已知从1~n的数字序列,按顺序出栈。每个数字入栈后有两种选择:1-立即出栈,2-等待后面的数字入栈出栈后,该数字再出栈。
现在给出一个数字序列,求该数字序列是否合法?
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> a;
stack<int> Min;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int n) {
if (a.size() == 0) {
a.push(n);
Min.push(n);
}
else {
a.push(n);
if (n < Min.top()) {
Min.push(n);
}
else {
Min.push(Min.top());
}
}
}
int pop() {
int num = a.top();
a.pop();
Min.pop();
return num;
}
int getMin() {
return Min.top();
}
bool empty() {
return a.empty();
}
int size() {
return a.size();
}
};
bool bringin(vector<int>& aa, stack<int>& a) {//入栈函数
if (!aa.empty()) {
a.push(aa[0]);
aa.erase(aa.begin());
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool ceshi(vector<int> &aa,stack<int> &a) {//测试函数
string s;
cin >> s;//输入你想测试的数字序列
int i;
if (bringin(aa, a) == false)//一开始的栈就是空的,所以第一步肯定要先让栈有元素,如果初始序列为空,那么直接返回flase
return false;
else {
for (i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
while (a.empty() || a.top() != (s[i] - '0')) {//一定不要弄错顺序,要先判断栈是否为空,若为空,当然要进行入栈操作
if (bringin(aa, a) == false)
return false;
}
if (a.top() == (s[i] - '0')) {//栈顶元素和判断位置的序列一致的话,就出栈。
a.pop();
}
}
}
if (i == s.size())//完美匹配上所有数字序列,返回true
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main() {
stack<int> a;
vector<int> aa = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//初始序列
cout << ceshi(aa, a);
return 0;
}
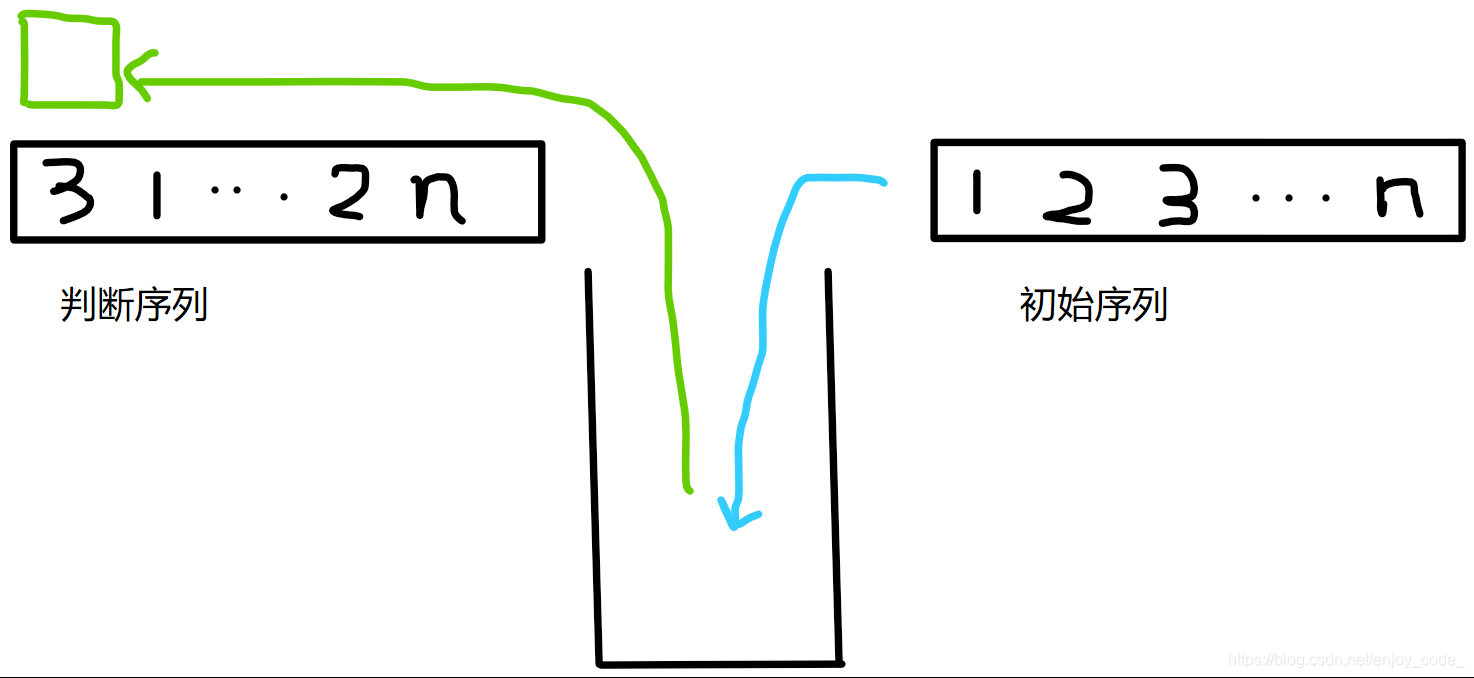
计算机绘图技术较差,望见谅。
主要就是 栈顶元素 和 s[ i ] 匹配,不同就继续入栈,相同就出栈。
细节上,多多考虑栈空时需要进行什么操作即可。
.
.
.
.
946.验证栈序列 (leetcode)
给定 pushed 和 popped 两个序列,每个序列中的 值都不重复,只有当它们可能是在最初空栈上进行的推入 push 和弹出 pop 操作序列的结果时,返回 true;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1]
输出:true
解释:我们可以按以下顺序执行:
push(1), push(2), push(3), push(4), pop() -> 4,
push(5), pop() -> 5, pop() -> 3, pop() -> 2, pop() -> 1
示例 2:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,3,5,1,2]
输出:false
解释:1 不能在 2 之前弹出。
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
stack<int> a;
for(int i =0;i<popped.size();i++){
while((a.empty()||a.top()!=popped[i])&&!pushed.empty()){
a.push(pushed[0]);
pushed.erase(pushed.begin());
}
if(a.top()==popped[i]){
a.pop();
}
}
if(a.size() == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
