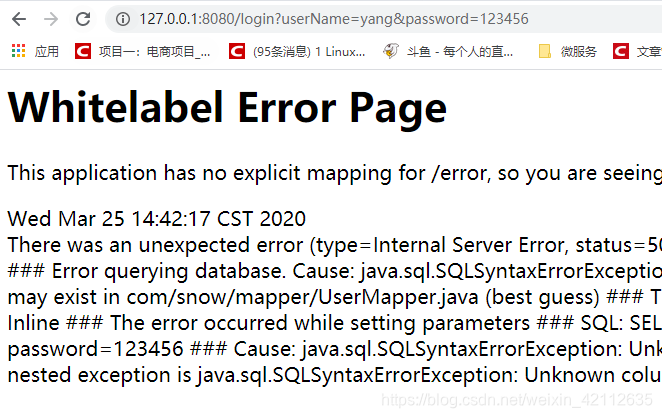
查看日志:
### Error querying database. Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'yang' in 'where clause'
### The error may exist in com/snow/mapper/UserMapper.java (best guess)
### The error may involve com.snow.mapper.UserMapper.login-Inline
### The error occurred while setting parameters
### SQL: SELECT * FROM user_info WHERE userName=yang AND password=123456
### Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'yang' in 'where clause'
; bad SQL grammar []; nested exception is java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'yang' in 'where clause'] with root cause
java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column 'yang' in 'where clause'
at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:120) ~[mysql-connector-java-8.0.19.jar:8.0.19]
at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:97) ~[mysql-connector-java-8.0.19.jar:8.0.19]
原因:$ 是字符串拼接,所以查询时字段为 varchar 时,需要添加 '。
再次测试,浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:8080/login?userName=yang&password=123456
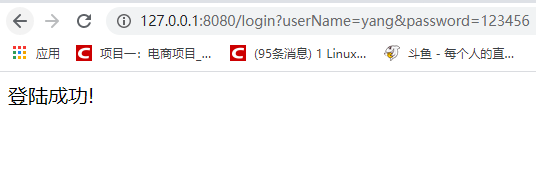
演示
SQL注入攻击
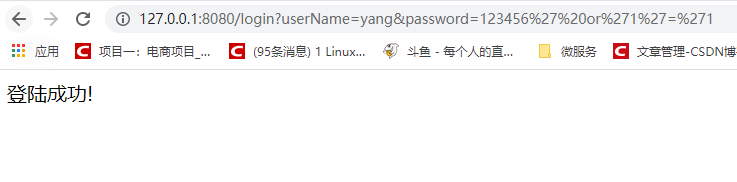
为什么浏览器访问地址会变成:
http://127.0.0.1:8080/login?userName=yang&password=123456%27or%271%27=%271
这是因为浏览器会将特殊的字符进行转码。
3 防止 SQL 注入攻击手段
不要使用拼接 SQL 语句方式、最好使用预编译方式,在 mybatis 编写 sql 语句的时候,最好使用 ? 传参数方式,不要使用 $ 传参数,因为 $ 传参数方式,可能会受到 sql 语句攻击。
package com.snow.controller;
import com.snow.entity.UserEntity;
import com.snow.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(UserEntity userEntity) {
System.out.println("账号密码信息:userEntity:" + userEntity.toString());
UserEntity login = userMapper.login(userEntity);
return login == null ? "登陆失败!" : "登陆成功!";
}
}
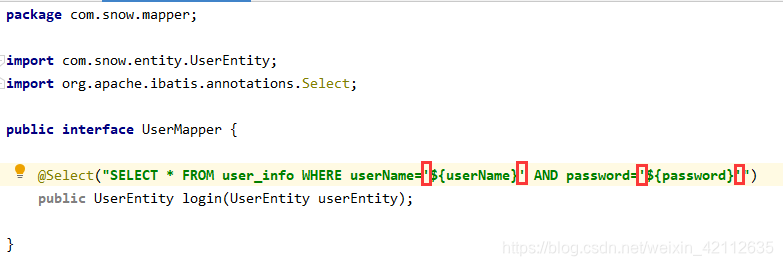
package com.snow.mapper;
import com.snow.entity.UserEntity;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user_info WHERE userName='${userName}' AND password='${password}'")
public UserEntity login(UserEntity userEntity);
}
3 MyBatis # 与 $ 区别
-
#{}:解析为一个JDBC预编译语句(prepared statement)的参数标记符,一个#{ }被解析为一个参数占位符,可以防止SQL注入问题。 -
${}:仅仅为一个纯碎的string替换,在动态SQL解析阶段将会进行变量替换。
